参考资料:https://redbyte.eu/en/blog/using-the-nginx-auth-request-module/
In this post I will describe one interesting customer request we had previously dealt with. This is an older project, but I think the problem is still relevant.
The customer has an existing web application that is hosted in a dedicated datacenter along with the entire HW infrastructure, which includes Citrix NetScaler - a load balancer and reverse proxy appliance with few extra features. One such feature is an authentication gateway, i.e. NetScaler only allows access to backend applications to authenticated users. The customer’s web application is, however, only one of many applications that together form a complex system. All the applications are hosted in the same data center and share the same domain users, i.e., the domain user can access every application with one username/password pair. Within each application, each domain user is mapped to an application user. The situation is schematically illustrated in the following figure.
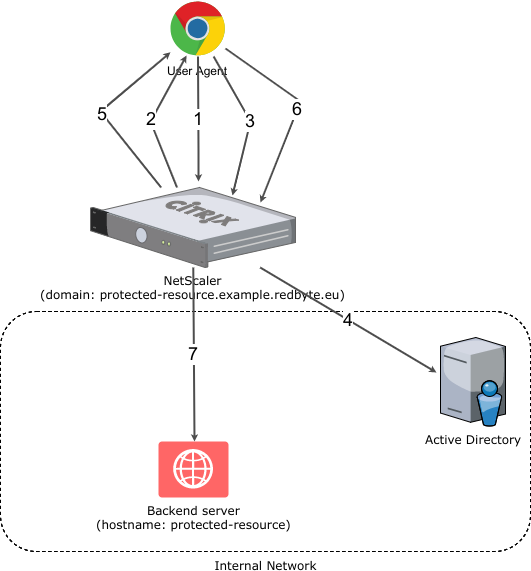
The simplified user authentication process consists of the following steps:
The problem with such setup is its testability. The customer has several staging environments and introducing NetScaler into these environments would be overkill (not counting the domain management for all the environments). The customer’s request was to somehow “bypass” NetScaler and all the complexity of user configuration and management without changing the code or configuration of the application. It had to look and behave as if NetScaler was there.
ngx_http_auth_request_moduleThe first solution that came to our minds was to use the excellent HAProxy load balancer (because we have several backends) and place a custom authentication proxy before it. Let’s call it FakeNetScaler (basically a reverse proxy server). This would mean that each HTTP request would be processed by two reverse proxies. Surely, there must be a more straightforward and simpler solution.
Another solution is to use NGINX HTTP Server along with the ngx_http_auth_request_module. The documentation for this module says, it implements client authorization based on the result of a subrequest. What exactly does this mean? The principle is quite simple - when you make an HTTP request to a protected URL, NGINX performs an internal subrequest to a defined authorization URL. If the result of the subrequest is HTTP 2xx, NGINX proxies the original HTTP request to the backend server. If the result of the subrequest is HTTP 401 or 403, access to the backend server is denied. By configuring NGINX, you can redirect those 401s or 403s to a login page where the user is authenticated and then redirected to the original destination. The entire authorization subrequest process is then repeated, but because the user is now authenticated the subrequest returns HTTP 200 and the original HTTP request is proxied to the backend server.
Naturally, NGINX only provides a mechanism to achieve this - the authorization server must be custom build for specific use case. In our case, FakeNetscaler is the authorization server - I will get to that later. Now let’s see how the ngx_http_auth_request_module works:
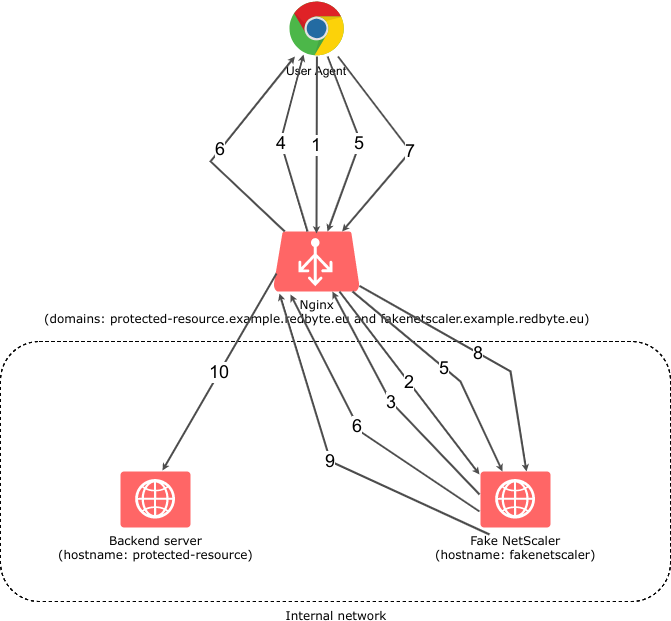
At first glance, this seems to be even more complex than the original NetScaler authentication process, but the truth is that I just described it using white box approach, where in case of NetScaler it was described as a black box (especially the points 3., 4. and 5.).
