1.简单介绍
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个请求一个线程,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接有I/O请求时才启动一个线程进行处理。
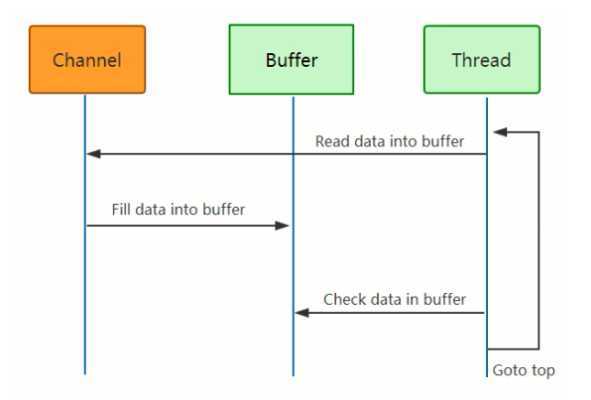
2.模型图
3.Buffer缓冲区
a.Buffer在Java NIO的作用
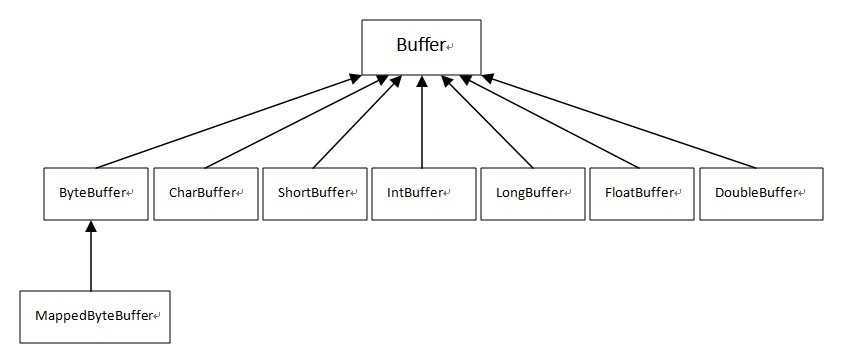
在Java NIO中,缓冲区的作用也是用来临时存储数据,可以理解为是I/O操作中数据的中转站。缓冲区直接为通道(Channel)服务,写入数据到通道或从通道读取数据,这样的操利用缓冲区数据来传递就可以达到对数据高效处理的目的。在NIO中主要有八种缓冲区类(其中MappedByteBuffer是专门用于内存映射的一种ByteBuffer):
b.Buffer的属性
容量(capacity):缓冲区能够容纳的数据元素的最大数量。这一容量在缓冲区创建时被设定,并且永远不能被改变
上界(limit):缓冲区的第一个不能被读或写的元素。或者说,缓冲区中现存元素的计数
位置(position):下一个要被读或写的元素的索引。位置会自动由相应的 get( )和 put( )函数更新
标记(mark):下一个要被读或写的元素的索引。位置会自动由相应的 get( )和 put( )函数更新一个备忘位置。调用 mark( )来设定 mark = postion。调用 reset( )设定 position =mark。标记在设定前是未定义的(undefined)。这四个属性之间总是遵循以下关系:0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
c.Buffer的简单实例
//Debug可以看出属性变化
public class BufferBasic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个长度为5,类型为int的buffer
IntBuffer intBuffer=IntBuffer.allocate(5);
//向buffer存放数据
for (int i = 0; i < intBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
intBuffer.put(i*2);
}
}
}
4.NIO通道
java.nio.channels包中的Channel接口的已知实现类:
FileChannel:从文件中读写数据。
DatagramChannel:能通过UDP读写网络中的数据。
SocketChannel:能通过TCP读写网络中的数据。
ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的TCP连接,像Web服务器那样。对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel。
a. FileChannel
a-1. 从文件中读取信息
/**
* 在通道中使用buffer读数据
*/
public class FileChannelNIO02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取输入流
File file = new File("f:\\file01.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//获取对应的channel
FileChannel fileChannel=fileInputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
//将通道数据读取到buffer
fileChannel.read(byteBuffer);
//将字节转为字符串
String str=new String(byteBuffer.array());
System.out.println(str);
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
a-2. 写入数据到文件中
public class FileChannelNIO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str="dcascs";
//创建一个输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("f:\\file01.txt");
//获取对应的filechannel
FileChannel fileChannel=fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//将str放入缓冲区
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
//对byteBuffer进行flip;
byteBuffer.flip();
//将bytebuffer写入到fileChannel
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
//关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
a-3. 数据从文件中读取或者写入到文件中
public class FileChannelNIO03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
//获取对应的channel
FileChannel fileChannel1=fileInputStream.getChannel();
//创建一个输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel fileChanne2= fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true){
//重置标志位
// byteBuffer.clear();
//循环读取
int read = fileChannel1.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(read);
if (read==-1){//表示读完
break;
}
//将buffer数据写入到fileChanne2
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChanne2.write(byteBuffer);
}
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
a-4. 使用transferFrom完成拷贝
/** * 使用transferFrom完成拷贝 */ public class FileChannelNIO04 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //获取输入流 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("f:\\a.jpg"); FileChannel fileChannel1=fileInputStream.getChannel(); //创建一个输出流 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream("f:\\b.jpg"); FileChannel fileChanne2= fileOutputStream.getChannel(); //使用transferFrom完成拷贝,将a.jpg拷贝到f盘下,名字为b.jpg fileChanne2.transferFrom(fileChannel1,0,fileChannel1.size()); fileChannel1.close(); fileChanne2.close(); fileInputStream.close(); fileOutputStream.close(); } }
a-5. ReadOnlyBuffer 只读模式
//只读
public class ReadOnlyBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个长度为5,类型为int的buffer
ByteBuffer buffer= ByteBuffer.allocate(50);
//向buffer存放数据
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i++) {
buffer.put((byte)i);
}
//读取转换
buffer.flip();
ByteBuffer readOnly=buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
System.out.println(readOnly);
while (readOnly.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(readOnly.get());
}
}
}
a-6. MappedByteBuffer 让文件直接在内存(堆外的内存)中进行修改;
/** * MappedByteBuffer直接在堆外内存修改,操作系统不需要拷贝一次 */ public class MappedByteBufferTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /** * RandomAccessFile随机访问文件类 * rw代表读写模式,不存在则新建 */ RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile=new RandomAccessFile("1.txt","rw"); //获取对应的通道 FileChannel fileChanne=randomAccessFile.getChannel(); /** * 参数1:读写模式 * 参数2:修改文件的起始位置 * 参数3:映射到内存的大小,即文件的字节数 */ MappedByteBuffer map = fileChanne.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 3); /** * 修改开始 * 参数一:修改的起始位置 * 参数二:该位置要修改成的数据 */ map.put(0,(byte)‘H‘); randomAccessFile.close(); } }
未完待续...............
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/hyy9527/p/13058141.html