现在广泛使用的霍夫变换是由 Richard Duda 和 Peter Hart 在公元1972年发明,并称之为广义霍夫变换,广义霍夫变换和更早前1962年的Paul Hough 的专利有关,这也是其名称的又来 。 经典的霍夫变换是侦测图片中的直线,之后,霍夫变换不仅能识别直线,也能够识别任何形状,常见的有圆形、椭圆形。霍夫变换在1962年申请为专利U.S. Patent 3,069,654,其专利名为"辨识复杂图案的方法及手段"(Method and Means for Recognizing Complex Patterns)。 任一条直线可以由斜率和截距来表示,在该专利中,利用斜率和截距来将一条直线参数化,然而这会导致无界的转换空间(unbounded transform space),因为斜率有可能是无限大。1981年,因为Dana H. Ballard 的一篇期刊论文 "Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes",让霍夫变换开始流行于电脑视觉界。
 |  |  |
OpenCV实现了以下两种霍夫线变换:
- 原理在上面的部分已经说明了. 它能给我们提供一组参数对
的集合来表示检测到的直线
- 在OpenCV 中通过函数 HoughLines 来实现
- 这是执行起来效率更高的霍夫线变换. 它输出检测到的直线的端点
- 在OpenCV 中它通过函数 HoughLinesP 来实现
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;using namespace std;
void help(){
cout << "\nThis program demonstrates line finding with the Hough transform.\n"
"Usage:\n"
"./houghlines <image_name>, Default is pic1.jpg\n" << endl;}
int main(int argc, char** argv){
const char* filename = argc >= 2 ? argv[1] : "pic1.jpg";
Mat src = imread(filename, 0);
if(src.empty())
{
help();
cout << "can not open " << filename << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat dst, cdst;
Canny(src, dst, 50, 200, 3);
cvtColor(dst, cdst, CV_GRAY2BGR);
#if 0
vector<Vec2f> lines;
HoughLines(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 100, 0, 0 );
for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
{
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
Point pt1, pt2;
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000*(-b));
pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000*(a));
pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000*(-b));
pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000*(a));
line( cdst, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, CV_AA);
}
#else
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 50, 50, 10 );
for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
{
Vec4i l = lines[i];
line( cdst, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0,0,255), 3, CV_AA);
}
#endifimshow("source", src);
imshow("detected lines", cdst);
waitKey();
return 0;}加载图片
Mat src = imread(filename, 0);if(src.empty()){
help();
cout << "can not open " << filename << endl;
return -1;}用Canny算子对图像进行边缘检测
Canny(src, dst, 50, 200, 3);现在我们将要执行霍夫线变换. 我们将会说明怎样使用OpenCV的函数做到这一点:
标准霍夫线变换
首先, 你要执行变换:
vector<Vec2f> lines;
HoughLines(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 100, 0, 0 );带有以下自变量:
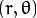 的容器 * rho : 参数极径
的容器 * rho : 参数极径 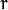 以像素值为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1 像素.
以像素值为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1 像素. 以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)
以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)通过画出检测到的直线来显示结果.
for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ ){
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
Point pt1, pt2;
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a*rho, y0 = b*rho;
pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000*(-b));
pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000*(a));
pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000*(-b));
pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000*(a));
line( cdst, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, CV_AA);}统计概率霍夫线变换
首先, 你要执行变换:
vector<Vec4i> lines;
HoughLinesP(dst, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 50, 50, 10 );带有以下自变量:
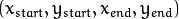 的容器
的容器 以像素值为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1 像素.
以像素值为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1 像素. 以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)
以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)通过画出检测到的直线来显示结果.
for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ ){
Vec4i l = lines[i];
line( cdst, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0,0,255), 3, CV_AA);}显示原始图像和检测到的直线:
imshow("source", src);imshow("detected lines", cdst);等待用户按键推出程序
waitKey();得到的结果使用的是在上面 代码 部分提到的更高级版代码. 霍夫线变换的代码没有改变, 唯一不同的是在GUI的部分加入了活动条可动态改变阈值.输入图像为:

通过执行统计概率霍夫线变换我们能得到下面的结果:
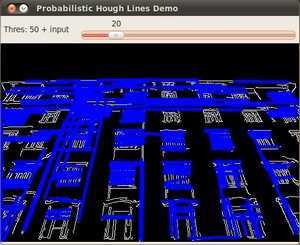
当你使用滑动条来改变 阈值 的时候会观察到检测到线的数目的改变. 这是因为: 如果你设置了一个更大的阈值, 能检测到的线的数目将更少 (你需要更多的点来表示一条能检测到的直线).
