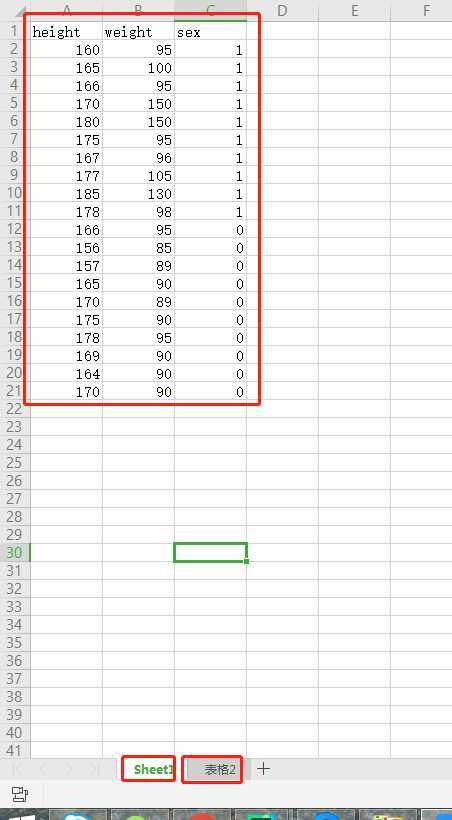
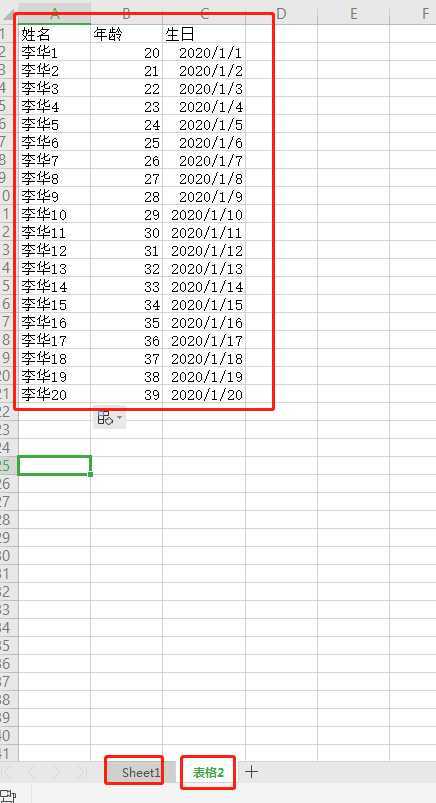
测试表格数据如下图:
表格名字:data1.xlsx
使用模块 import xlrd
下载:python -m pip install xlrd
1、读取所有的Sheet表
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*-
import xlrd
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
pass
filename = ‘data1.xlsx‘
f = xlrd.open_workbook(filename) # 打开Excel
all_sheets = f.sheets() # 找到所有的表
print(‘表的数量‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
print(len(all_sheets)) # 打印表的数量
print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
for sheet in all_sheets:
name = sheet.name
print(‘每个表的名字‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
print(name) # 遍历打印表的名字
print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
运行结果
-----------------------表的数量----------------------- 2 -------------------------------------------------- ----------------------每个表的名字---------------------- Sheet1 -------------------------------------------------- ----------------------每个表的名字---------------------- 表格2 --------------------------------------------------
2、读取第一个表格数据(采用读取单元格形式)
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*-
import xlrd
if __name__ == ‘__main__‘:
pass
filename = ‘data1.xlsx‘
f = xlrd.open_workbook(filename) # 打开Excel
all_sheets = f.sheets() # 找到所有的表
# print(‘表的数量‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
# print(len(all_sheets)) # 打印表的数量
# print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
for sheet in all_sheets:
name = sheet.name
# print(‘每个表的名字‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
# print(name) # 遍历打印表的名字
# print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
if len(all_sheets) > 1:
sheet1 = all_sheets[0]
print(‘sheet1 表名‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
print(sheet1.name) # 打印表1的名字
print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
rows = sheet1.nrows
print(‘sheet1 的行数‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
print(rows)
print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
lines = sheet1.ncols
print(‘sheet1 的列数‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
print(lines)
print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
# 遍历Sheet1的数据
print(‘sheet1 的数据如下‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
for row in range(rows):
for line in range(lines):
data = sheet1.cell(row, line).value
print(data)
print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘))
运行结果
--------------------sheet1 表名--------------------- Sheet1 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的行数-------------------- 21 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的列数-------------------- 3 -------------------------------------------------- -------------------sheet1 的数据如下------------------- height weight sex 160.0 95.0 1.0 165.0 100.0 1.0 166.0 95.0 1.0 170.0 150.0 1.0 180.0 150.0 1.0 175.0 95.0 1.0 167.0 96.0 1.0 177.0 105.0 1.0 185.0 130.0 1.0 178.0 98.0 1.0 166.0 95.0 0.0 156.0 85.0 0.0 157.0 89.0 0.0 165.0 90.0 0.0 170.0 89.0 0.0 175.0 90.0 0.0 178.0 95.0 0.0 169.0 90.0 0.0 164.0 90.0 0.0 170.0 90.0 0.0 --------------------------------------------------
