ConfigurationApplicationContext扩展于ApplicationContext,新增了两个主要的方法,refresh()和close(),让ApplicationxContext具有启动,刷新和关闭应用上下文的能力。
在获取ApplicationContext实例后,就可以像BeanFactory一样调用getBean(beanName)返回Bean了。
ApplicationContext的初始化和BeanFactory有一个重大区别:
Spring支持基于类注解的配置方式,主要功能来源于Spring名为javaCOnfig的子项目。JavaConfig已升级为Spring核心框架的一部分,一个标注@Configuration注解的POJO即可提供Spring所需的Bea配置信息。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.smart.Car;
@Configuration
public class Beans {
@Bean(name = "car")
public Car buildCar() {
Car car = new Car();
car.setBrand("红旗CA72");
car.setMaxSpeed(200);
return car;
}
}
和基于XMl文件的配置方式相比,类注解的配置方式可以很容易地让开发者控制Bean的初始化过程,比基于XML文件的配置方式更灵活。
WebApplicationContext是专门为Web应用准备的,它允许从Web根目录的路径中装载配置文件并完成初始化工作。从WebApplicationContext中可以获得ServletContext的引用。整个Web应用上下文对象将作为属性放置到ServletContext中,以便Web应用环境可以访问Spring应用上下文。
Spring为此专门提供了一个工具类WebApplicationContextUtils,通过该类的getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) ,可以从ServletContext中获取WebApplicationContext的实例。
/**
* Scope identifier for request scope: "request".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_REQUEST = "request";
/**
* Scope identifier for session scope: "session".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_SESSION = "session";
/**
* Scope identifier for the global web application scope: "application".
* Supported in addition to the standard scopes "singleton" and "prototype".
*/
String SCOPE_APPLICATION = "application";
Web应用比一般的应用拥有更多特性,因此WebApplicationContext扩展了ApplicationContext。WebApplicationContext定义了一个常量ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,在上下文启动时,WebApplicationContext实例即以此为键放置在
