假设有一个用户表, 对应的用户实体:
public class User {
@Id
Long id;
//姓名
String name;
//性别,男0女1
String sex;
//年龄
Integer age;
//部门, 用户-部门多对一关系
@ManyToOne
Department dept;
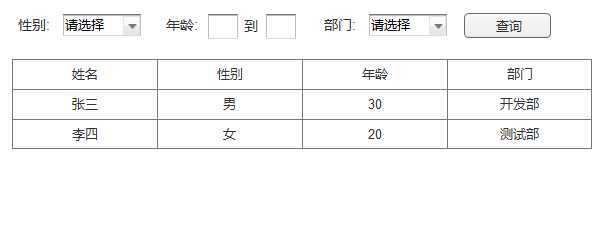
}前端需要实现这样的查询:
其中部门支持多选;
jpa里的复杂查询一般使用@Query完成, 但是@Query并不支持动态过滤条件, 过滤条件在编译时就已经确定;
可能的实现方式:
entityManager.createQuery(sql)查询; 简单好理解, 但是失去了jpa对jpql的类型检查, 可能编译不出错但是运行时出错; @Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> , JpaSpecificationExecutor<User>{
/**
* 根据多个过滤条件查询用户
* @param sex, 性别, 如果为null表示不限制性别, 查询所有性别;
* @param minAge, 年龄下限, 如果小于零表示不限制年龄
* @param maxAge, 年龄上限
* @param deptIds, 部门id的list, 一定不能为空, 包含-1L表示查询所有部门
* @return
*/
@Query("select user from User user where" +
"(:sex is null or user.sex = :sex) and" +
"(:minAge < 0 or (user.age>=:minAge and user.age<=:maxAge) ) and" +
"(-1L in :deptIds or user.dept.id in :deptIds)")
List<User> findUser(String sex,Integer minAge,Integer maxAge,List<Long> deptIds);
}完整的jpql语句:
select user from User user where
(:sex is null or user.sex = :sex) and
(:minAge < 0 or (user.age>=:minAge and user.age<=:maxAge) ) and
(-1L in :deptIds or user.dept.id in :deptIds)这种方式相对来说实现简单好理解, 可能会影响一些查询速度, 需要service层配合处理参数;
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/QIAOXINGXING001/p/13218858.html