(1)本机环境:VMware® Workstation 15 Pro + Ubuntu18.04.4 LTS
1.1 将同学提供的文件:mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch和用迅雷下载的:linux-5.4.34.tar.xz置于一个空文件夹下。
1.2 右键打开终端,执行
xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar
解压缩linux-5.4.34.tar.xz。
1.3 继续执行
cd linux-5.4.34 patch -p1 < ../mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch sudo apt install build-essential libncurses-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev make defconfig make -j$(nproc) #时间略久,请耐心等待
make结束后应该会出现如下界面
继续
sudo apt install qemu
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
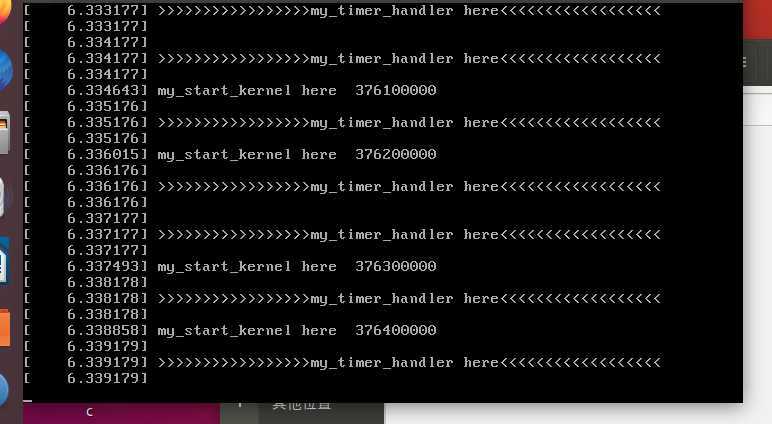
qemu窗口出现my_start_kernel在不停的输出,my_timer_handler时钟中断处理程序周期性执行。
这就是我们模拟出的具有时钟中断的C代码执行环境。
mymain.c关键代码
void __init my_start_kernel(void) { int i = 0; while(1) { i++; if(i%100000 == 0) pr_notice("my_start_kernel here %d \n",i); } }
myinterrupt.c关键代码,(中断处理程序的上下文环境,周期性地产生的时钟中断信号,能够触发myinterrupt.c
/*
* Called by timer interrupt. */ void my_timer_handler(void) { pr_notice("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>my_timer_handler here<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<\n\n"); }
在mykernel目录下创建mypcb.h 头文件,用来定义进程控制块(Process Control Block)。
/* * linux/mykernel/mypcb.h */ #define MAX_TASK_NUM 4 #define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*8 /* CPU-specific state of this task */ struct Thread { unsigned long ip; unsigned long sp; }; typedef struct PCB{ int pid; volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */ char stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE]; /* CPU-specific state of this task */ struct Thread thread; unsigned long task_entry; struct PCB *next; }tPCB; void my_schedule(void);
对mymain.c进行修改,这里是mykernel内核代码的入口,负责初始化内核的各个组成部分。
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
/* * linux/mykernel/mymain.c */ #include "mypcb.h" tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM]; tPCB * my_current_task = NULL; volatile int my_need_sched = 0; void my_process(void); void __init my_start_kernel(void) { int pid = 0; int i; /* Initialize process 0*/ task[pid].pid = pid; task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */ task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process; task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]; task[pid].next = &task[pid]; /*fork more process */ for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++) { memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB)); task[i].pid = i; task[i].state = -1; task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]; task[i].next = task[i-1].next; task[i-1].next = &task[i]; } /* start process 0 by task[0] */ pid = 0; my_current_task = &task[pid]; asm volatile( "movq %1,%%rsp\n\t" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to rsp */ "pushq %1\n\t" /* push rbp */ "pushq %0\n\t" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */ "ret\n\t" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to rip */ : : "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/ ); }
void my_process(void)
{
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -\n",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +\n",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}
修改myinterrupt.c
/* * linux/mykernel/myinterrupt.c * * Kernel internal my_timer_handler * Change IA32 to x86-64 arch, 2020/4/26 * * Copyright (C) 2013, 2020 Mengning * */ #include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/string.h> #include <linux/ctype.h> #include <linux/tty.h> #include <linux/vmalloc.h> #include "mypcb.h" extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM]; extern tPCB * my_current_task; extern volatile int my_need_sched; volatile int time_count = 0; /* * Called by timer interrupt. * it runs in the name of current running process, * so it use kernel stack of current running process */ void my_timer_handler(void) { if(time_count%1000 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1) { printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<\n"); my_need_sched = 1; } time_count ++ ; return; } void my_schedule(void) { tPCB * next; tPCB * prev; if(my_current_task == NULL || my_current_task->next == NULL) { return; } printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<\n"); /* schedule */ next = my_current_task->next; prev = my_current_task; if(next->state == 0)/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */ { my_current_task = next; printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<\n",prev->pid,next->pid); /* switch to next process */ asm volatile( "pushq %%rbp\n\t" /* save rbp of prev */ "movq %%rsp,%0\n\t" /* save rsp of prev */ "movq %2,%%rsp\n\t" /* restore rsp of next */ "movq $1f,%1\n\t" /* save rip of prev */ "pushq %3\n\t" "ret\n\t" /* restore rip of next */ "1:\t" /* next process start here */ "popq %%rbp\n\t" : "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip) : "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip) ); } return; }
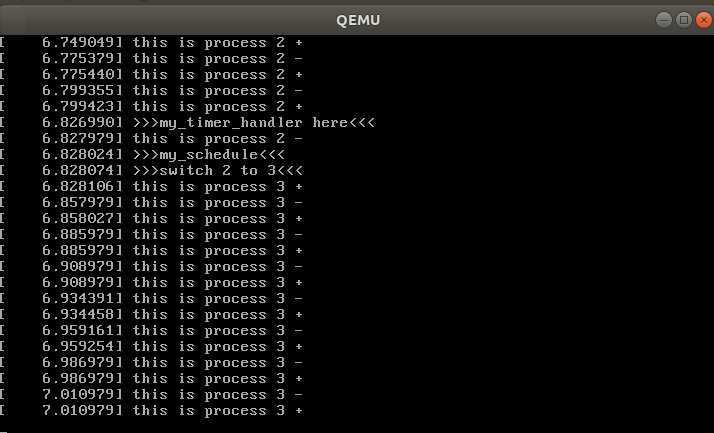
重新编译,运行结果:
相关原理请见https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/SzpN1BNty5aPDZhNdCO5yA
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/gfsh/p/12869968.html