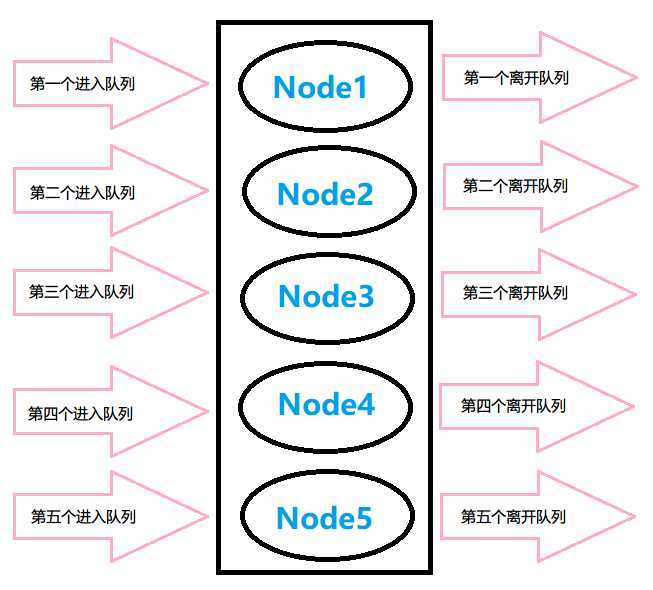
队列(Queue)也是一种线性结构,可以理解为排队,即先排队的要先离开,后排队的后离开,如果用数组来实现一个循环队列,那经过若干次的插入取出操作后队列的数据可能单单看数组的下标已经看不出先后顺序了,但是要通过一定的取模算法来让队列总是实现先进先出的特性。
- 队列只允许在表前端进行出队列操作,只允许在表末端进行入队列操作。
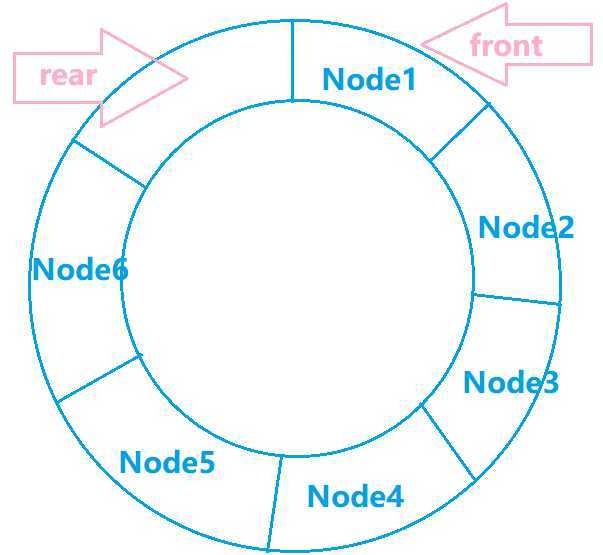
- 队头front
- 队尾rear
顺序队列在内存中申请了一片连续的空间,front指针指向队头元素,当队列为空时front指针在-1位置,此时rear = front = 0,否则rear指向末尾元素。
当rear为maxSize时,队列就满了,此时此顺序队列将再也无法进行进队列操作。
为了使队列中的空间能重复利用可以使用循环队列,当front或rear增1时就进行取模运算,使其永远不越界,并且越界后直接回到起始位置。
当队列为空时front = rear,而当队列满时也有front = rear,为了避免这种情况我们让队列尾部的空间永远为空,让rear指向这个空域。
package com.cnblog.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.management.RuntimeErrorException;
/**
* 顺序队列的数组实现
* 功能:进队列、出队列、查看队头数据、显示队列、full、empty
* @author 炫酷100
*/
public class ArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TestQueue
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(3);
char key = ‘ ‘; // 接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
// 输出一个菜单
while(loop){
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列中取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);// 接收第一个字符
switch (key) {
case ‘s‘:
queue.showQueue();
break;
case ‘e‘:
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
case ‘a‘:
System.out.println("输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case ‘g‘:
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据为%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case ‘h‘:
try {
int headData = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列数据头的数据是d%\n", headData);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
// 使用数组模拟一个队列-编写一个叫做ArrayQueue的类
class ArrayQueue {
private int maxSize; // 队列最大容量
private int front; // 对列头
private int rear; // 队列尾
private int[] arr; // 队列
// 创建队列的构造器
public ArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize){
this.maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
front = -1; // 指向队列头部,指向队列头的前一个位置
rear = -1; // 指向队列尾部,指向队列尾的位置
}
// 判断队列是否满
public boolean isFull(){
return rear ==maxSize - 1;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rear == front;
}
// 添加数据到队列
public void addQueue(int n){
// 判断队列是否满
if(this.isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满!");
return;
}
rear++; // 后指针后移
arr[rear] = n;
}
// 从队列获取数据
public int getQueue(){
// 判空
if (this.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("没有数据!!");
// 通过抛异常处理
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据!");
}
front++;
int get = arr[front];
arr[front] = 0;
return get;
}
// 遍历
// 显示队列中所有数组
public void showQueue(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i,arr[i]);
}
}
// 显示队列中头数据
public int headQueue(){
// 判空
if (this.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列空!");
throw new RuntimeException("队列空!");
}
return arr[front + 1];
}
}
package com.cnblog.queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 循环队列数组实现
* @author 炫酷100
*
*/
public class CircleArrayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("数组模拟环形数组");
// TestQueue
CircleArray queue = new CircleArray(4);
char key = ‘ ‘; // 接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
// 输出一个菜单
while(loop){
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列中取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);// 接收第一个字符
switch (key) {
case ‘s‘:
queue.showQueue();
break;
case ‘e‘:
scanner.close();
loop = false;
break;
case ‘a‘:
System.out.println("输入一个数");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.addQueue(value);
break;
case ‘g‘:
try {
int res = queue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据为%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case ‘h‘:
try {
int headData = queue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列数据头的数据是d%\n", headData);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
class CircleArray{
private int maxSize; // 队列最大容量
// 将front变量的含义做调整,使其指向队列的第一个元素,初始值front为0
private int front; // 对列头
// 将rear便令的含义做调整,使其指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置,空出一个位置,初始值rear为0
private int rear; // 队列尾
private int[] arr; // 使用该数组模拟队列存放数据
// Constructor
public CircleArray(int arrMaxSize){
this.maxSize = arrMaxSize;
arr = new int[maxSize];
}
// Full
private boolean isFull(){
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
// Empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return rear == front;
}
// Add
public void addQueue(int n){
// 判断队列是否满
if(this.isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满!");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
// rear后移,考虑取模
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
// Get
public int getQueue(){
// 判空
if (this.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("没有数据!!");
// 通过抛异常处理
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据!");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
// Show
public void showQueue(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空");
return;
}
// 思路:从front开始遍历,遍历多少个元素就可以了
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++){
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize ,arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
// 当前当前队列有效数据个数
public int size(){
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
// Head
public int headQueue(){
// 判空
if (this.isEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列空!");
throw new RuntimeException("队列空!");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/torain/p/13200601.html