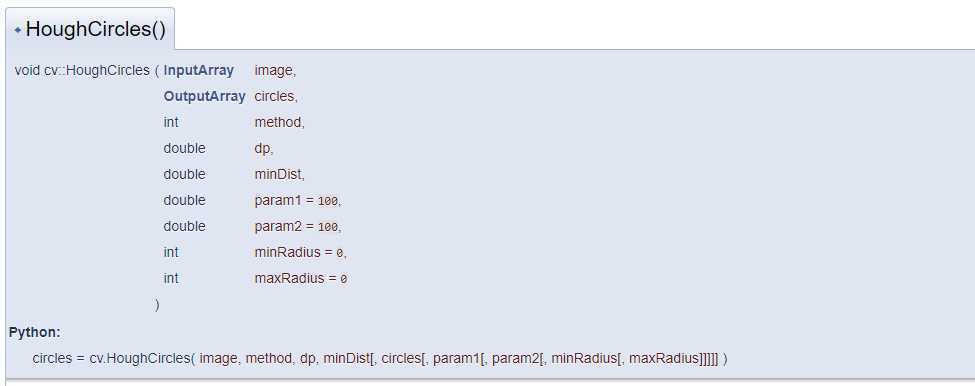
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
Finds circles in a grayscale image using the Hough transform.
The function finds circles in a grayscale image using a modification of the Hough transform.
Example:
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <math.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat img, gray;
if( argc != 2 || !(img=imread(argv[1], 1)).data)
return -1;
cvtColor(img, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// smooth it, otherwise a lot of false circles may be detected
GaussianBlur( gray, gray, Size(9, 9), 2, 2 );
vector<Vec3f> circles;
HoughCircles(gray, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT,2, gray.rows/4, 200, 100 );
for( size_t i = 0; i < circles.size(); i++ )
{
Point center(cvRound(circles[i][0]), cvRound(circles[i][1]));
int radius = cvRound(circles[i][2]);
// draw the circle center
circle( img, center, 3, Scalar(0,255,0), -1, 8, 0 );
// draw the circle outline
circle( img, center, radius, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, 8, 0 );
}
namedWindow( "circles", 1 );
imshow( "circles", img );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
Note
It also helps to smooth image a bit unless it‘s already soft. For example, GaussianBlur() with 7x7 kernel and 1.5x1.5 sigma or similar blurring may help.
| image | 8-bit, single-channel, grayscale input image. |
| circles | Output vector of found circles. Each vector is encoded as 3 or 4 element floating-point vector |
| method | Detection method, see HoughModes. The available methods are HOUGH_GRADIENT and HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT. |
| dp | Inverse ratio of the accumulator resolution to the image resolution. For example, if dp=1 , the accumulator has the same resolution as the input image. If dp=2 , the accumulator has half as big width and height. For HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT the recommended value is dp=1.5, unless some small very circles need to be detected. |
| minDist | Minimum distance between the centers of the detected circles. If the parameter is too small, multiple neighbor circles may be falsely detected in addition to a true one. If it is too large, some circles may be missed. |
| param1 | First method-specific parameter. In case of HOUGH_GRADIENT and HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT, it is the higher threshold of the two passed to the Canny edge detector (the lower one is twice smaller). Note that HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT uses Scharr algorithm to compute image derivatives, so the threshold value shough normally be higher, such as 300 or normally exposed and contrasty images. |