ServletContext属性列表中,可以通过以下语句从Web容器中获取WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext wac = (WebApplicationContext)servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext扩展了WebApplicationContext,允许通过配置的方式实例化WebApplicationContext,同时定义了两个重要的方法。
WebApplicationContext初始化方式和BeanFactory、ApplicationContext有所区别,因为WebApplicationContext需要ServletContext实例,它必须在拥有Web容器的前提下才能完成启动工作。可以在web.xml中配置自启动的Servlet或定义Web容器监听器(ServletContextListener),借助二者中的任何一个,就可以完成SpringWeb应用上下文的工作。
Spring分别提供了用于启动WebApplicationContext的Servlet和Web容器监听器
<!-- 配置spring核心监听器,默认会以 /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml作为配置文件 -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- contextConfigLocation参数用来指定Spring的配置文件 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
在不支持容器监听器的低版本web容器中,可采用ContextLoaderServlet完成相同的工作
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springContextLoaderServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderServlet</servlet-class>
<loader-on-startup>1</loader-on-startup>
</servlet>
由于WebApplicationContext 需要使用日志功能,可将log4j的配置文件放置在类路径 WEB-INF/classes下
通过HierarchicalBeanFactory接口,Spring的IOC容器可以建立父子层级关联的容器体系,子容器可以访问父容器中的bean,但父容器不能访问子容器中的bean。在容器内,bean的IDb必须是唯一的,但子容器可以拥有和父容器id相同的Bean。
父子容器层级体系增强了Spring容器架构的扩展性和灵活性,以为第三方可以通过编程的方式为一个已经存在的容器添加一个或多个特殊用途的子容器,以提供一些额外的功能。
Spring使用父子容器实现了很多功能,比如在SpringMVC中,展现层Bean位于一个子容器中,而业务层和持久层bean位于父容器中,这样展现层就可以引用业务层和持久层的Bean,而业务层和持久层Bean则看不到展现层bean。
Web容器中的Servlet拥有明确的生命周期,Spring容器中的Bean也拥有相似的生命周期。Bean的生命周期由多个特定的生命阶段组成,每个阶段都开出了一扇门(实现方法),允许外界借此对Bean进行控制。
Spring可以从两方面定义Bean的生命周期:第一个层面是Bean的作用范围;第二个层面是实例化Bean时所经历的一系列阶段。下面对BeanFactory和ApplicationContext中Bean的生命周期进行分析。
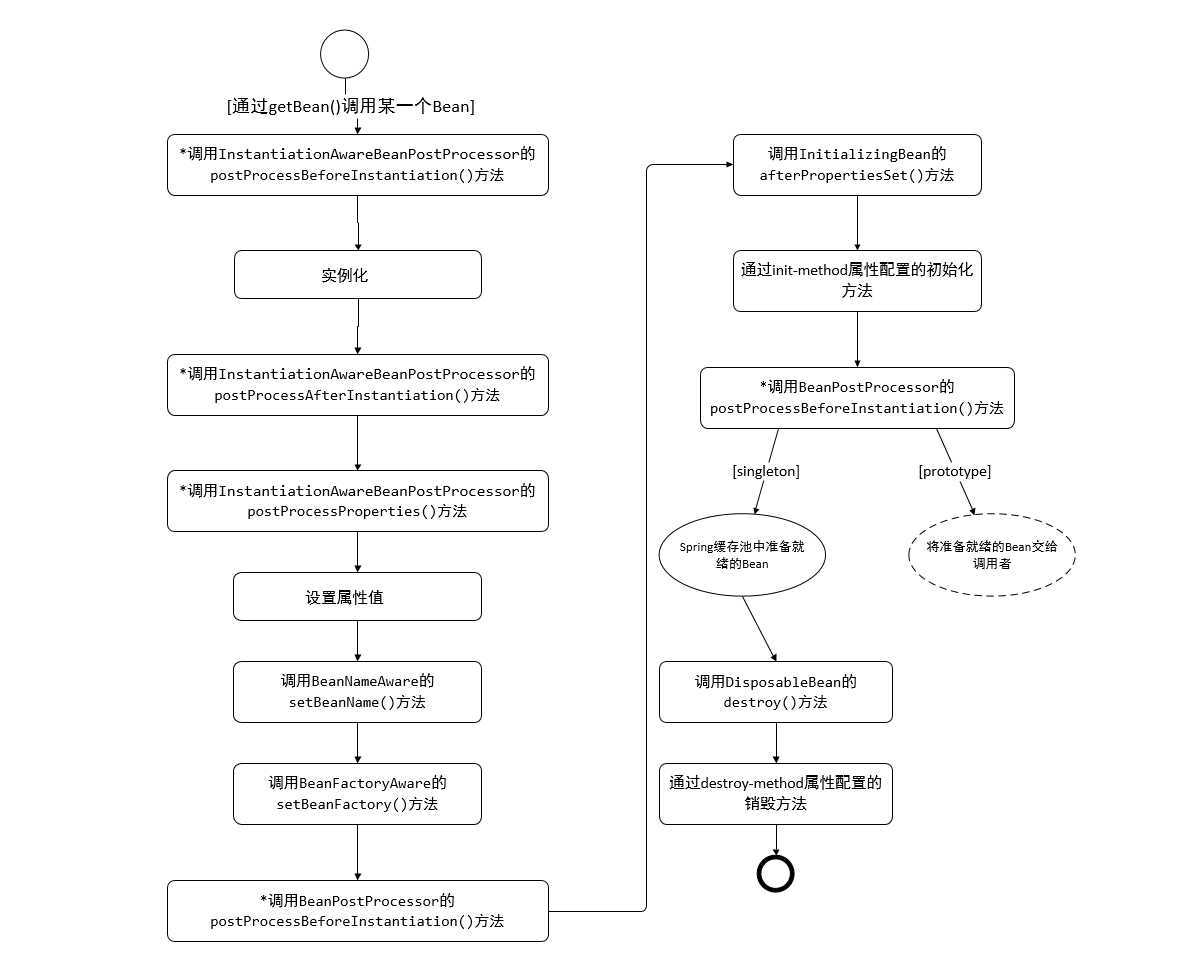
1、生命周期图
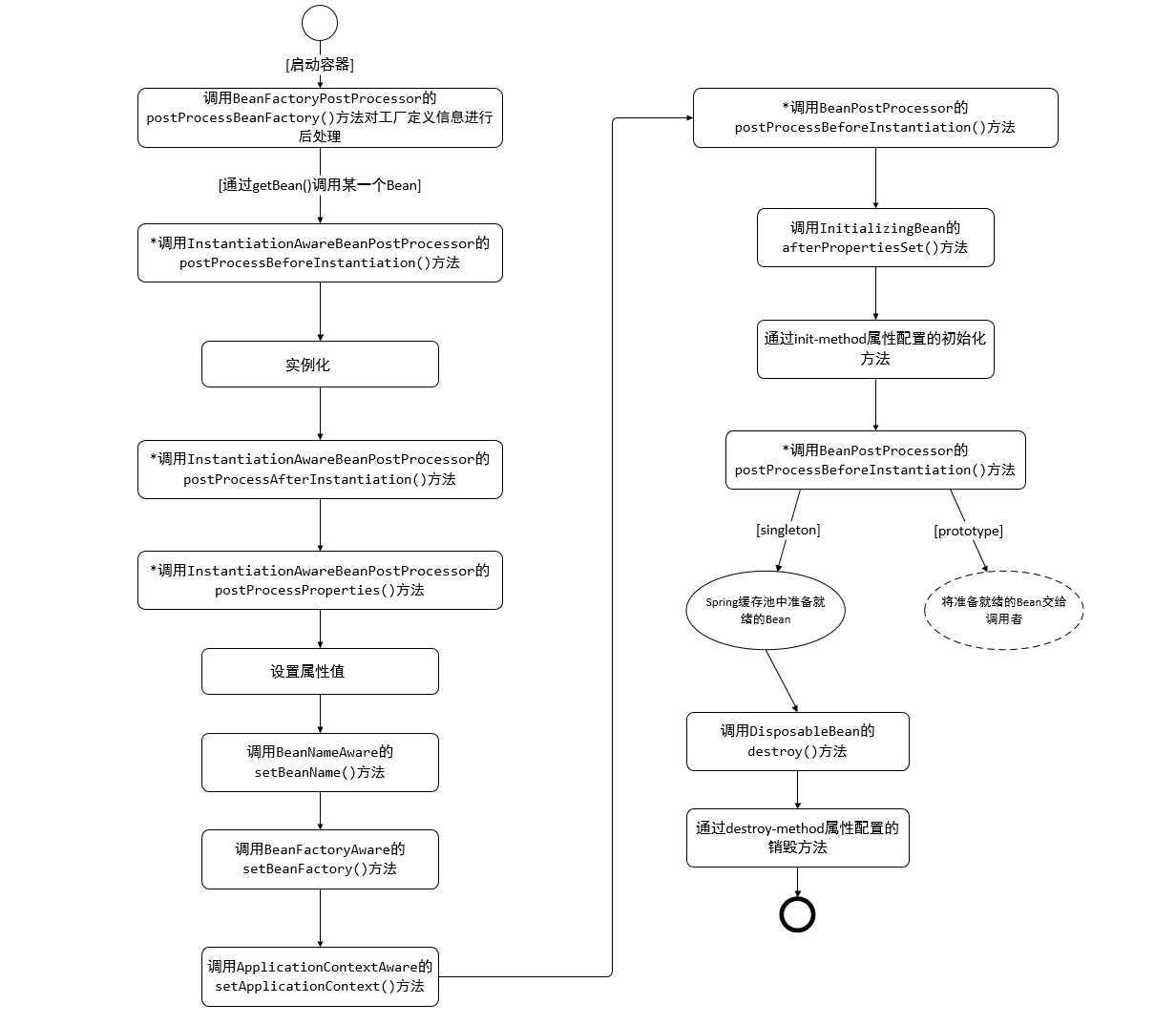
