因为词嵌入的训练是非常耗资源的,所以ML从业者通常 都是 选择加载训练好 的 词嵌入(Embedding)数据集。(不用自己训练啦~~~)
任务:
导入 预训练词向量,使用余弦相似性(cosine similarity)计算相似度
使用词嵌入来解决 “Man is to Woman as King is to __.” 之类的 词语类比问题
修改词嵌入 来减少它们的性别歧视
import numpy as np
from w2v_utils import *
导入词向量,这个任务中,使用 50维的GloVe向量 来表示单词,导入 load the word_to_vec_map.
words, word_to_vec_map = read_glove_vecs(‘data/glove.6B.50d.txt‘) # Embedding vector已知
print(list(words)[:10])
print(word_to_vec_map[‘mauzac‘])
[‘1945gmt‘, ‘mauzac‘, ‘kambojas‘, ‘4-b‘, ‘wakan‘, ‘lorikeet‘, ‘paratroops‘, ‘wittkower‘, ‘messageries‘, ‘oliver‘]
[ 0.049225 -0.36274 -0.31555 -0.2424 -0.58761 0.27733
0.059622 -0.37908 -0.59505 0.78046 0.3348 -0.90401
0.7552 -0.30247 0.21053 0.03027 0.22069 0.40635
0.11387 -0.79478 -0.57738 0.14817 0.054704 0.973
-0.22502 1.3677 0.14288 0.83708 -0.31258 0.25514
-1.2681 -0.41173 0.0058966 -0.64135 0.32456 -0.84562
-0.68853 -0.39517 -0.17035 -0.54659 0.014695 0.073697
0.1433 -0.38125 0.22585 -0.70205 0.9841 0.19452
-0.21459 0.65096 ]
导入的数据:
words: 词汇表中单词集.
word_to_vec_map: dictionary 映射单词到它们的 GloVe vector 表示.
Embedding vectors vs one-hot vectors
one-hot向量不能很好捕捉单词之间的相似度水平(每一个one-hot向量与任何其他one-hot向量有相同的欧几里得距离(Euclidean distance))
Embedding vector,如Glove vector提供了许多关于 单个单词含义 的有用信息
下面介绍如何使用 GloVe向量 来度量两个单词之间的 相似性
为了测量两个单词之间的相似性, 我们需要一个方法来测量两个单词的两个embedding vectors的相似性程度。 给定两个向量 \(u\) 和 \(v\), cosine similarity 定义如下:
\(u \cdot v\) 是两个向量的点积(内积)
\(||u||_2\) 向量 \(u\) 的范数(长度)
\(\theta\) 是 \(u\) 与 \(v\) 之间的夹角角度
余弦相似性 依赖于 \(u\) and \(v\) 的角度.
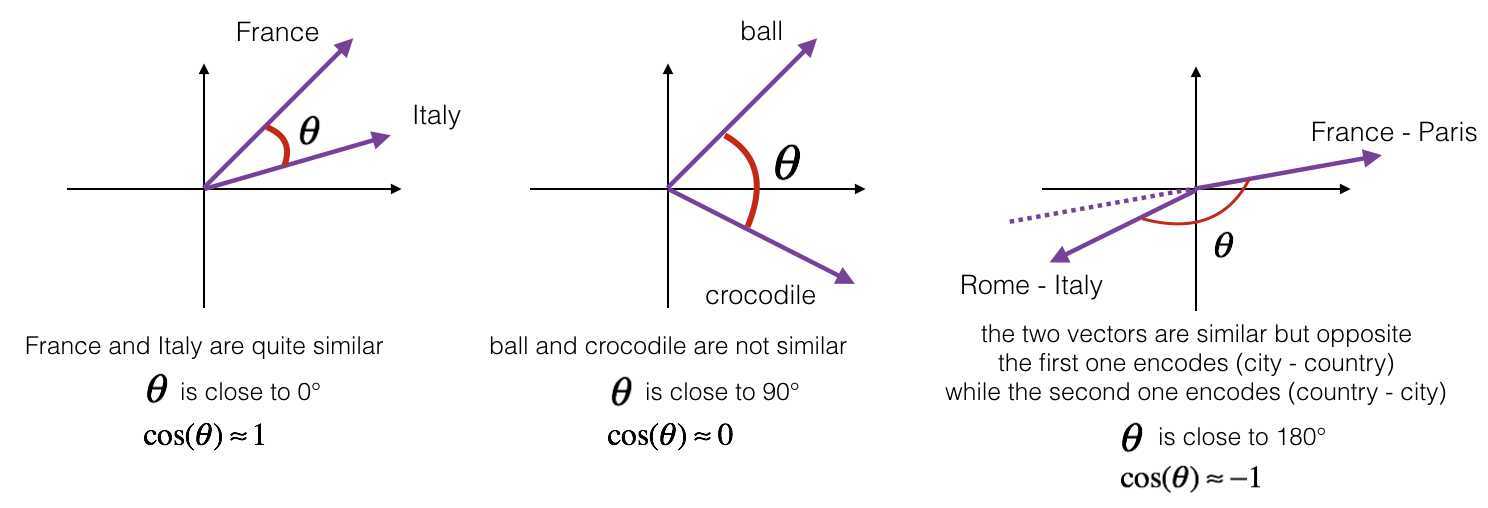
Exercise: 实现函数 cosine_similarity() 来计算两个词向量之间的 相似性.
