1.简单介绍
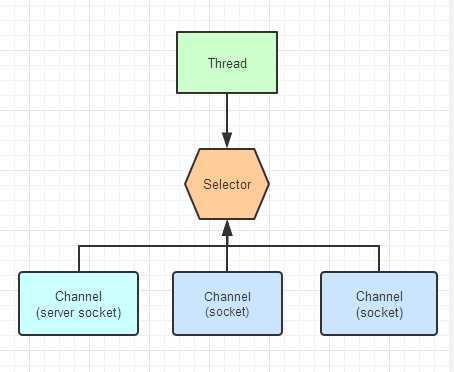
选择器提供选择执行已经就绪的任务的能力.从底层来看,Selector提供了询问通道是否已经准备好执行每个I/O操作的能力。Selector 允许单线程处理多个Channel。仅用单个线程来处理多个Channels的好处是,只需要更少的线程来处理通道。事实上,可以只用一个线程处理所有的通道,这样会大量的减少线程之间上下文切换的开销。
2.示例图
3.Selector的使用
3.1. 创建Selector
Selector对象是通过调用静态工厂方法open()来实例化的,如下:
Selector Selector=Selector.open()
3.2 将Channel注册到Selector
3.2.1.要实现Selector管理Channel,需要将channel注册到相应的Selector上,如下:
channel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey key= channel.register(selector,SelectionKey,OP_READ);
3.2.2.通过调用通道的register()方法会将它注册到一个选择器上。与Selector一起使用时,Channel必须处于非阻塞模式下,否则将抛出IllegalBlockingModeException异常,这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式,而套接字通道都可以。另外通道一旦被注册,将不能再回到阻塞状态,此时若调用通道的configureBlocking(true)将抛出BlockingModeException异常。
3.2.3.register()方法的第二个参数是“interest集合”,表示选择器所关心的通道操作,它实际上是一个表示选择器在检查通道就绪状态时需要关心的操作的比特掩码。比如一个选择器对通道的read和write操作感兴趣,那么选择器在检查该通道时,只会检查通道的read和write操作是否已经处在就绪状态。
它有以下四种操作类型:
Connect 连接
Accept 接受
Read 读
Write 写
3.2.4.需要注意并非所有的操作在所有的可选择通道上都能被支持,比如ServerSocketChannel支持Accept,而SocketChannel中不支持。我们可以通过通道上的validOps()方法来获取特定通道下所有支持的操作集合。
JAVA中定义了四个常量来表示这四种操作类型:
SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
SelectionKey.OP_READ
SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
4. select()方法介绍
int select():阻塞到至少有一个通道在你注册的事件上就绪了。
int select(long timeout):和select()一样,但最长阻塞时间为timeout毫秒。
int selectNow():非阻塞,只要有通道就绪就立刻返回。
5.创建NIO-Selector服务端

/** * 服务端 */ public class NioSelectorServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1.创建serverSocketChannel ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2.创建selector对象 Selector selector=Selector.open(); //3.绑定端口在服务端监听 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6668)); //4.设置为非阻塞 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //5.将serverSocketChannel通道注册到selector,事件为: serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //6.循环等待客户 while (true){ if (selector.select(5000)==0){//没有事件发生 System.out.println("5秒内没有事件发生...."); continue; } //7.如果返回值大于0,获得相对应的selectionKeys集合 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //迭代器遍历集合 Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ //获取selectionKey SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); //根据key做不同的响应 if (key.isAcceptable()){//如果事件是OP_ACCEPT,则有客户链接 //给该客户生成一个通道 SocketChannel socketChannel=serverSocketChannel.accept(); System.out.println("客户端连接ok,socketChannel:"+serverSocketChannel.hashCode()); //设置为非阻塞 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //将socketChannel注册到selector socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024)); }if (key.isReadable()){//如果是OP_READ //通过key反向得到socketChannel SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //获得channel关联的buffer ByteBuffer byteBuffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment(); channel.read(byteBuffer); System.out.println("从客户端发来消息:"+new String(byteBuffer.array())); } //手动移除当前key iterator.remove(); } } } }
6.创建NIO-Selector客户端

public class NioSelectorClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建socketChannel SocketChannel socketChannel=SocketChannel.open(); //2.设置非阻塞 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3.获取链接服务器端口和地址 InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",6666); //4.链接服务器 if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)){//判断是否链接上服务端 while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()){ System.out.println("客户端链接中,此时不会阻塞,可以........."); } } //5.如果链接ok,发送数据 String message="hello,world"; //设置buffer的容量 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes()); //6.将buffer数据写入到socketChannel socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); System.in.read(); } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/hyy9527/p/13058248.html