Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
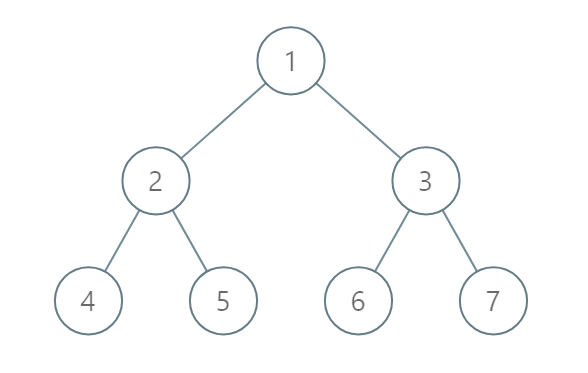
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
1000 nodes.0 and 1000.二叉树的垂序遍历。题意跟314题非常像,但是314只要求我们找到横坐标一样的元素,把他们合成一组;但是这个题是要求不光是横坐标相同的元素分在一组,同时要求要对坐标和节点值排序,所以会用到treemap和PriorityQueue。treemap可以输出key是有序的hashmap,所以用来存储坐标;PriorityQueue可以存节点值。整体思路是用DFS前序遍历,遍历树不难,难的是要处理好数据怎么存。
时间O(nlogn) - 因为有PriorityQueue的排序
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } 8 * } 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { 12 TreeMap<Integer, TreeMap<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>>> map = new TreeMap<>(); 13 dfs(root, 0, 0, map); 14 List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(); 15 for (TreeMap<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>> ys : map.values()) { 16 list.add(new ArrayList<>()); 17 for (PriorityQueue<Integer> nodes : ys.values()) { 18 while (!nodes.isEmpty()) { 19 list.get(list.size() - 1).add(nodes.poll()); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 return list; 24 } 25 26 private void dfs(TreeNode root, int x, int y, TreeMap<Integer, TreeMap<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>>> map) { 27 if (root == null) { 28 return; 29 } 30 if (!map.containsKey(x)) { 31 map.put(x, new TreeMap<>()); 32 } 33 if (!map.get(x).containsKey(y)) { 34 map.get(x).put(y, new PriorityQueue<>()); 35 } 36 map.get(x).get(y).offer(root.val); 37 dfs(root.left, x - 1, y + 1, map); 38 dfs(root.right, x + 1, y + 1, map); 39 } 40 }
[LeetCode] 987. Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/cnoodle/p/12881028.html