Reminder: \(u\) 的范式定义为 \(||u||_2 = \sqrt{\sum_{i=1}^{n} u_i^2}\)
提示: 使用 np.dot, np.sum, or np.sqrt 很有用.
# GRADED FUNCTION: cosine_similarity
def cosine_similarity(u, v):
"""
Cosine similarity reflects the degree of similarity between u and v
Arguments:
u -- a word vector of shape (n,)
v -- a word vector of shape (n,)
Returns:
cosine_similarity -- the cosine similarity between u and v defined by the formula above.
"""
distance = 0.0
### START CODE HERE ###
# Compute the dot product between u and v (≈1 line)
dot = np.sum(u * v)
# Compute the L2 norm of u (≈1 line)
norm_u = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(u)))
# Compute the L2 norm of v (≈1 line)
norm_v = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(v)))
# Compute the cosine similarity defined by formula (1) (≈1 line)
cosine_similarity = dot / (norm_u * norm_v)
### END CODE HERE ###
return cosine_similarity
测试:
father = word_to_vec_map["father"]
mother = word_to_vec_map["mother"]
ball = word_to_vec_map["ball"]
crocodile = word_to_vec_map["crocodile"]
france = word_to_vec_map["france"]
italy = word_to_vec_map["italy"]
paris = word_to_vec_map["paris"]
rome = word_to_vec_map["rome"]
print("cosine_similarity(father, mother) = ", cosine_similarity(father, mother))
print("cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile) = ",cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile))
print("cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy) = ",cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy)) # (国家-首都, 首都-国家)-->接近-1
print("cosine_similarity(france - paris, italy - rome) = ",cosine_similarity(france - paris, italy - rome))
cosine_similarity(father, mother) = 0.890903844289
cosine_similarity(ball, crocodile) = 0.274392462614
cosine_similarity(france - paris, rome - italy) = -0.675147930817
cosine_similarity(france - paris, italy - rome) = 0.675147930817
随意的修改单词,查看他们相似性。
在词类比工作(word analogy task)中,我们完成句子:
"a is to b as c is to ____".
举例:
‘man is to woman as king is to queen‘ .
我们尝试找到一个单词 d,使得相关的单词向量 \(e_a, e_b, e_c, e_d\) 以下列方式关联:
\(e_b - e_a \approx e_d - e_c\)
我们将使用cosine similarity测量 \(e_b - e_a\) 和 \(e_d - e_c\) 的相似性.
Exercise:完成函数complete_analogy 实现 word analogies.
# GRADED FUNCTION: complete_analogy
def complete_analogy(word_a, word_b, word_c, word_to_vec_map):
"""
Performs the word analogy task as explained above: a is to b as c is to ____.
Arguments:
word_a -- a word, string
word_b -- a word, string
word_c -- a word, string
word_to_vec_map -- dictionary that maps words to their corresponding vectors.
Returns:
best_word -- the word such that v_b - v_a is close to v_best_word - v_c, as measured by cosine similarity
"""
# convert words to lower case
word_a, word_b, word_c = word_a.lower(), word_b.lower(), word_c.lower()
### START CODE HERE ###
# Get the word embeddings v_a, v_b and v_c (≈1-3 lines)
e_a, e_b, e_c = word_to_vec_map[word_a],word_to_vec_map[word_b],word_to_vec_map[word_c]
### END CODE HERE ###
words = word_to_vec_map.keys()
max_cosine_sim = -100 # Initialize max_cosine_sim to a large negative number
best_word = None # Initialize best_word with None, it will help keep track of the word to output
# loop over the whole word vector set
for w in words:
# to avoid best_word being one of the input words, pass on them.
if w in [word_a, word_b, word_c] :
continue
### START CODE HERE ###
# Compute cosine similarity between the vector (e_b - e_a) and the vector ((w‘s vector representation) - e_c) (≈1 line)
cosine_sim = cosine_similarity(e_b - e_a,word_to_vec_map[w] - e_c)
# If the cosine_sim is more than the max_cosine_sim seen so far,
# then: set the new max_cosine_sim to the current cosine_sim and the best_word to the current word (≈3 lines)
if cosine_sim > max_cosine_sim:
max_cosine_sim = cosine_sim
best_word = w
### END CODE HERE ###
return best_word
测试:
triads_to_try = [(‘italy‘, ‘italian‘, ‘spain‘), (‘india‘, ‘delhi‘, ‘japan‘), (‘man‘, ‘woman‘, ‘boy‘), (‘small‘, ‘smaller‘, ‘large‘)]
for triad in triads_to_try:
print (‘{} -> {} :: {} -> {}‘.format( *triad, complete_analogy(*triad,word_to_vec_map)))
italy -> italian :: spain -> spanish
india -> delhi :: japan -> tokyo
man -> woman :: boy -> girl
small -> smaller :: large -> larger
也存在一些单词,算法不能给出正确答案:
triad = [‘small‘, ‘smaller‘, ‘big‘]
print (‘{} -> {} :: {} -> {}‘.format( *triad, complete_analogy(*triad, word_to_vec_map)))
small -> smaller :: big -> competitors
Cosine similarity 求两个词向量的相似度不错
对于NLP应用,通常使用预训练好的词向量数据集
Sequence Model-week2编程题1(词向量的运算)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/douzujun/p/13211014.html