1 事务的隔离级别
1.1 数据库事务并发问题
假设现在有两个事务:Transaction01和Transaction02并发执行。
①脏读
[1]Transaction01将某条记录的AGE值从20修改为30。
[2]Transaction02读取了Transaction01更新后的值:30。
[3]Transaction01回滚,AGE值恢复到了20。
[4]Transaction02读取到的30就是一个无效的值。
②不可重复读
[1]Transaction01读取了AGE值为20。
[2]Transaction02将AGE值修改为30。
[3]Transaction01再次读取AGE值为30,和第一次读取不一致。
③幻读
[1]Transaction01读取了STUDENT表中的一部分数据。
[2]Transaction02向STUDENT表中插入了新的行。
[3]Transaction01读取了STUDENT表时,多出了一些行。
1.2 隔离级别
数据库系统必须具有隔离并发运行各个事务的能力,使它们不会相互影响,避免各种并发问题。一个事务与其他事务隔离的程度称为隔离级别。SQL标准中规定了多种事务隔离级别,不同隔离级别对应不同的干扰程度,隔离级别越高,数据一致性就越好,但并发性越弱。
①读未提交:READ UNCOMMITTED
允许Transaction01读取Transaction02未提交的修改。
②读已提交:READ COMMITTED
要求Transaction01只能读取Transaction02已提交的修改。
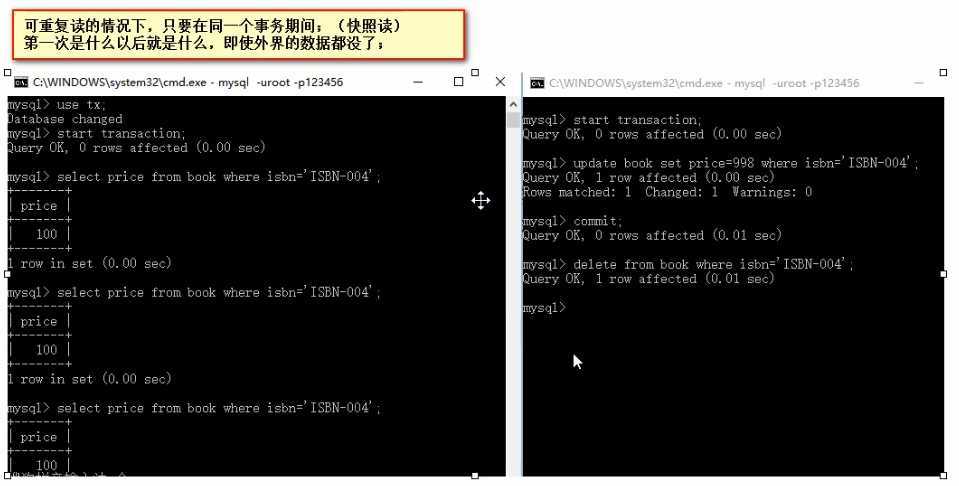
③可重复读:REPEATABLE READ
确保Transaction01可以多次从一个字段中读取到相同的值,即Transaction01执行期间禁止其它事务对这个字段进行更新。
④串行化:SERIALIZABLE
确保Transaction01可以多次从一个表中读取到相同的行,在Transaction01执行期间,禁止其它事务对这个表进行添加、更新、删除操作。可以避免任何并发问题,但性能十分低下。
⑤各个隔离级别解决并发问题的能力见下表
|
|
脏读 |
不可重复读 |
幻读 |
|
READ UNCOMMITTED |
有 |
有 |
有 |
|
READ COMMITTED |
无 |
有 |
有 |
|
REPEATABLE READ |
无 |
无 |
有 |
|
SERIALIZABLE |
无 |
无 |
无 |
⑥各种数据库产品对事务隔离级别的支持程度
|
|
Oracle |
MySQL |
|
READ UNCOMMITTED |
× |
√ |
|
READ COMMITTED |
√ |
√ |
|
REPEATABLE READ |
× |
√(默认) |
|
SERIALIZABLE |
√ |
√ |
修改MySQL隔离级别
SET [SESSION | GLOBAL] TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL {READ UNCOMMITTED | READ COMMITTED | REPEATABLE READ | SERIALIZABLE}
如:SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED;
查询MySQL的隔离级别
SELECT @@global.tx_isolation; //查询全局隔离级别
SELECT @@session.tx_isolation;//查询当前会话隔离级别
SELECT @@tx_isolation;//同上
事务操作
开启事务 start transaction;
提交事务 commit;
回滚事务 rollback;
脏读:
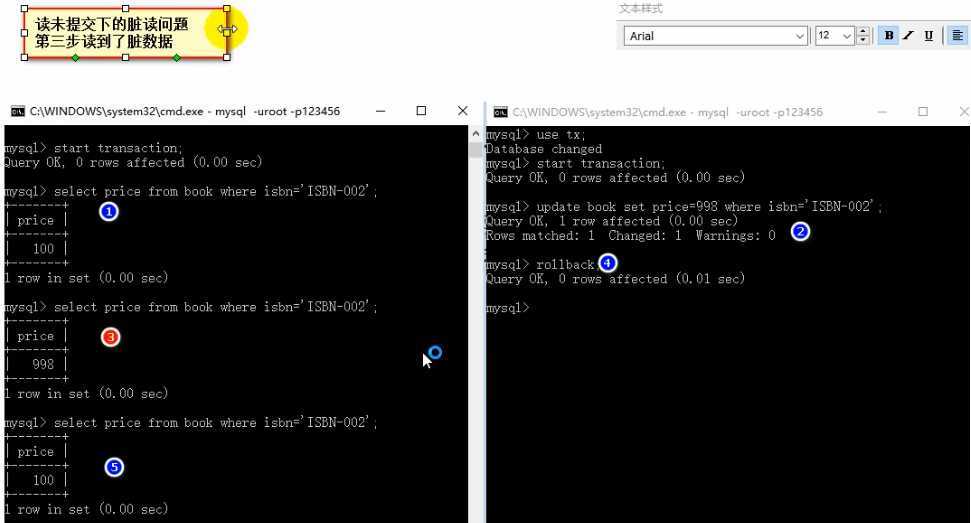
可重复度:
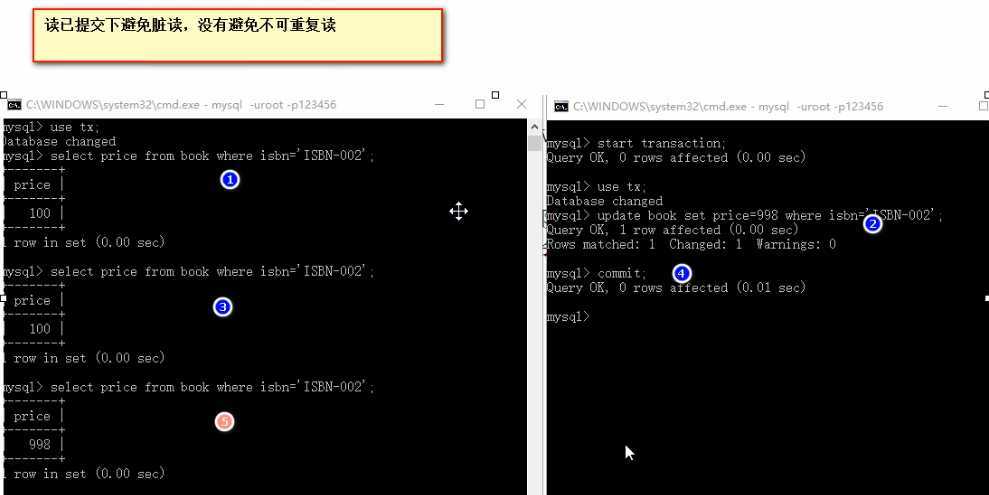
不可重复度:
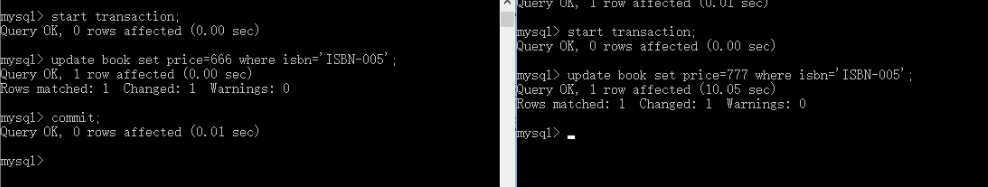
并发修改:底层会自动进行排队等待
事务的传播行为
简介
当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播。例如:方法可能继续在现有事务中运行,也可能开启一个新事务,并在自己的事务中运行。
事务的传播行为可以由传播属性指定。Spring定义了7种类传播行为。
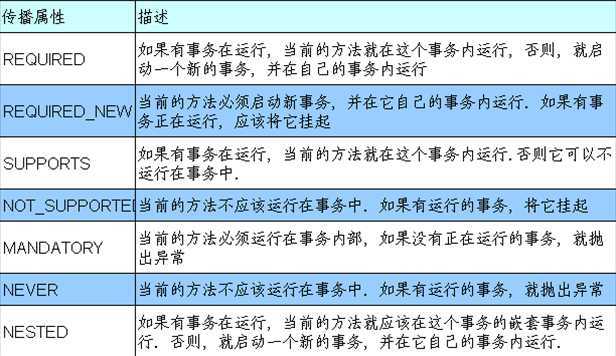
事务传播属性可以在@Transactional注解的propagation属性中定义。
说明
①REQUIRED传播行为