| param2 | Second method-specific parameter. In case of HOUGH_GRADIENT, it is the accumulator threshold for the circle centers at the detection stage. The smaller it is, the more false circles may be detected. Circles, corresponding to the larger accumulator values, will be returned first. In the case of HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT algorithm, this is the circle "perfectness" measure. The closer it to 1, the better shaped circles algorithm selects. In most cases 0.9 should be fine. If you want get better detection of small circles, you may decrease it to 0.85, 0.8 or even less. But then also try to limit the search range [minRadius, maxRadius] to avoid many false circles. |
| minRadius | Minimum circle radius. |
| maxRadius | Maximum circle radius. If <= 0, uses the maximum image dimension. If < 0, HOUGH_GRADIENT returns centers without finding the radius. HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT always computes circle radiuses. |
HOUGH圆检测,得益于一个新算法HOUGH_GRADIENT_ALT支持,比以前有很大程度的精度提升,测试对比如下:
对于这个算法,我的评测是使用它来处理“不知道半径”的情况,效果要比原算法好;但是目前我们只采用原算法。
在自动化分析数位图片的问题里,其中一个常有的子问题是侦测某些简单的直线、圆形、椭圆形。在多数情况下,边缘侦测器(edge detector)会先用来做图片前处理,将原本的图片变成只含有边缘的图片。 因为图片的不完美或是边缘侦测的不完美,导致有些点(point)或像素(pixel)缺漏,或是有噪声使得边缘侦测器所得的边界偏离了实际的边界。所以无法直观的将检测出的边缘分成直线、圆形、椭圆形的集合, 而霍夫变换解决上述问题,借由霍夫变换算法中的投票步骤,在复杂的参数空间中找到图形的参数,电脑可以由参数得知该边缘(edge)是哪种形状。
2.1 最简单的霍夫变换是在图像中识别直线。
2.1.1 在平面直角坐标系(x-y)中,一条直线可以用方程式
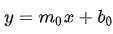
表示,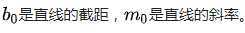 而
而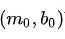 可以视为参数空间
可以视为参数空间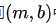 中的一点。当直线垂直于轴时,斜率为无限大, 若用电脑数值计算时会很不方便。
中的一点。当直线垂直于轴时,斜率为无限大, 若用电脑数值计算时会很不方便。
2.1.2 Duda 和 Hart 提出使用Hesse normal form来表示直线的参数,但是这个本身的原理比较繁琐,我们可以通过图像和极坐标的方法来进行简化。
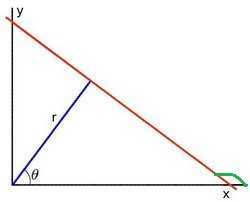
另一方面,这条直线的斜率(红色)是tan(PI-Θ) = tan(PI/2 + Θ),根据诱导公式: tan(π/2+α)=-cotα ,也就是斜率为:-cot(Θ)
根据2.1.1中得到的定义,这条直线可以表示为:
那么给定一个点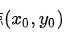 ,通过该点的所有直线的参数
,通过该点的所有直线的参数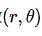 的集合,会在
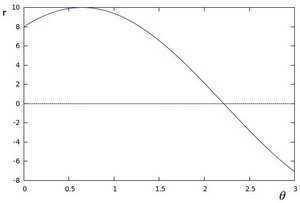
的集合,会在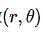 平面上形成一个三角函数,可由下方程式证明
平面上形成一个三角函数,可由下方程式证明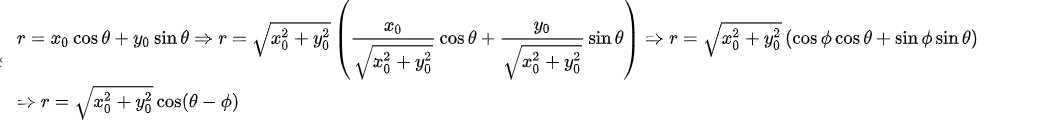
因此,给定很多点,判断这些点是否共线(concurrent lines)的问题,经由霍夫变换之后,变成判断一堆曲线(每一个点在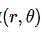 平面上代表一条曲线)是否 在
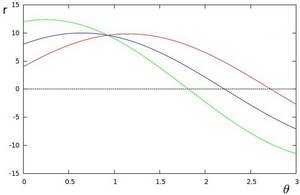
平面上代表一条曲线)是否 在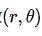 平面上相交于同一点的问题(concurrent curves)。继续上面那张抽象的图,如果两个不同点进行上述操作后得到的曲线在平面相交, 这就意味着它们通过同一条直线. 例如,接上面的例子我们继续绘图, 得到下图:
平面上相交于同一点的问题(concurrent curves)。继续上面那张抽象的图,如果两个不同点进行上述操作后得到的曲线在平面相交, 这就意味着它们通过同一条直线. 例如,接上面的例子我们继续绘图, 得到下图:
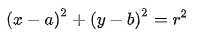
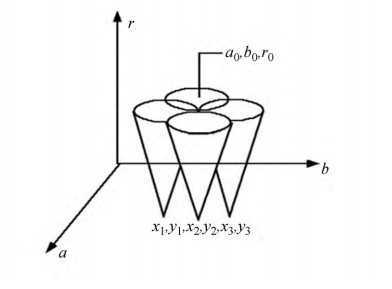
For each pixel(x,y)
For each radius r = 10 to r = 60 // the possible radius
For each theta t = 0 to 360 // the possible theta 0 to 360
a = x – r * cos(t * PI / 180); //polar coordinate for center
b = y – r * sin(t * PI / 180); //polar coordinate for center
A[a,b,r] +=1; //voting
end
end
end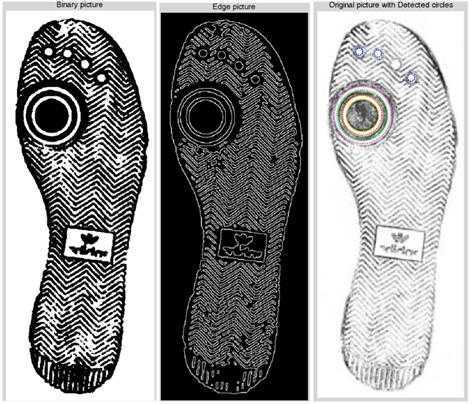
带有以下自变量:
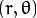 的容器 *
的容器 *  以像素值为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1 像素.
