nginx 配置文件详解
1:nginx配置文件的结构:
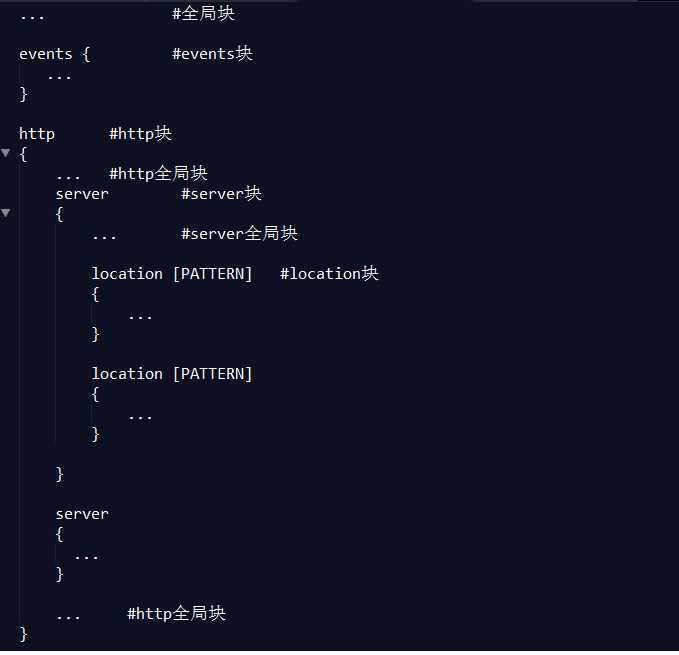
1、全局块:配置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等。
2、events块:配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数,选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求,是否允许同时接受多个网路连接,开启多个网络连接序列化等。
3、http块:可以嵌套多个server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,mime-type定义,日志自定义,是否使用sendfile传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等。
4、server块:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个http中可以有多个server。
5、location块:配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
2、原配置文件(nginx.conf) 说明:
#user nobody; #开启进程数 <=CPU数 worker_processes 1; #错误日志保存位置 #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #进程号保存文件 #pid logs/nginx.pid; #每个进程最大连接数(最大连接=连接数x进程数)每个worker允许同时产生多少个链接,默认1024 events { worker_connections 1024; } http { #文件扩展名与文件类型映射表 include mime.types; #默认文件类型 default_type application/octet-stream; #日志文件输出格式 这个位置相于全局设置 #log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ # ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘ # ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘; #请求日志保存位置 #access_log logs/access.log main; #打开发送文件 sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; #连接超时时间 keepalive_timeout 65; #打开gzip压缩 #gzip on; #client_header_buffer_size 4k; 设定请求缓冲, 客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。 这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,一般一个请求头的大小不会超过1k, 不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。 分页大小可以用命令getconf PAGESIZE 取得。 [root@web001 ~]# getconf PAGESIZE 4096 但也有client_header_buffer_size超过4k的情况,但是client_header_buffer_size该值必须设置为“系统分页大小”的整倍数。 #client_header_buffer_size 4k; #large_client_header_buffers 4 4k; #设定负载均衡的服务器列表 #upstream myproject { #weigth参数表示权值,权值越高被分配到的几率越大 #max_fails 当有#max_fails个请求失败,就表示后端的服务器不可用,默认为1,将其设置为0可以关闭检查 #fail_timeout 在以后的#fail_timeout时间内nginx不会再把请求发往已检查出标记为不可用的服务器 #} #webapp #upstream myapp { # server 192.168.122.133:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s; # server 192.168.122.134:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s; #} #配置虚拟主机,基于域名、ip和端口 server { #监听端口 listen 9000; #监听域名 server_name localhost; #charset koi8-r; #nginx访问日志放在logs/host.access.log下,并且使用main格式(还可以自定义格式) #access_log logs/host.access.log main; #返回的相应文件地址 location / { #负载均衡反向代理 #proxy_pass http://myapp; #返回根路径地址(相对路径:相对于/usr/local/nginx/) root html; #默认访问文件 index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html #错误页面及其返回地址 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root # concurs with nginx‘s one # #location ~ /\.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }
3: 配置文件详细参数说明:
woker_processes 2
在配置文件的顶级main部分,worker角色的工作进程的个数,master进程是接收并分配请求给worker处理。这个数值简单一点可以设置为cpu的核数:
可以使用:grep ^processor /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l 查看cpu核数,
也是 auto 值,如果开启了ssl和gzip更应该设置成与逻辑CPU数量一样甚至为2倍,可以减少I/O操作。如果nginx服务器还有其它服务,可以考虑适当减少。
....................
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dw3306/p/12942174.html