当bookService的purchase()方法被另一个事务方法checkout()调用时,它默认会在现有的事务内运行。这个默认的传播行为就是REQUIRED。因此在checkout()方法的开始和终止边界内只有一个事务。这个事务只在checkout()方法结束的时候被提交,结果用户一本书都买不了。
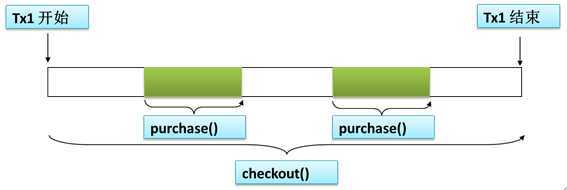
②REQUIRES_NEW传播行为
表示该方法必须启动一个新事务,并在自己的事务内运行。如果有事务在运行,就应该先挂起它。
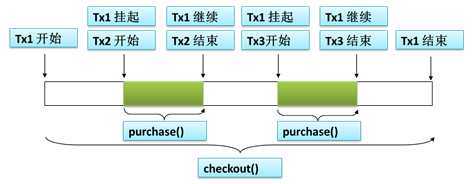
案例代码:
BookDao.java:
1 package com.atguigu.dao; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 4 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; 5 import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; 6 7 @Repository 8 public class BookDao { 9 10 @Autowired 11 JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; 12 13 /** 14 * 1、减余额 15 * 16 * 减去某个用户的余额 17 */ 18 public void updateBalance(String userName,int price){ 19 String sql = "UPDATE account SET balance=balance-? WHERE username=?"; 20 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, price,userName); 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * 2、按照图书的ISBN获取某本图书的价格 25 * @return 26 */ 27 public int getPrice(String isbn){ 28 String sql = "SELECT price FROM book WHERE isbn=?"; 29 return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class, isbn); 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 3、减库存;减去某本书的库存;为了简单期间每次减一 34 */ 35 public void updateStock(String isbn){ 36 String sql = "UPDATE book_stock SET stock=stock-1 WHERE isbn=?"; 37 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, isbn); 38 } 39 40 /** 41 * 4、改图书价格 42 * @param isbn 43 * @param price 44 */ 45 public void updatePrice(String isbn,int price){ 46 String sql = "update book set price=? where isbn=?"; 47 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, price,isbn); 48 } 49 }
BookService.java:
1 package com.atguigu.service; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 6 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 7 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 8 import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation; 9 import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation; 10 import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; 11 12 import com.atguigu.dao.BookDao; 