以像素值为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1 像素. 以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)
以弧度为单位的分辨率. 我们使用 1度 (即CV_PI/180)static void HoughLinesStandard( InputArray src, OutputArray lines, int type,float rho, float theta,int threshold, int linesMax,double min_theta, double max_theta )
{
CV_CheckType(type, type == CV_32FC2 || type == CV_32FC3, "Internal error");
Mat img = src.getMat();
int i, j;
float irho = 1 / rho;
CV_Assert( img.type() == CV_8UC1 );
CV_Assert( linesMax > 0 );
const uchar* image = img.ptr();
int step = (int)img.step;
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
int max_rho = width + height;
int min_rho = -max_rho;
CV_CheckGE(max_theta, min_theta, "max_theta must be greater than min_theta");
int numangle = cvRound((max_theta - min_theta) / theta);
int numrho = cvRound(((max_rho - min_rho) + 1) / rho);
Mat _accum = Mat::zeros( (numangle+2), (numrho+2), CV_32SC1 );
std::vector<int> _sort_buf;
AutoBuffer<float> _tabSin(numangle);
AutoBuffer<float> _tabCos(numangle);
int *accum = _accum.ptr<int>();
float *tabSin = _tabSin.data(), *tabCos = _tabCos.data();
// create sin and cos table
createTrigTable( numangle, min_theta, theta, irho, tabSin, tabCos);
// stage 1. fill accumulator
for( i = 0; i < height; i++ )
for( j = 0; j < width; j++ )
{
if( image[i * step + j] != 0 )
for(int n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
int r = cvRound( j * tabCos[n] + i * tabSin[n] );
r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
accum[(n+1) * (numrho+2) + r+1]++;
}
}
// stage 2. find local maximums
findLocalMaximums( numrho, numangle, threshold, accum, _sort_buf );
// stage 3. sort the detected lines by accumulator value
std::sort(_sort_buf.begin(), _sort_buf.end(), hough_cmp_gt(accum));
// stage 4. store the first min(total,linesMax) lines to the output buffer
linesMax = std::min(linesMax, (int)_sort_buf.size());
double scale = 1./(numrho+2);
lines.create(linesMax, 1, type);
Mat _lines = lines.getMat();
for( i = 0; i < linesMax; i++ )
{
LinePolar line;
int idx = _sort_buf[i];
int n = cvFloor(idx*scale) - 1;
int r = idx - (n+1)*(numrho+2) - 1;
line.rho = (r - (numrho - 1)*0.5f) * rho;
line.angle = static_cast<float>(min_theta) + n * theta;
if (type == CV_32FC2)
{
_lines.at<Vec2f>(i) = Vec2f(line.rho, line.angle);
}
else
{
CV_DbgAssert(type == CV_32FC3);
_lines.at<Vec3f>(i) = Vec3f(line.rho, line.angle, (float)accum[idx]);
}
}
}static void
HoughLinesSDiv( InputArray image, OutputArray lines, int type,
float rho, float theta, int threshold,
int srn, int stn, int linesMax,
double min_theta, double max_theta )
{
CV_CheckType(type, type == CV_32FC2 || type == CV_32FC3, "Internal error");
#define _POINT(row, column)\
(image_src[(row)*step+(column)])
Mat img = image.getMat();
int index, i;
int ri, ti, ti1, ti0;
int row, col;
float r, t; /* Current rho and theta */
float rv; /* Some temporary rho value */
int fn = 0;
float xc, yc;
const float d2r = (float)(CV_PI / 180);
int sfn = srn * stn;
int fi;
int count;
int cmax = 0;
std::vector<hough_index> lst;
CV_Assert( img.type() == CV_8UC1 );
CV_Assert( linesMax > 0 );
threshold = MIN( threshold, 255 );
