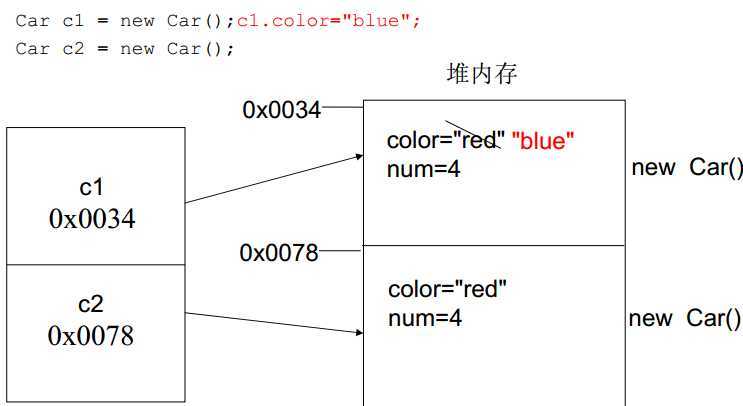
class Car{//对Car这类事物进行描述
String color = "red";
int num = 4;
void show(){
System.out.println("color="+color+",num="+num);
}
}
class CarDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Car c = new Car();//建立对象
C.color = "black";//对对象的属性进行修改
c.show();//使用对象的功能
}
}
Person p = new Person("zhangsan",20);
上面这条语句在执行过程中做了哪些事?
new用到了Person.class,所以会先找到Person.class文件并加载到内存中。static代码块,如果有的话,给Person.class类进行初始化。p变量。匿名对象是对象的简化形式
匿名对象的两种使用形式
class CarDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Car c = new Car();//建立对象
C.color = "black";//对对象的属性进行修改
c.show();//使用对象的功能
/*用匿名对象的方式操作如下*/
new Car().num = 5;
new Car().color = "blue";
new Car().show();
}
}
class CarDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Car c = new Car();//建立对象
show(c);//调用show()方法
/*将匿名对象作为实际参数进行传递,调用show()方法,如下操作*/
show(new Car());
}
public static void show(Car c){
c.num = 3;
c.color = "black";
c.run();
}
}
private关键字是一种修饰符,表示私有的。class Person{
private int age;
public void setAge(int a){
if(a>0 && a<130){
age = a;
speak();
}
else
System.out.println("年龄有误!");
}
public void getAge(){
return age;
}
void speak(){
Syetem.out.println("age="+age);
}
}
class PersonDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
p.setAge = 20;
p.speak();
}
}
class Person{
Person(){//构造方法
System.out.println("Person run!");
}
}
class PersonDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
}
}
public修饰,那么默认的构造方法也带有public修饰。public修饰,那么默认的构造方法,也没有public修饰。{
System.out.println("这是一个构造代码块!")
}
this代表其所在方法所属对象的引用。this所在的方法,this就代表哪个对象。this语句只能定义在构造方法的第一行。因为初始化要先执行。this来表示这个对象。this表示。static关键字作用static是一个修饰符,用于修饰成员(成员变量、成员方法)class Person{
String name;//成员变量,实例变量
static String country = "CN";//静态的成员表变量,类变量
}
this、super关键字。因为静态优先于对象存在,所以静态方法中不可以出现this。要从两方面下手。因为静态修饰的内容有成员方法和成员变量
什么时候定义静态变量(类变量)呢?
什么时候定义静态方法?
class Person{
String name;
public void show1(){
System.out.println(name+"heihei");
}
public static void show2(){
System.out.println("haha");
}
}
class PersonDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
p.show1();
Person.show2();
}
}
每一个应用程序中都有共性的功能,可以将这些功能进行抽取,独立封装,以便复用。
class ArrayTool{
private ArrayTool(){}
public static int getMax(int[] arr){//获取最大值
int max = 0;
for(int x=1; x<arr.length; x++){
if(arr[x] > arr[max])
max = x;
}
return arr[max];
}
public static int getMin(int[] arr){//获取最小值
int min = 0;
for(int x=1; x<arr.length; x++){
if(arr[x] < arr[min])
min = x;
}
return arr[min];
}
public static void selectSort(int[] arr){//选择排序
for(int x=0; x<arr.length-1; x++){
for(int y=x+1; y<arr.length; y++){
if(arr[x] > arr[y]){
swap(arr,x,y);
}
}
}
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr){//冒泡排序
for(int x=0; x<arr.length-1; x++){
for(int y=0; y<arr.length-x-1; y++){
if(arr[y] > arr[y+1]){
swap(arr,y,y+1);
}
}
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr, int a, int b){//交换数据
int temp = arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b] = temp;
}
public static void printArray(int[] arr){//打印数组
System.out.print("[");
for(int x=0; x<arr.length; x++){
if(x! = arr.length-1)
System.out.print(arr[x]+", ");
else
System.out.print(arr[x]+"]");
}
}
}
class ArrayToolDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = {2,6,34,83,9,6,};
/*ArrayTool tool = new ArrayTool();
int max = tool.getMax(arr);
