A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a binary tree which has the following properties:
If we swap the left and right subtrees of every node, then the resulting tree is called the Mirror Image of a BST.
Now given a sequence of integer keys, you are supposed to tell if it is the preorder traversal sequence of a BST or the mirror image of a BST.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤1000). Then N integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, first print in a line YES if the sequence is the preorder traversal sequence of a BST or the mirror image of a BST, or NO if not. Then if the answer is YES, print in the next line the postorder traversal sequence of that tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input 1:
7
8 6 5 7 10 8 11
Sample Output 1:
YES
5 7 6 8 11 10 8
Sample Input 2:
7
8 10 11 8 6 7 5
Sample Output 2:
YES
11 8 10 7 5 6 8
Sample Input 3:
7
8 6 8 5 10 9 11
Sample Output 3:
NO
给定一个输入序列,判断它是否是一棵二叉搜索树或其镜像树的前序遍历序列,如果是,输出 YES 以及它的后序遍历序列;如果不是,输出 NO。
二叉搜索树的定义:
镜像树:交换原二叉搜索树每个节点的左右子树。所以它满足:
首先我们应该明白一个道理:
一般情况下,我们要根据一棵二叉树的前序遍历结果和中序遍历结果才能得到它的后序遍历结果,但这里为什么只需要前序遍历结果就可以得到后序遍历结果?
二叉搜索树又叫二叉排序树,由它的定义就知道它本身是有序的,对一棵二叉搜索树进行中序遍历,得到就是一个非降序有序序列,这也可以作为一种排序方法。
所以如果给出的序列的确是一棵二叉搜索树的前序遍历的话,对它进行一次排序就能得到它的中序遍历结果,前序+中序就能得到后序,所以需要明白这个隐含条件。
你可以选择用给出的输入构造出一棵二叉搜索树,然后再对这棵树进行前序遍历,判断得到的结果是否和输入一致,如果不一致,那就输出 NO,如果一致就输出这这棵树的后序遍历结果。
我这里参考了柳神的代码,采用了一种更为简单的方法。
可以想象一下,根据 前序遍历结果和中序遍历结果能得到正确的后序遍历结果,那,如果给出的前序结果是错误的呢(它不是一棵二叉搜索树的前序结果),那肯定不能得到正确的后序遍历结果,假如我用一个vector来保存在此过程中得到的节点序列,那么最终这个vector中的节点个数肯定不够原来输入的个数(当然前提是算法正确)。
所以我们可以假设这个输入序列是对的,然后利用这个输入序列去得到后序序列并保存,如果最终得到的结果中节点个数不够,那说明它不是正确的前序遍历,否则就直接输出得到的结果。
当然这里还多了一步,如果把它当作前序遍历序列不能得到正确结果,我们还要把它当作二叉搜索树的镜像树的前序结果再执行一次这个过程,如果这次还不能得到正确结果,那说明它的确是错误的前序序列。
接下来我们来研究一下这个算法怎么写:
对于一棵二叉搜索树,因为它的有序性,对他进行前序遍历(根,左子树,右子树),得到的序列肯定满足这个样子:根节点 所有比它小的节点 所有比它的大的节点。
比如下面这棵二叉搜索树
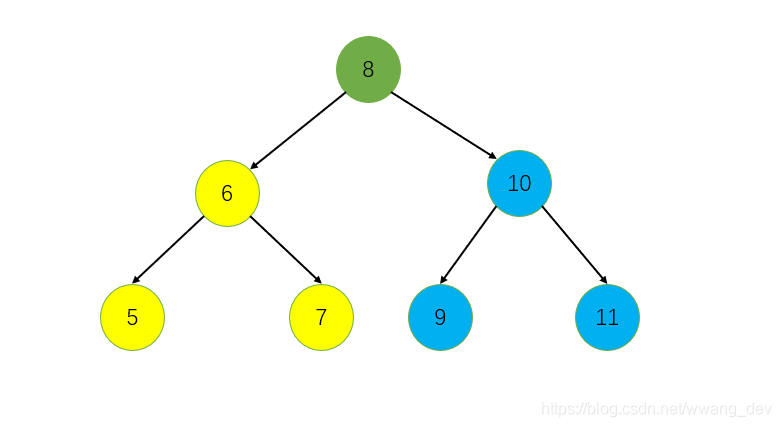
它的前序遍历结果是 8 567 91011,是不是很有特点,我们能根据这个很好的划分出它的左右子树:
8,设置左指针i,初始是8的下一个位置,右指针j,初始是当前树最后一个有效位置i从左往右,扫描前序序列,遇到比根小的就i++,会停在9的位置;j从右往左,扫描前序序列,遇到比根大于或等于的就j--,最后会停在7的位置j + 1 == i,对于每一个二叉搜索树的前序遍历都应该满足这个特点,所以这里可以作为函数的一个出口,不满足,就退出vector,注意顺序不能乱!从上面可以看出:
i == j + 1 就退出根的位置 > 最后一个有效位置,就直接退出。上面的过程是针对于 把输入序列当作二叉搜索树的前序遍历进行的,如果要把输入序列当作镜像树的前序遍历序列呢?很简单,根据对称性,只需要把 i 和 j 的扫描时的判断条件取个反就行了,也就是 > 变成 <=,> 变成 <=.
所以你可以写成两个函数分别处理这两种情况,也可以设置一个标志在函数内部分情况,我选择第二种,直接看代码很清楚。
综上,总体执行流程为:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
// 前序遍历序列,后序遍历序列
vector<int> pre, post;
// 是否当作二叉搜索树的镜像树处理
bool ismirror = false;
// 当前处理的树的根节点在前序序列中的下标
// 当前处理的树最后一个节点在前序序列中的有效位置
void GetPost(int root, int tail) {
// 最小的树就一个节点,root=tail
if (root > tail) return;
int i = root + 1, j = tail;
// 当作二叉搜索树树处理
if (!ismirror) {
// 左孩子都小于根
while (i <= tail && pre[i] < pre[root]) i++;
// 右孩子都大于等于根
while (j > root && pre[root] <= pre[j]) j--;
// 当作二叉搜索树的镜像树处理
} else {
// 左孩子都大于等于根
while (i <= tail && pre[i] >= pre[root]) i++;
// 右孩子都小于根
while (j > root && pre[root] > pre[j]) j--;
}
// 不满足二叉搜索树前序遍历结果特点
if (i != j + 1) return;
// 对左子树执行此操作
GetPost(root + 1, j);
// 对右子树执行此操作
GetPost(i, tail);
// 保存当前根
post.push_back(pre[root]);
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
pre.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) cin >> pre[i];
// 当作前序遍历结果,尝试得到后序结果
GetPost(0, n - 1);
// 所得结果节点个数错误
if (post.size() != n) {
// 改变标志位
ismirror = true;
post.clear();
// 当作镜像树前序遍历结果,尝试获取后序结果
GetPost(0, n - 1);
}
// 所得结果正确
if (post.size() == n) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
cout << post[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) cout << " " << post[i];
// 所得结果依然错误
} else {
cout << "NO";
}
return 0;
}
PAT 1043 Is It a Binary Search Tree (25分) 由前序遍历得到二叉搜索树的后序遍历
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/codervivi/p/13126320.html