const uchar* image_src = img.ptr();
int step = (int)img.step;
int w = img.cols;
int h = img.rows;
float irho = 1 / rho;
float itheta = 1 / theta;
float srho = rho / srn;
float stheta = theta / stn;
float isrho = 1 / srho;
float istheta = 1 / stheta;
int rn = cvFloor( std::sqrt( (double)w * w + (double)h * h ) * irho );
int tn = cvFloor( 2 * CV_PI * itheta );
lst.push_back(hough_index(threshold, -1.f, 0.f));
// Precalculate sin table
std::vector<float> _sinTable( 5 * tn * stn );
float* sinTable = &_sinTable[0];
for( index = 0; index < 5 * tn * stn; index++ )
sinTable[index] = (float)cos( stheta * index * 0.2f );
std::vector<uchar> _caccum(rn * tn, (uchar)0);
uchar* caccum = &_caccum[0];
// Counting all feature pixels
for( row = 0; row < h; row++ )
for( col = 0; col < w; col++ )
fn += _POINT( row, col ) != 0;
std::vector<int> _x(fn), _y(fn);
int* x = &_x[0], *y = &_y[0];
// Full Hough Transform (it‘s accumulator update part)
fi = 0;
for( row = 0; row < h; row++ )
{
for( col = 0; col < w; col++ )
{
if( _POINT( row, col ))
{
int halftn;
float r0;
float scale_factor;
int iprev = -1;
float phi, phi1;
float theta_it; // Value of theta for iterating
// Remember the feature point
x[fi] = col;
y[fi] = row;
fi++;
yc = (float) row + 0.5f;
xc = (float) col + 0.5f;
/* Update the accumulator */
t = (float) fabs( cvFastArctan( yc, xc ) * d2r );
r = (float) std::sqrt( (double)xc * xc + (double)yc * yc );
r0 = r * irho;
ti0 = cvFloor( (t + CV_PI*0.5) * itheta );
caccum[ti0]++;
theta_it = rho / r;
theta_it = theta_it < theta ? theta_it : theta;
scale_factor = theta_it * itheta;
halftn = cvFloor( CV_PI / theta_it );
for( ti1 = 1, phi = theta_it - (float)(CV_PI*0.5), phi1 = (theta_it + t) * itheta;
ti1 < halftn; ti1++, phi += theta_it, phi1 += scale_factor )
{
rv = r0 * std::cos( phi );
i = (int)rv * tn;
i += cvFloor( phi1 );
assert( i >= 0 );
assert( i < rn * tn );
caccum[i] = (uchar) (caccum[i] + ((i ^ iprev) != 0));
iprev = i;
if( cmax < caccum[i] )
cmax = caccum[i];
}
}
}
}
// Starting additional analysis
count = 0;
for( ri = 0; ri < rn; ri++ )
{
for( ti = 0; ti < tn; ti++ )
{
if( caccum[ri * tn + ti] > threshold )
count++;
}
}
if( count * 100 > rn * tn )
{
HoughLinesStandard( image, lines, type, rho, theta, threshold, linesMax, min_theta, max_theta );
return;
}
std::vector<uchar> _buffer(srn * stn + 2);
uchar* buffer = &_buffer[0];
uchar* mcaccum = buffer + 1;
count = 0;
for( ri = 0; ri < rn; ri++ )
{
for( ti = 0; ti < tn; ti++ )
{
if( caccum[ri * tn + ti] > threshold )
{
count++;
memset( mcaccum, 0, sfn * sizeof( uchar ));
for( index = 0; index < fn; index++ )
{
int ti2;
float r0;
yc = (float) y[index] + 0.5f;
xc = (float) x[index] + 0.5f;
// Update the accumulator
t = (float) fabs( cvFastArctan( yc, xc ) * d2r );
r = (float) std::sqrt( (double)xc * xc + (double)yc * yc ) * isrho;
ti0 = cvFloor( (t + CV_PI * 0.5) * istheta );
ti2 = (ti * stn - ti0) * 5;
r0 = (float) ri *srn;
for( ti1 = 0; ti1 < stn; ti1++, ti2 += 5 )
{
rv = r * sinTable[(int) (std::abs( ti2 ))] - r0;
i = cvFloor( rv ) * stn + ti1;
i = CV_IMAX( i, -1 );
i = CV_IMIN( i, sfn );
mcaccum[i]++;
assert( i >= -1 );
assert( i <= sfn );
}
}
// Find peaks in maccum...