It should be clear now, how the ngx_http_auth_request_module works. Let’s look at the NGINX configuration file for protected-resource.example.redbyte.eu domain:
1server {
2 listen 443 ssl;
3 server_name protected-resource.example.redbyte.eu;
4
5 # ssl and server configuration left out
6
7 location / {
8 auth_request /auth;
9 error_page 401 = @error401;
10
11 auth_request_set $user $upstream_http_x_forwarded_user;
12 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-User $user;
13 proxy_pass http://protected-resource:8080;
14 }
15
16 location /auth {
17 internal;
18 proxy_set_header Host $host;
19 proxy_pass_request_body off;
20 proxy_set_header Content-Length "";
21 proxy_pass http://fakenetscaler:8888;
22 }
23
24 location @error401 {
25 add_header Set-Cookie "NSREDIRECT=$scheme://$http_host$request_uri;Domain=.example.redbyte.eu;Path=/";
26 return 302 https://fakenetscaler.example.redbyte.eu;
27 }
28
29}The most important lines are:
/ NGINX will execute the authorization subrequest to the /auth URLhttp://fakenetscaler:8888, which is a host on the internal networkNGINX configuration file for authorization server domain fakenetscaler.example.redbyte.eu:
1server {
2 listen 443 ssl;
3 server_name fakenetscaler.example.redbyte.eu;
4
5 # ssl and server configuration left out
6
7 location / {
8 proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
9 proxy_pass http://fakenetscaler:8888;
10 }
11}As you can see, it is a reverse proxy to a backend server at http://fakenetscaler:8888 running the autorization HTTP server.
So far, we have only played with NGINX server configuration. Let’s look at the FakeNetscaler authorization server. As I mentioned earlier, NGINX only provides an authorization framework, the authorization server needs to be custom build and tailored to customer’s requirements:
/auth request and decide whether or not the user is authenticated on a cookie. If it is, it will respond with HTTP 200 if it does not, HTTP 401/ displays the login page/ submit the login form. If a user has entered the correct login and password, the cookie establishes that the user is authenticated and redirects it to the original destination based on the information stored in the Cookie. If the user did not enter the correct login information, the login page with the error description will be displayed again/auth request and based on the cookie value, decide whether user is logged in or not. In case the user is logged in the HTTP response code is 200, 401 otherwise./ URL displays the login page/ URL submits the login form. If the user has entered a valid username and password, a login cookie is created and the browser is redirected to original destination. If the user did not enter valid username or password the login page with error message is displayed.This should be a really simple service and we are going to implement it using the Go programming language. Go has a rich standard library including a very capable HTTP server. There is no need for a third party server runtime (e.g. as in most Java deployments).
Please, judge yourself, this is a complete source code of FakeNetScaler server:
1package main
2
3import (
4 "flag"
5 "fmt"
6 "github.com/BurntSushi/toml"
7 "github.com/codegangsta/negroni"
8 "github.com/gorilla/securecookie"
9 "github.com/julienschmidt/httprouter"
10 "gopkg.in/unrolled/render.v1"
11 "log"
12 "net/http"
13 "time"
14)
15
16var (
17 nsCookieName = "NSLOGIN"
18 nsCookieHashKey = []byte("SECURE_COOKIE_HASH_KEY")
19 nsRedirectCookieName = "NSREDIRECT"
20 cfg config
21)
22
23type config struct {
24 // e.g. https://protected-resource.example.redbyte.eu
25 DefaultRedirectUrl string
26 // shared password
27 Password string
28 // shared domain prefix between protected resource and auth server
29 // e.g. .example.redbyte.eu (note the leading dot)
30 Domain string
31}
32
33func main() {
34
35 // configuration
36 port := flag.Int("port", 8888, "listen port")
37 flag.Parse()
38 var err error
39 if cfg, err = loadConfig("config.toml"); err != nil {
40 log.Fatal(err)
41 }
42
43 // template renderer
44 rndr := render.New(render.Options{
45 Directory: "templates",
46 IsDevelopment: false,
47 })
48
49 // router
50 router := httprouter.New()
51 router.GET("/", indexHandler(rndr))
52 router.POST("/", loginHandler(rndr))
53 router.GET("/auth", authHandler)
54
55 // middleware and static content file server
56 n := negroni.New(negroni.NewRecovery(), negroni.NewLogger(),
57 &negroni.Static{
58 Dir: http.Dir("public"),
59 Prefix: ""})