1.什么是零拷贝
一种避免 CPU 将数据从一块存储拷贝到另外一块存储的技术。针对操作系统中的设备驱动程序、文件系统以及网络协议堆栈而出现的各种零拷贝技术极大地提升了特定应用程序的性能,并且使得这些应用程序可以更加有效地利用系统资源。这种性能的提升就是通过在数据拷贝进行的同时,允许 CPU 执行其他的任务来实现的。
2.数据拷贝
2.1. 传统方式下的数据拷贝原理
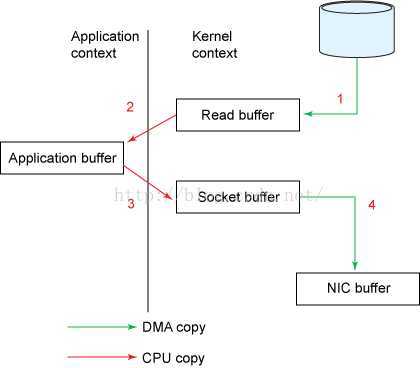
①一个read系统调用后,DMA执行了一次数据拷贝,从磁盘到内核空间
②read结束后,发生第二次数据拷贝,由cpu将数据从内核空间拷贝至用户空间
③send系统调用,cpu发生第三次数据拷贝,由cpu将数据从用户空间拷贝至内核空间(socket缓冲区)
④send系统调用结束后,DMA执行第四次数据拷贝,将数据从内核拷贝至协议引擎
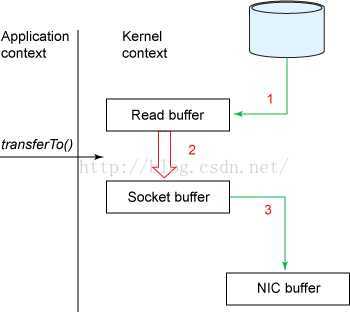
2.1. 基于NIO的数据零拷贝(sendfile)
public class IOServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7001); ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open(); //绑定 serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress); //创建buffer ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); while (true){ //获得socketChannel SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); int readcount=0; while (-1!=readcount){ try{ readcount = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer); }catch (Exception e){ break; } byteBuffer.rewind();//倒带,让position=0,mark作废 } } } }
3.2. 客户端
public class IOClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); // socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 7001)); socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 7001)); String fileName = "1.txt"; //获取文件通道 FileChannel fileChannel = new FileInputStream(fileName).getChannel(); //发送开始计时 Long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); /** transferTo实现零拷贝 * 无论文件大小 *在Linux系统下运行transferTo一次性可以传输完成 * 在windows下一次只能发送8M,超出范围文件需要分段传输 * transferTo(long position, long count,WritableByteChannel target) *参数1:文件传输时的位置,作为分段传输的标注点 * 参数2:文件大小 * 参数3.通道 */ long l = fileChannel.transferTo(0, fileChannel.size(), socketChannel); System.out.println("发送的字节总数="+l+",耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-startTime)); //关闭 fileChannel.close(); } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/hyy9527/p/13059760.html