for( index = 0; index < sfn; index++ )
{
int pos = (int)(lst.size() - 1);
if( pos < 0 || lst[pos].value < mcaccum[index] )
{
hough_index vi(mcaccum[index],
index / stn * srho + ri * rho,
index % stn * stheta + ti * theta - (float)(CV_PI*0.5));
lst.push_back(vi);
for( ; pos >= 0; pos-- )
{
if( lst[pos].value > vi.value )
break;
lst[pos+1] = lst[pos];
}
lst[pos+1] = vi;
if( (int)lst.size() > linesMax )
lst.pop_back();
}
}
}
}
}
lines.create((int)lst.size(), 1, type);
Mat _lines = lines.getMat();
for( size_t idx = 0; idx < lst.size(); idx++ )
{
if( lst[idx].rho < 0 )
continue;
if (type == CV_32FC2)
{
_lines.at<Vec2f>((int)idx) = Vec2f(lst[idx].rho, lst[idx].theta);
}
else
{
CV_DbgAssert(type == CV_32FC3);
_lines.at<Vec3f>((int)idx) = Vec3f(lst[idx].rho, lst[idx].theta, (float)lst[idx].value);
}
}
}static void
HoughLinesProbabilistic( Mat& image,
float rho, float theta, int threshold,
int lineLength, int lineGap,
std::vector<Vec4i>& lines, int linesMax )
{
Point pt;
float irho = 1 / rho;
RNG rng((uint64)-1);
CV_Assert( image.type() == CV_8UC1 );
int width = image.cols;
int height = image.rows;
int numangle = cvRound(CV_PI / theta);
int numrho = cvRound(((width + height) * 2 + 1) / rho);
#if defined HAVE_IPP && IPP_VERSION_X100 >= 810 && !IPP_DISABLE_HOUGH
CV_IPP_CHECK()
{
IppiSize srcSize = { width, height };
IppPointPolar delta = { rho, theta };
IppiHoughProbSpec* pSpec;
int bufferSize, specSize;
int ipp_linesMax = std::min(linesMax, numangle*numrho);
int linesCount = 0;
lines.resize(ipp_linesMax);
IppStatus ok = ippiHoughProbLineGetSize_8u_C1R(srcSize, delta, &specSize, &bufferSize);
Ipp8u* buffer = ippsMalloc_8u_L(bufferSize);
pSpec = (IppiHoughProbSpec*) ippsMalloc_8u_L(specSize);
if (ok >= 0) ok = ippiHoughProbLineInit_8u32f_C1R(srcSize, delta, ippAlgHintNone, pSpec);
if (ok >= 0) {ok = CV_INSTRUMENT_FUN_IPP(ippiHoughProbLine_8u32f_C1R, image.data, (int)image.step, srcSize, threshold, lineLength, lineGap, (IppiPoint*) &lines[0], ipp_linesMax, &linesCount, buffer, pSpec);};
ippsFree(pSpec);
ippsFree(buffer);
if (ok >= 0)
{
lines.resize(linesCount);
CV_IMPL_ADD(CV_IMPL_IPP);
return;
}
lines.clear();
setIppErrorStatus();
}
#endif
Mat accum = Mat::zeros( numangle, numrho, CV_32SC1 );
Mat mask( height, width, CV_8UC1 );
std::vector<float> trigtab(numangle*2);
for( int n = 0; n < numangle; n++ )
{
trigtab[n*2] = (float)(cos((double)n*theta) * irho);
trigtab[n*2+1] = (float)(sin((double)n*theta) * irho);
}
const float* ttab = &trigtab[0];
uchar* mdata0 = mask.ptr();
std::vector<Point> nzloc;
// stage 1. collect non-zero image points
for( pt.y = 0; pt.y < height; pt.y++ )
{
const uchar* data = image.ptr(pt.y);
uchar* mdata = mask.ptr(pt.y);
for( pt.x = 0; pt.x < width; pt.x++ )
{
if( data[pt.x] )
{
mdata[pt.x] = (uchar)1;
nzloc.push_back(pt);
}
else
mdata[pt.x] = 0;
}
}
int count = (int)nzloc.size();
// stage 2. process all the points in random order
for( ; count > 0; count-- )
{
// choose random point out of the remaining ones
int idx = rng.uniform(0, count);
int max_val = threshold-1, max_n = 0;
Point point = nzloc[idx];
Point line_end[2];
float a, b;
int* adata = accum.ptr<int>();
int i = point.y, j = point.x, k, x0, y0, dx0, dy0, xflag;
int good_line;
const int shift = 16;
// "remove" it by overriding it with the last element
nzloc[idx] = nzloc[count-1];
// check if it has been excluded already (i.e. belongs to some other line)
if( !mdata0[i*width + j] )
continue;
// update accumulator, find the most probable line
for( int n = 0; n < numangle; n++, adata += numrho )
{
int r = cvRound( j * ttab[n*2] + i * ttab[n*2+1] );