System.out.println("max="+max);*/
int max = ArrayTool.getMax(arr);
System.out.println("max="+max);
}
}
从以上代码可以看出,虽然可以通过建立ArrayTool的对象使用工具方法,对数据进行操作。发现了问题:
ArrayTool并未封装特有数据。ArrayTool对象中的特有方法。这时就考虑,让程序更严谨,是不需要对象的。可以将ArrayTool中的方法都定义成static的。直接通过类名调用。
通常工具类中定义的都是静态方法。
将方法静态后,可以方面使用,但是该类还是可以被其他程序建立对象的,为了更为严谨,强制让该类不能建立对象。可以通过构造方法私有化完成。
能隐藏起来的都隐藏起来。
接下来,将ArrayTool.class文件发送给其他人,其他人只要将该文件设置到classpath路径下,就可以使用该工具类。但是,很遗憾,该类中到底定义了多少个方法,对方却不清楚。因为该类并没有使用说明书。
开始制作程序的说明书,java的说明书通过文档注释来完成。
/**
这是一个可以对数组进行操作的工具类,该类中提供了获取最值,排序等功能。
@author 小杨
@version v1.2
*/
public class ArrayTool{
/**
空参构造方法
*/
private ArrayTool(){}
/**
获取一个整形数组中的最大值
@param arr 接收一个int类型的数组。
@return 会返回一个该数组中最大值
*/
public static int getMax(int[] arr){//获取最大值
int max = 0;
for(int x=1; x<arr.length; x++){
if(arr[x] > arr[max])
max = x;
}
return arr[max];
}
/**
获取一个整形数组中的最小值
@param arr 接收一个int类型的数组。
@return 会返回一个该数组中最小值
*/
public static int getMin(int[] arr){//获取最小值
int min = 0;
for(int x=1; x<arr.length; x++){
if(arr[x] < arr[min])
min = x;
}
return arr[min];
}
/**
给int数组中的数据进行选择排序
@param arr 接收一个int类型的数据
*/
public static void selectSort(int[] arr){//选择排序
for(int x=0; x<arr.length-1; x++){
for(int y=x+1; y<arr.length; y++){
if(arr[x] > arr[y]){
swap(arr,x,y);
}
}
}
}
/**
给int数组中的数据进行冒泡排序
@param arr 接收一个int类型的数据
*/
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr){//冒泡排序
for(int x=0; x<arr.length-1; x++){
for(int y=0; y<arr.length-x-1; y++){
if(arr[y] > arr[y+1]){
swap(arr,y,y+1);
}
}
}
}
/**
给数组中元素进行位置的置换
@param arr 接收一个int类型的数值
@param a 要置换的位置
@param b 要置换的位置
*/
private static void swap(int[] arr, int a, int b){//交换数据
int temp = arr[a];
arr[a] = arr[b];
arr[b] = temp;
}
/**
用于打印数组中的元素,打印形式是:[element1,element2,...]
*/
public static void printArray(int[] arr){//打印数组
System.out.print("[");
for(int x=0; x<arr.length; x++){
if(x! = arr.length-1)
System.out.print(arr[x]+", ");
else
System.out.print(arr[x]+"]");
}
}
}
static{
静态代码块中的执行语句;
}
class StaticCode{
static {
System.out.println("a");
}
}
class StaticCodeDemo{
static{
System.out.println("b");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
new StaticCode();
new StaticCode();
System.out.println("over");
}
static{
System.out.println("c");
}
}
//...java StaticCodeDemo
//执行结果:b c a over
public static void main(String[] args){
}
public:代表着函数的访问权限是最大的。static:代表着主函数随着类的加载就已经存在了。void:主函数没有具体的返回值。main:不是关键字,但是是一个特殊的单词,可以被jvm识别(String[] args):函数的参数,参数类型是一个数组,该数组中的元素是字符串。(字符串类型的数组)jvm识别调用。jvm在调用主函数时,传入的是new String[0]。class Single{
private Single(){}
private static Single s = new Single();
public static Single getInstance(){
return s;
}
}
class SingleDemo{
public static void main(String[] args){
Single ss = getInstance();
}
}
对于事物该怎么描述,还怎么描述。当需要将该事物的对象保证在内存中唯一时,就将以上三步加上即可。
//一种实现方式,这种实现方式用的多,定义单例设计模式,建议使用该方式
//这个是先初始化对象,称为:饿汉式
//Single类一进内存,就已经创建好了对象。
class Single{
private Single(){}
private static Single s = new Single();
public static Single getInstance(){
return s;
}
}
//另一种实现方式
//对象是方法被调用时,才初始化,也叫做对象的延时加载,称为:懒汉式
//Single类进内存,对象还没有存在,只有调用了getInstance方法时,才建立对象。
class Single{
private static Single s = null;
private Single(){}
public static Single getInstance(){
if(s==null)
s = new Single;
return s;
}
}
//以上两种实现形式都可以!
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yxc-160206/p/13200152.html