Java线程实现的两种方式:
1.继承Thread类
2.实现java.lang.Runnable接口
此类实例化的对象即线程,此类的常用构造方法:
1.public Thread(); 创建一个新的线程对象
2.public Thread(String threadName); 创建一个名为threadName的线程对象;
Thread对象需要一个任务来执行,在run();方法中填写任务代码,start();方法启动该线程
import java.lang.Thread; import java.io.*; public class threadTest extends Thread { private int time = 10; public void run() { while (true) { int result = 11 - time; System.out.println("this is the " + result + " times"); if(--time == 0) { return; } } } public static void main(String[] args){ new threadTest().start(); } }
输出结果
this is the 1 times this is the 2 times this is the 3 times this is the 4 times this is the 5 times this is the 6 times this is the 7 times this is the 8 times this is the 9 times this is the 10 times
如果start()调用已启动线程,程序会抛出IllegalThreadStateException异常
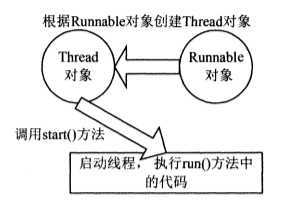
若需继承其他类,还要实现多线程的话,实现多线程方法可以用实现Runnable接口来实现。
构造方法:
public Thread(Runnable traget);
public Thread(Runnable traget, String name);
通过实现Runnable接口方法实现的多线程,其实是编写实现了Runnable的类,实例化该类对象,以此创建Runnable对象。再使用构造方法构造Thread实例,使用start();方法启动
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yus-1994/p/12996178.html