2、生命周期的流程
Bean在应用上下文中的生命周期和在BeanFactory中的生命周期类似,不同的是,如果Bean实现了org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware接口,则会增加一个调用该接口方法setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) 的步骤,如上图。
此外还增加了BeanFactoryPostProcessor对配置信息进行加工处理。Spring框架还提供了多个工厂后处理器,如CustomEditorConfigurer、PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer。
ApplicationContext和BeanFactory另一个最大的不同之处在于:前者会利用Java反射机制自动识别出配置文件中定义的BeanPostProcessor、InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并将它们自动注册到应用上下文中;而后者需要在代码中通过手工调用addBeanPostProcessor()方法进行注册。这也是为什么在应用开发中普遍使用ApplicationContext而很少使用BeanFactory的原因之一。
在ApplicationContext中,只需在配置文件中通过
3、使用工厂后处理器实例
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor{
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory bf) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition bd = bf.getBeanDefinition("car");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("brand", "奇瑞QQ");
System.out.println("调用MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory()!");
}
}
xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd">
<bean id="car" class="com.smart.Car"
p:brand="红旗CA72"
p:maxSpeed="200"/>
<!--注册Bean后处理器-->
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.smart.context.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
<!--工厂后处理器-->
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class="com.smart.context.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
BeanPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor会自动被ApplicationContext识别并注册到容器中。
BeanFactoty和ApplicationContext
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/nangonghui/p/13193660.html