3.1 加入工程前的准备工作
执行 make s3c24x0_defconfig,加入配置,然后执行 make menuconfig
System configuration 中关掉配置 Init system 和 /bin/sh
Target packages 中关掉配置 BusyBox
Filesystem images 中关掉配置 tar the root filesystem
3.2 uboot 配置
uboot 的配置与 交叉编译工具链相似。
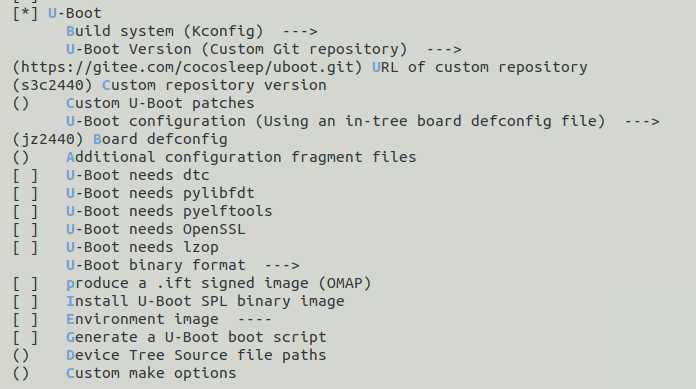
make menuconfig 进入配置菜单中,在 bootloader 中进行配置,选中 U-boot ,就可以打开 U-boot 的配置了:
- Build system:uboot 的构建系统,早期的 uboot 并不像现在的版本一样使用的是 kconfig,而是自定义的一套编译机制。选择 Kconfig
- U-Boot Version:uboot 的版本,里面包含一个最新版本,或者选择本地的压缩包,或者是自定义版,或者自定义的 git 版本,或者自定义的 Mercurial 版本,或者自定义的 svn 版本。一般我们都会对 uboot 进行改动,所以一般都是自定义的版本,当然选择公版的话,就得自己打补丁,对我自己玩的版本来说,我是选择 git 版本,我只需要维护我自己的 git 上面的 uboot 的版本即可。
- URL of custom repository:git 的地址,我填入的是自己的 git 版本地址。因为这个工程是私有的,需要输入密码和账户才能下载,所以不公开。这里填入的就是 git clone 后面的地址
- U-Boot configuration:
- Using an in-tree board defconfig file:使用 uboot 中的板defconfig文件
- Using a custom board (def)config file:使用自定义板配置文件
- 这两个选项,一个是使用 uboot 中的 xxx_defconfig 文件,选择这个后,后面需要提供一个uboot 中的 defconfig 文件,另一个选项,则是在 buildroot 中源码树中配置的。我的版本是选第一项
- U-Boot binary format:uboot 的二进制文件格式,一般都是选 bin 文件格式
- 至于其他选项,根据自己的工程进行配置即可。
3.3 编译
配置完成后,保存配置,进行测试编译。
编译成功。

修改下Makefile 下的 distclean,删除掉 uboot,因为 uboot 是通过单独的 git 工程进行管理的,所以不需要。

执行 make update-defconfig 更新配置文件。执行 make distclean ,清除一下,上传 git。
至于 Uboot 如何做前期修改之类的,查看博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/kele-dad/p/12791390.html
三、buildroot 添加 uboot 工程
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/kele-dad/p/13127240.html



