? 如果使用==判断俩个对象是否相等,这个只是从地址看是否相等,而与我们的需求是不符合的。即使俩个对象地址是不同的,如果它的属性是相同的,那么可判定这俩个对象相等。
未重写equals方法:
public class Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
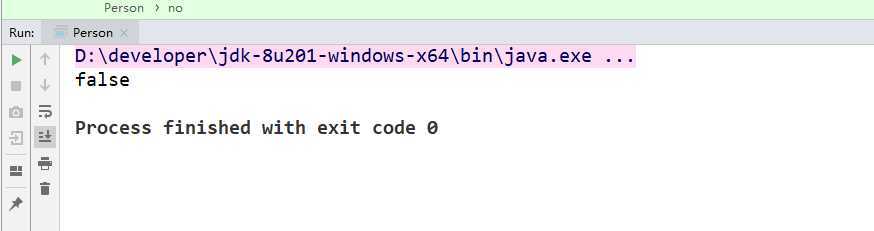
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
}
public int no;
public String name;
}
运行截图:
重写equals方法后:
public class Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
}
public int no;
public String name;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) o;
if (no != person.no) {
return false;
}
return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;
}
}
运行截图: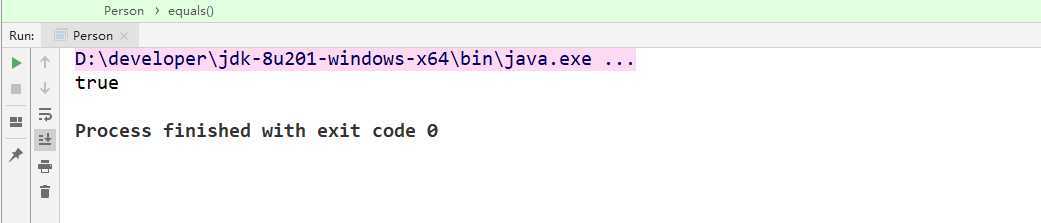
? 由于在hashMap中在put时,散列函数根据它的哈希值找到对应的位置,如果该位置有原素,首先会使用hashCode方法判断,如果没有重写hashCode方法,那么即使俩个对象属性相同hashCode方法也会认为他们是不同的元素,又因为Set是不可以有重复的,所以这会产生矛盾,那么就需要重写hashCode方法。
没有重写hashCode方法
public class Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
HashMap<Person, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(p1,1);
map.put(p2,2);
System.out.println(map.get(new Person()));
}
public int no;
public String name;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) o;
if (no != person.no) {
return false;
}
return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;
}
}
运行截图: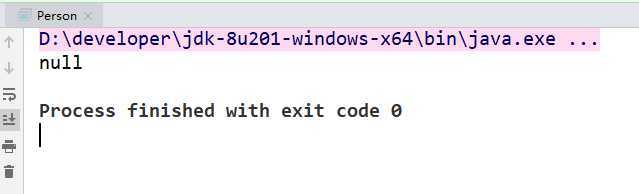
重写了hashCode方法
public class Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
HashMap<Person, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(p1,1);
map.put(p2,2);
System.out.println(map.get(new Person()));
}
public int no;
public String name;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Person person = (Person) o;
if (no != person.no) {
return false;
}
return name != null ? name.equals(person.name) : person.name == null;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = no;
result = 31 * result + (name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0);
return result;
}
}
运行截图: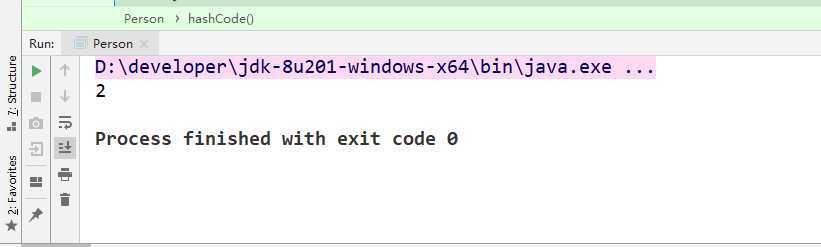
HashMap中为啥要重写hashcode和equals方法
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/pavi/p/12920553.html