13 14 @Service 15 public class BookService { 16 17 @Autowired 18 BookDao bookDao; 19 20 21 22 // @Autowired 23 // BookService bookService; 24 25 /** 26 * 事务细节: 27 * isolation-Isolation:事务的隔离级别; 28 * 29 * 30 * 31 * noRollbackFor-Class[]:哪些异常事务可以不回滚 32 * noRollbackForClassName-String[](String全类名): 33 * 34 * rollbackFor-Class[]:哪些异常事务需要回滚; 35 * rollbackForClassName-String[]: 36 * 37 * 异常分类: 38 * 运行时异常(非检查异常):可以不用处理;默认都回滚; 39 * 编译时异常(检查异常):要么try-catch,要么在方法上声明throws 40 * 默认不回滚; 41 * 42 * 事务的回滚:默认发生运行时异常都 回滚,发生编译时异常不会回滚; 43 * noRollbackFor:哪些异常事务可以不回滚;(可以让原来默认回滚的异常给他不回滚) 44 * noRollbackFor={ArithmeticException.class,NullPointerException.class} 45 * noRollbackForClassName 46 * 47 * rollbackFor:原本不回滚(原本编译时异常是不回滚的)的异常指定让其回滚; 48 * 49 * readOnly-boolean:设置事务为只读事务: 50 * 可以进行事务优化; 51 * readOnly=true:加快查询速度;不用管事务那一堆操作了。 52 * 53 * timeout-int(秒为单位):超时:事务超出指定执行时长后自动终止并回滚 54 * @throws FileNotFoundException 55 * 56 * 57 * propagation-Propagation:事务的传播行为; 58 * 传播行为(事务的传播+事务的行为); 59 * 如果有多个事务进行嵌套运行,子事务是否要和大事务共用一个事务; 60 * 传播行为: 61 * AService{ 62 * tx_a(){ 63 * //a的一些方法 64 * tx_b(){ 65 * } 66 * tx_c(){ 67 * } 68 * } 69 * } 70 * 71 * 72 */ 73 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) 74 public void checkout(String username,String isbn){ 75 //1、减库存 76 bookDao.updateStock(isbn); 77 78 int price = bookDao.getPrice(isbn); 79 // try { 80 // Thread.sleep(3000); 81 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { 82 // e.printStackTrace(); 83 // } 84 //2、减余额 85 bookDao.updateBalance(username, price); 86 87 //int i = 10/0; 88 //new FileInputStream("D://hahahahha.aa"); 89 } 90 91 92 @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) 93 public void updatePrice(String isbn,int price){ 94 bookDao.updatePrice(isbn, price); 95 } 96 97 98 99 /** 100 * 根据业务的特性;进行调整 101 * isolation=Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED:读出脏数据 102 * 103 * 104 * READ_COMMITTED;实际上业务逻辑中用的最多的也是这个; 105 * REPEATABLEP_READ; 106 * @param isbn 107 * @return 108 */ 109 @Transactional(readOnly=true) 110 public int getPrice(String isbn){ 111 return bookDao.getPrice(isbn); 112 } 113 114 115 @Transactional 116 public void mulTx(){ 117 118 //ioc.getBean("BookSerice"); 119 checkout("Tom", "ISBN-001"); 120 121 updatePrice("ISBN-002", 998); 122 123 int i=10/0; 124 } 125 }