r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
int val = ++adata[r];
if( max_val < val )
{
max_val = val;
max_n = n;
}
}
// if it is too "weak" candidate, continue with another point
if( max_val < threshold )
continue;
// from the current point walk in each direction
// along the found line and extract the line segment
a = -ttab[max_n*2+1];
b = ttab[max_n*2];
x0 = j;
y0 = i;
if( fabs(a) > fabs(b) )
{
xflag = 1;
dx0 = a > 0 ? 1 : -1;
dy0 = cvRound( b*(1 << shift)/fabs(a) );
y0 = (y0 << shift) + (1 << (shift-1));
}
else
{
xflag = 0;
dy0 = b > 0 ? 1 : -1;
dx0 = cvRound( a*(1 << shift)/fabs(b) );
x0 = (x0 << shift) + (1 << (shift-1));
}
for( k = 0; k < 2; k++ )
{
int gap = 0, x = x0, y = y0, dx = dx0, dy = dy0;
if( k > 0 )
dx = -dx, dy = -dy;
// walk along the line using fixed-point arithmetic,
// stop at the image border or in case of too big gap
for( ;; x += dx, y += dy )
{
uchar* mdata;
int i1, j1;
if( xflag )
{
j1 = x;
i1 = y >> shift;
}
else
{
j1 = x >> shift;
i1 = y;
}
if( j1 < 0 || j1 >= width || i1 < 0 || i1 >= height )
break;
mdata = mdata0 + i1*width + j1;
// for each non-zero point:
// update line end,
// clear the mask element
// reset the gap
if( *mdata )
{
gap = 0;
line_end[k].y = i1;
line_end[k].x = j1;
}
else if( ++gap > lineGap )
break;
}
}
good_line = std::abs(line_end[1].x - line_end[0].x) >= lineLength ||
std::abs(line_end[1].y - line_end[0].y) >= lineLength;
for( k = 0; k < 2; k++ )
{
int x = x0, y = y0, dx = dx0, dy = dy0;
if( k > 0 )
dx = -dx, dy = -dy;
// walk along the line using fixed-point arithmetic,
// stop at the image border or in case of too big gap
for( ;; x += dx, y += dy )
{
uchar* mdata;
int i1, j1;
if( xflag )
{
j1 = x;
i1 = y >> shift;
}
else
{
j1 = x >> shift;
i1 = y;
}
mdata = mdata0 + i1*width + j1;
// for each non-zero point:
// update line end,
// clear the mask element
// reset the gap
if( *mdata )
{
if( good_line )
{
adata = accum.ptr<int>();
for( int n = 0; n < numangle; n++, adata += numrho )
{
int r = cvRound( j1 * ttab[n*2] + i1 * ttab[n*2+1] );
r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
adata[r]--;
}
}
*mdata = 0;
}
if( i1 == line_end[k].y && j1 == line_end[k].x )
break;
}
}
if( good_line )
{
Vec4i lr(line_end[0].x, line_end[0].y, line_end[1].x, line_end[1].y);
lines.push_back(lr);
if( (int)lines.size() >= linesMax )
return;
}
}
}
static void HoughCircles( InputArray _image, OutputArray _circles,
int method, double dp, double minDist,
double param1, double param2,
int minRadius, int maxRadius,
int maxCircles, double param3 )
{
CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION();
int type = CV_32FC3;
if( _circles.fixedType() )
{
type = _circles.type();
CV_CheckType(type, type == CV_32FC3 || type == CV_32FC4, "Wrong type of output circles");
}
CV_Assert(!_image.empty() && _image.type() == CV_8UC1 && (_image.isMat() || _image.isUMat()));
CV_Assert(_circles.isMat() || _circles.isVector());
if( dp <= 0 || minDist <= 0 || param1 <= 0 || param2 <= 0)
CV_Error( Error::StsOutOfRange, "dp, min_dist, canny_threshold and acc_threshold must be all positive numbers" );
int cannyThresh = cvRound(param1), accThresh = cvRound(param2), kernelSize = cvRound(param3);
minRadius = std::max(0, minRadius);
if(maxCircles < 0)
maxCircles = INT_MAX;
bool centersOnly = (maxRadius < 0);
if( maxRadius <= 0 )
maxRadius = std::max( _image.rows(), _image.cols() );
else if( maxRadius <= minRadius )
maxRadius = minRadius + 2;
switch( method )
{
case CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT:
if (type == CV_32FC3)
HoughCirclesGradient<Vec3f>(_image, _circles, (float)dp, (float)minDist,
