感谢作者:本文来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/longfurcat/p/10293819.html
前言:
本文整理以下SecurityContext的存储方式
Securitycontext接口
顾名思义 ,安全上下文,及存储认证授权的相关信息,实际上就是存储“当前用户”账号信息和相关权限信息。这个接口只有两个方法,Authentication对象getter,setter方法
package org.springframework.security.core.context; import java.io.Serializable; import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable { Authentication getAuthentication(); void setAuthentication(Authentication var1); }
注意Securitycontext存储的authentication对象是经过验证的,所以他会带有权限,他的getAuthorities()方法返回相关权限
package org.springframework.security.core; import java.io.Serializable; import java.security.Principal; import java.util.Collection; public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable { Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); Object getCredentials(); Object getDetails(); Object getPrincipal(); boolean isAuthenticated(); void setAuthenticated(boolean var1) throws IllegalArgumentException; }
前面说的“当前用户” 实际上指的是当前这个请求所对那个的用户,那么怎么直到当前用户是谁呢。由于一个请求从凯斯到结束都是由一个线程处理。这个线程中途不会处理其他请求,所以这段时间内,线程和用户是意义对应的。SecurityContextHolder工具类就是把SecurityContext存储在当前线程中。
SecuritycontextHolder可以用来设置获取Securitycontext.他的主要给矿建内部使用的,可以利用它获取当前用户Securitycontext进行请求检查,和访问控制
在Web环境中,SecurityContextHolder是利用ThreadLocal来存储SecurityContext的
我们直到servlet中线程池是被池化复用的,一旦处理完当前的请求,它可能马上会被分配到处理其他的请求,而且不能保证用户下次请求会被分配到同一个线程。所以存放在线程里避免,请求一旦结束,就没了,如果没有确保存,不是每次请求都要重新认证登陆。想想看,我们没有权限框架,哦我们怎么处理。
想到了把,Session。如果我们不用权限框架,我们一般把认证的结果存放到session中,同理,它可把认证结果存储到session中。
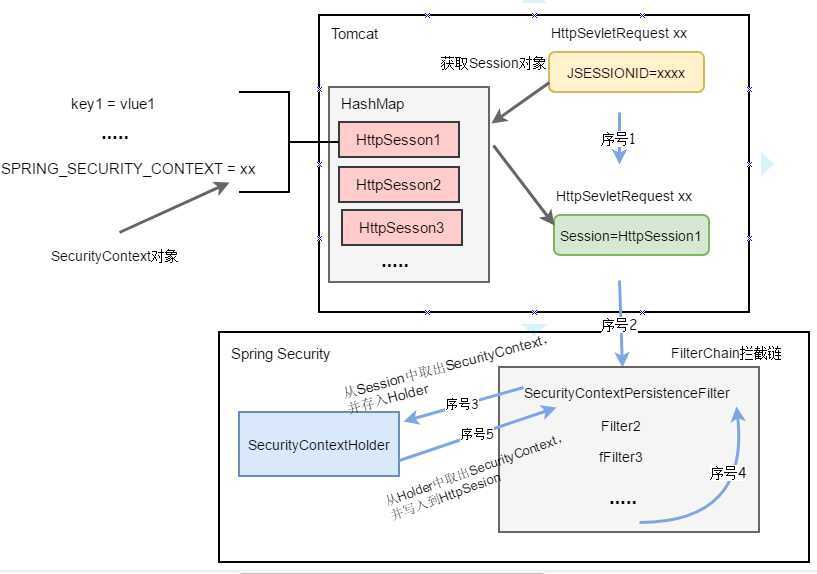
securitycontextpresistenceFilter是Security的拦截器,而且是拦截链中的第一个拦截器。请求来林的时候,httpsession中把securitycontext取出来,然后放入SecurityContexthodler中。把所有的拦截器都处理完成后,在把Securitycontext 存入到httpSession中。并清楚Securitycontextholdeer内的引用。
ublic void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res; if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) { // ensure that filter is only applied once per request chain.doFilter(request, response); return; } final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE); if (forceEagerSessionCreation) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(); if (debug && session.isNew()) { logger.debug("Eagerly created session: " + session.getId()); } } HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request, response); //利用HttpSecurityContextRepository从HttpSesion中获取SecurityContext对象 //如果没有HttpSession,即浏览器第一次访问服务器,还没有产生会话。 //它会创建一个空的SecurityContext对象 SecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder); try { //把SecurityContext放入到SecurityContextHolder中 SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution); //执行拦截链,这个链会逐层向下执行 chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse()); } finally { //当拦截器都执行完的时候把当前线程对应的SecurityContext从SecurityContextHolder中取出来 SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder .getContext(); // Crucial removal of SecurityContextHolder contents - do this before anything // else. SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(); //利用HttpSecurityContextRepository把SecurityContext写入HttpSession repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse()); request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED); if (debug) { logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed"); } } }
有人可能对tomcat建立会话的流程不熟悉,这里稍微的整理一下,是这样的,当客户浏览器打开后,第一次访问的Tomcat服务器,Tomcat会将i一个HttpSession。将HttpSession 存入concurentHashMap,key 是sessiondi valueshi HttpSession.请求完毕,在返回的保温中添加set-cooke:jessionid = xxx..然后客户端会保存这个cookie ,当浏览器再次访问的时候,就会带上这个cookei ,根据jessionid把对应的httpsession对此昂取出来,放入httpServletRequest对象里边。
.HttpSession会一直存在服务端,实际上是存在运行内存中。除非Session过期 OR Tomcat奔溃 OR 服务器奔溃,否则会话信息不会消失。
2.如无特殊处理,Cookie JSESSIONID会在浏览器关闭的时候清除。
3.Tomcat中HttpSesion的默认过期时间为30分钟。
4.这些处理都在Security的拦截链之前完成。
SpringSecurity_SecurityContext 接口
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dousil/p/12922772.html