MulService.java:
1 package com.atguigu.service; 2 3 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 5 import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; 6 7 @Service 8 public class MulService { 9 10 @Autowired 11 private BookService bookService; 12 13 @Transactional 14 public void mulTx(){ 15 //都是可以设置的; 16 //传播行为来设置这个事务方法是不是和之前的大事务共享一个事务(使用同一条连接); 17 //REQUIRED 18 bookService.checkout("Tom", "ISBN-001"); 19 20 //REQUIRED REQUIRES_NEW 21 bookService.updatePrice("ISBN-002", 998); 22 23 //int i = 10/0; 24 } 25 26 }
tx.xml:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" 6 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd"> 9 10 <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"></context:component-scan> 11 12 13 <!-- 0、引入外部配置文件 --> 14 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:dbconfig.properties" /> 15 <!-- 1、配置数据源 --> 16 <bean id="pooledDataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> 17 <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property> 18 <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> 19 <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property> 20 <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property> 21 </bean> 22 <!-- 2、配置JdbcTemplate操作数据库 value="#{pooledDataSource}" ref="pooledDataSource"--> 23 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 24 <property name="dataSource" value="#{pooledDataSource}"></property> 25 </bean> 26 27 <!-- 3、配置声明式事务 28 1)、Spring中提供事务管理器(事务切面),配置这个事务管理器 29 2)、开启基于注解的事务式事务;依赖tx名称空间 30 3)、给事务方法加注解 31 --> 32 <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> 33 <property name="dataSource" ref="pooledDataSource"></property> 34 </bean> 35 36 <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> 37 38 39 </beans>
TxTest.java:
1 package com.atguigu.test; 2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 3 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 7 8 import com.atguigu.service.BookService; 9 import com.atguigu.service.MulService; 10 11 public class TxTest { 12 13 ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx.xml"); 14 15 /** 16 * 有事务的业务逻辑,容器中保存的是这个业务逻辑的代理对象 17 * @throws FileNotFoundException 18 * 19 * 20 * multx(){ 21 * //REQUIRED 22 * A(){ 23 * //REQUIRES_NEW 24 * B(){} 25 * //REQUIRED 26 * c(){} 27 * } 28 * 29 * //REQUIRES_NEW 30 * D(){ 31 * DDDD()// REQUIRES_NEW不崩,REQUIRED崩 32 * //REQUIRED 33 * E(){ 34 * //REQUIRES_NEW 35 * F(){ 36 * //10/0(E崩,G崩,D崩,A,C崩) 37 * } 38 * } 39 * //REQUIRES_NEW 40 * G(){} 41 * } 42 * 43 * 44 * 10/0(B成功,D整个分支下全部成功) 45 * 任何处崩,已经执行的REQUIRES_NEW都会成功; 46 * 47 * 如果是REQUIRED;事务的属性都是继承于大事务的; 48 * 而propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW可以调整 49 * 默认:REQUIRED; 50 * 51 * REQUIRED:将之前事务用的connection传递给这个方法使用; 52 * REQUIRES_NEW:这个方法直接使用新的connection; 53 * } 54 * 55 */ 56 @Test 57 public void test() throws FileNotFoundException { 58 BookService bookService = ioc.getBean(BookService.class); 59 60 //MulService bean = ioc.getBean(MulService.class); 61 //bean.mulTx(); 62 63 //bookService.checkout("Tom", "ISBN-001"); 64 //int price = bookService.getPrice("ISBN-001"); 65 //System.out.println("读取到的数据:"+price); 66 //System.out.println(bookService.getClass()); 67 68 //效果都没改(相当于回滚了),虽然mulTx的两个方法都开新车 69 //bookService.mulTx(); 70 71 System.out.println(bookService.getClass()); 72 //如果是MulService --mulTx()---调用bookService两个方法 73 //BookService---mulTx()--直接调用两个方法 74 75 /*** 76 * MulServiceProxy.mulTx(){ 77 * bookServiceProxy.checkout(); 78 * bookServiceProxy.updatePrice(); 79 * } 80 * 81 * 82 * 本类方法的嵌套调用就只是一个事务; 83 * BookServiceProxy.mulTx(){ 84 * checkout(); 85 * updatePrice(); 86 * //相当于 87 * bookDao.updateStock(isbn); 88 * int price = bookDao.getPrice(isbn); 89 * bookDao.updateBalance(username, price); 90 * 91 * bookDao.updatePrice(isbn, price); 92 * } 93 */ 94 95 } 96 97 }
流程图解:
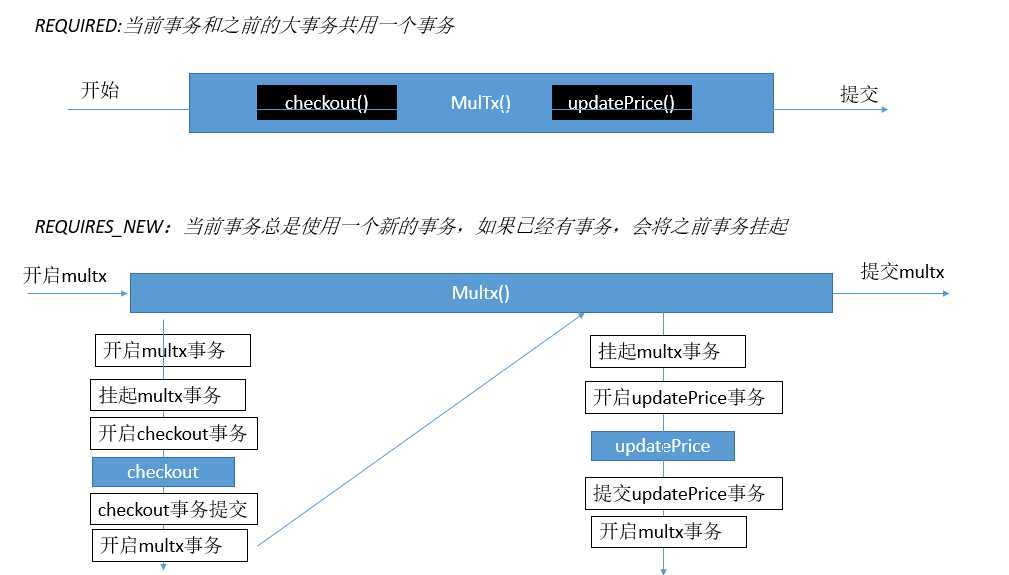
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/116970u/p/13081650.html