本次来说说BeanFactory的后置处理器,从源码来看它是位于refresh函数的第四步,为了方便你查阅我把refresh贴出来。
1 @Override 2 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 3 // 方法加锁避免多线程同时刷新Spring上下文 4 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 5 // 准备上下文刷新 6 prepareRefresh(); 7 8 // 告诉子类刷新内部的beanFactory返回新的BeanFactory 9 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 10 11 // 在当前上下文中准备要beanFactory 12 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 13 14 try { 15 // 允许在上下文子类中对beanFactory进行后置处理 16 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 17 18 // 在上下文中将BeanFactory处理器注册为Bean 19 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 20 21 // 注册Bean处理器用于拦截Bean的创建 22 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 23 24 // 在上下文中初始化国际化信息 25 initMessageSource(); 26 27 // 在上下文中初始化event multicaster(事件多播器) 28 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 29 30 // 在指定的上下文子类中初始化其他指定的beans 31 onRefresh(); 32 33 // 检查并注册事件监听 34 registerListeners(); 35 36 // 实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)单例 37 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 38 39 // 最后一步:发布相应的事件 40 finishRefresh(); 41 } 42 43 catch (BeansException ex) { 44 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 45 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 46 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 47 } 48 49 // 如果出现异常则销毁已创建的单例 50 destroyBeans(); 51 52 // 重置活动标志 53 cancelRefresh(ex); 54 55 // 将异常传递给调用者 56 throw ex; 57 } 58 59 finally { 60 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring‘s core, since we 61 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 62 resetCommonCaches(); 63 } 64 } 65 }
postProcessBeanFactory(),顾名思义,它就是创建BeanFactory之后的一些操作。从源码上看,它是一个空函数,主要是为了给子类提供可扩展点的,是一个可选项。
1 protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 2 }
像我们直接通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext初始化的话,是不会有任何扩展点的。但如果是Web程序的话便会初始化一些Web程序需要的东西。
综上所述:postProcessBeanFactory(),主要是为了给子类提供可扩展点的,是一个可选项。
由上面我们可以来看下Web的一些扩展点(org.springframework.web.context.support.AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext#postProcessBeanFactory)。
1 @Override 2 protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { 3 beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig)); 4 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class); 5 beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class); 6 7 WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext); 8 WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig); 9 }
上面的代码大同小异,先是添加了bean的后置处理器,然后忽略了一些Aware。
我看主要看下web扩展点的关键代码,也就是WebApplicationContextUtils。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
registerWebApplicationScopes:
1 public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ServletContext sc) { 2 beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_REQUEST, new RequestScope()); 3 beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_SESSION, new SessionScope(false)); 4 beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_GLOBAL_SESSION, new SessionScope(true)); 5 if (sc != null) { 6 ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc); 7 beanFactory.registerScope(WebApplicationContext.SCOPE_APPLICATION, appScope); 8 // Register as ServletContext attribute, for ContextCleanupListener to detect it. 9 sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope); 10 } 11 12 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory()); 13 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory()); 14 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory()); 15 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory()); 16 if (jsfPresent) { 17 FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory); 18 } 19 }
2-10行代码主要是注册了web的scope,如request、session、globalSession、application这些scope。以及后面的注册特殊的依赖类型等等,这不是我们的重点,不做赘述。
这里我们需要知道,在Spring容器中默认只注册了singleton、prototype,向上面的四种都是需要手动注册的,这也就是为什么还需要调用2-10行代码的原因了。
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
registerEnvironmentBeans:注册和Environment有关的beans。
Scope是什么:
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
自定义Scope:
我们首先来下web的定制scope是如何实现的,同样是基于接口Scope,只不过封装了一层AbstractRequestAttributesScope。
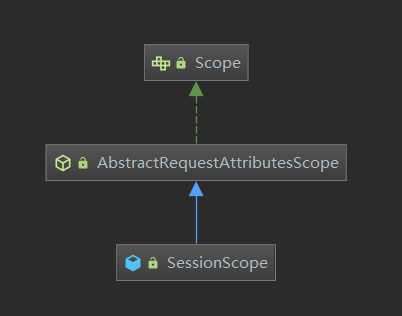
所以如果要自定义一个scope的话,只需要实现以下Scope接口。这里我们直接用Spring封装好的SimpleThreadScope作为demo。
1、使用代码的方式注册一个新的scope:
1 public class TestSpring { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Properties properties = System.getProperties(); 5 properties.setProperty("config", "beans"); 6 7 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("${config}.xml"); 8 TestBean testBean = ctx.getBean(TestBean.class); 9 testBean.run(); 10 11 ctx.getBeanFactory().registerScope("thread", new SimpleThreadScope()); 12 } 13 }
2、使用配置方式:
1 <!-- 自定义scope map --> 2 <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.CustomScopeConfigurer"> 3 <property name="scopes"> 4 <map> 5 <entry key="myScope" value="com.jdr.spring.scope.MyScope"/> 6 </map> 7 </property> 8 </bean> 9 10 <!-- 使用自定义scope的bean --> 11 <bean id="scopeTestBean" class="com.jdr.spring.scope.ScopeTestBean" scope="myScope"> 12 <!-- 让Bean符合自定义的作用域 --> 13 <!--<aop:scoped-proxy/>--> 14 </bean>
Spring源码学习笔记(六、Spring启动流程解析:BeanFactory后置处理)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/bzfsdr/p/12984608.html