minRadius, maxRadius, cannyThresh,
accThresh, maxCircles, kernelSize, centersOnly);
else if (type == CV_32FC4)
HoughCirclesGradient<Vec4f>(_image, _circles, (float)dp, (float)minDist,
minRadius, maxRadius, cannyThresh,
accThresh, maxCircles, kernelSize, centersOnly);
else
CV_Error(Error::StsError, "Internal error");
break;
default:
CV_Error( Error::StsBadArg, "Unrecognized method id. Actually only CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT is supported." );
}
}
void HoughCircles( InputArray _image, OutputArray _circles,
int method, double dp, double minDist,
double param1, double param2,
int minRadius, int maxRadius )
{
HoughCircles(_image, _circles, method, dp, minDist, param1, param2, minRadius, maxRadius, -1, 3);
}static void HoughCirclesGradient(InputArray _image, OutputArray _circles,
float dp, float minDist,
int minRadius, int maxRadius, int cannyThreshold,
int accThreshold, int maxCircles, int kernelSize, bool centersOnly)
{
CV_Assert(kernelSize == -1 || kernelSize == 3 || kernelSize == 5 || kernelSize == 7);
dp = max(dp, 1.f);
float idp = 1.f/dp;
Mat edges, dx, dy;
Sobel(_image, dx, CV_16S, 1, 0, kernelSize, 1, 0, BORDER_REPLICATE);
Sobel(_image, dy, CV_16S, 0, 1, kernelSize, 1, 0, BORDER_REPLICATE);
Canny(dx, dy, edges, std::max(1, cannyThreshold / 2), cannyThreshold, false);
Mutex mtx;
int numThreads = std::max(1, getNumThreads());
std::vector<Mat> accumVec;
NZPointSet nz(_image.rows(), _image.cols());
parallel_for_(Range(0, edges.rows),
HoughCirclesAccumInvoker(edges, dx, dy, minRadius, maxRadius, idp, accumVec, nz, mtx),
numThreads);
int nzSz = cv::countNonZero(nz.positions);
if(nzSz <= 0)
return;
Mat accum = accumVec[0];
for(size_t i = 1; i < accumVec.size(); i++)
{
accum += accumVec[i];
}
accumVec.clear();
std::vector<int> centers;
// 4 rows when multithreaded because there is a bit overhead
// and on the other side there are some row ranges where centers are concentrated
parallel_for_(Range(1, accum.rows - 1),
HoughCirclesFindCentersInvoker(accum, centers, accThreshold, mtx),
(numThreads > 1) ? ((accum.rows - 2) / 4) : 1);
int centerCnt = (int)centers.size();
if(centerCnt == 0)
return;
std::sort(centers.begin(), centers.end(), hough_cmp_gt(accum.ptr<int>()));
std::vector<CircleType> circles;
circles.reserve(256);
if (centersOnly)
{
// Just get the circle centers
GetCircleCenters(centers, circles, accum.cols, minDist, dp);
}
else
{
std::vector<EstimatedCircle> circlesEst;
if (nzSz < maxRadius * maxRadius)
{
// Faster to use a list
NZPointList nzList(nzSz);
nz.toList(nzList);
// One loop iteration per thread if multithreaded.
parallel_for_(Range(0, centerCnt),
HoughCircleEstimateRadiusInvoker<NZPointList>(nzList, nzSz, centers, circlesEst, accum.cols,
accThreshold, minRadius, maxRadius, dp, mtx),
numThreads);
}
else
{
// Faster to use a matrix
// One loop iteration per thread if multithreaded.
parallel_for_(Range(0, centerCnt),
HoughCircleEstimateRadiusInvoker<NZPointSet>(nz, nzSz, centers, circlesEst, accum.cols,
accThreshold, minRadius, maxRadius, dp, mtx),
numThreads);
}
// Sort by accumulator value
std::sort(circlesEst.begin(), circlesEst.end(), cmpAccum);
// Create Circles
CreateCircles(circlesEst, circles);
RemoveOverlaps(circles, minDist);
}
if (circles.size() > 0)
{
int numCircles = std::min(maxCircles, int(circles.size()));
Mat(1, numCircles, cv::traits::Type<CircleType>::value, &circles[0]).copyTo(_circles);
return;
}
}HoughCircle内容整编(HoughTransform和CircleHoughTransform)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/jsxyhelu/p/13191015.html