重点基本上在两个rotate里面
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 200005
struct Node{
int key,height;
Node* lc;
Node* rc;
};
Node* root = NULL;
Node* newnode(int key){
Node* node = new Node();
node->key=key;
node->height=1;
node->lc=node->rc=NULL;
return node;
}
int h(Node* root){
if(root==NULL)return 0;
return root->height;
}
int getBalance(Node* root){
if(root==NULL)return 0;
return h(root->lc)-h(root->rc);
}
Node* leftRotate(Node* root){
Node* t=root->rc;
root->rc=t->lc;
t->lc=root;
root->height=max(h(root->lc),h(root->rc))+1;
t->height=max(h(t->lc),h(t->rc))+1;
return t;
}
Node* rightRotate(Node* root){
Node* t=root->lc;
root->lc=t->rc;
t->rc=root;
root->height=max(h(root->lc),h(root->rc))+1;
t->height=max(h(t->lc),h(t->rc))+1;
return t;
}
Node* LRRotate(Node* root){
root->lc=leftRotate(root->lc);
return rightRotate(root);
}
Node* RLRotate(Node* root){
root->rc=rightRotate(root->rc);
return leftRotate(root);
}
Node* rotate(Node* root){
int balance=getBalance(root);
if(balance == 2 && getBalance(root->lc)>=0)//右旋
return rightRotate(root);
if(balance == -2 && getBalance(root->rc)<0)//左旋
return leftRotate(root);
if(balance == 2)//左旋+右旋
return LRRotate(root);
if(balance == -2)//右旋+左旋
return RLRotate(root);
return root;
}
Node* insert(Node* root, int key){
if(root == NULL)return newnode(key);
if(key==root->key)return root;
if(key<root->key) root->lc = insert(root->lc,key);
else if(key>root->key) root->rc = insert(root->rc,key);
root->height = max(h(root->lc),h(root->rc))+1;
return root=rotate(root); // 调整平衡
}
Node* minValueNode(Node *root){//找root子树里最小值
Node* res=root;
while(res->lc)res=res->lc;
return res;
}
Node* del(Node* root, int key){
if(root == NULL)return root;
if(key<root->key)root->lc=del(root->lc,key);
else if(key>root->key)root->rc=del(root->rc,key);
else {//删该点
if(root->lc==NULL || root->rc==NULL){//缺了一个儿子
Node* t=root->lc?root->lc:root->rc;
if(t==NULL){t=root;root=NULL;}//叶子节点
else *root=*t;
free(t);
}
else {//把右子树最小结点提上来
Node* t = minValueNode(root->rc);
root->key = t->key;
root->rc = del(root->rc,t->key);
}
}
if(root==NULL)return root;//root是叶子
root->height = max(h(root->lc),h(root->rc))+1;
return root=rotate(root);
}
void printPre(Node* root){
if(root==NULL)return;
cout<<root->key<<‘\n‘;
printPre(root->lc);
printPre(root->rc);
}
void printMid(Node* root){
if(root==NULL)return;
printMid(root->lc);
cout<<root->key<<‘\n‘;
printMid(root->rc);
}
int main(){/*
root = insert(root,10);
root = insert(root,20);
root = insert(root,30);
root = insert(root,40);
root = insert(root,35);
*/
root = insert(root, 9);
root = insert(root, 5);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 0);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 11);
root = insert(root, -1);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 2);
root = del(root,9);
printMid(root);
puts("");
root = del(root,1);
printMid(root);
}
红黑树的其它原理和AVL高度相似,不同之处在于其保持平衡的策略
1.红黑树是一棵平衡二叉搜索树,其中序遍历单调不减。
2.节点是红色或黑色。
3.根节点是黑色。
4.每个叶节点(也有称外部节点的,目的是将红黑树变为真二叉树,即NULL节点,空节点)是黑色的。
5.每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(换句话说,从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
6.从根节点到每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点(这个数值叫做黑高度)。
所以,往红黑树里insert结点时的结点必定先设置为红色(保证性质6)。如果出现了双红现象,以下分为两种情况
设插入的点是x
1.不用rotate,只需要重新染色:x的父亲和叔叔都是红色
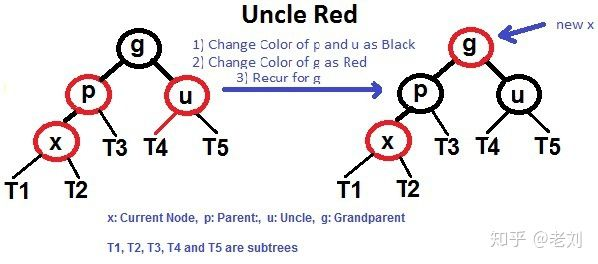
2.需要rotate : x的父亲p是红色,叔叔u是黑色,此时rotate(x的祖父g),然后将p和g重新染色
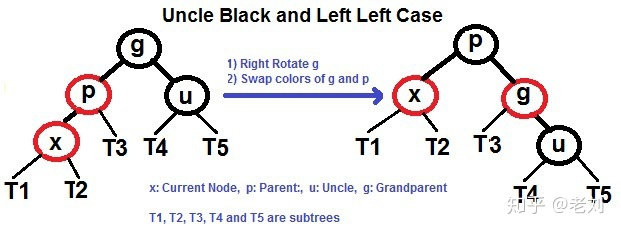
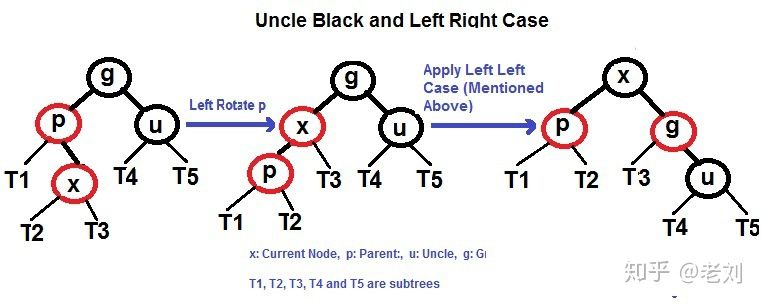
和AVL一样,rotate会有另外一种情况,此时需要rotate两下!
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zsben991126/p/13184945.html