读取第一个表格数据(采用一行一行读取形式)
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*- import xlrd if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: pass filename = ‘data1.xlsx‘ f = xlrd.open_workbook(filename) # 打开Excel all_sheets = f.sheets() # 找到所有的表 # print(‘表的数量‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(len(all_sheets)) # 打印表的数量 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for sheet in all_sheets: name = sheet.name # print(‘每个表的名字‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(name) # 遍历打印表的名字 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) if len(all_sheets) > 1: sheet1 = all_sheets[0] print(‘sheet1 表名‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(sheet1.name) # 打印表1的名字 print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) rows = sheet1.nrows print(‘sheet1 的行数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(rows) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) lines = sheet1.ncols print(‘sheet1 的列数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(lines) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # 遍历Sheet1的数据 # print(‘sheet1 的数据如下‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # for row in range(rows): # for line in range(lines): # data = sheet1.cell(row, line).value # print(data) # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for row in range(rows): row_data = sheet1.row_values(row) print(row_data) # 一行一行遍历
运行结果
D:\Python37_64\python.exe D:/B_CODE/Python/读取CSV文件/ReadXLSX.py --------------------sheet1 表名--------------------- Sheet1 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的行数-------------------- 21 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的列数-------------------- 3 -------------------------------------------------- [‘height‘, ‘weight‘, ‘sex‘] [160.0, 95.0, 1.0] [165.0, 100.0, ‘‘] [166.0, 95.0, 1.0] [170.0, 150.0, 1.0] [180.0, 150.0, 1.0] [175.0, 95.0, 1.0] [167.0, 96.0, 1.0] [177.0, 105.0, 1.0] [185.0, 130.0, 1.0] [178.0, 98.0, 1.0] [166.0, 95.0, 0.0] [156.0, 85.0, 0.0] [157.0, 89.0, 0.0] [165.0, 90.0, 0.0] [170.0, 89.0, 0.0] [175.0, 90.0, 0.0] [178.0, 95.0, 0.0] [169.0, 90.0, 0.0] [164.0, 90.0, 0.0] [170.0, 90.0, 0.0] Process finished with exit code 0
读取第一个表格数据(采用一列一列读取形式)
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*- import xlrd if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: pass filename = ‘data1.xlsx‘ f = xlrd.open_workbook(filename) # 打开Excel all_sheets = f.sheets() # 找到所有的表 # print(‘表的数量‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(len(all_sheets)) # 打印表的数量 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for sheet in all_sheets: name = sheet.name # print(‘每个表的名字‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(name) # 遍历打印表的名字 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) if len(all_sheets) > 1: sheet1 = all_sheets[0] print(‘sheet1 表名‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(sheet1.name) # 打印表1的名字 print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) rows = sheet1.nrows print(‘sheet1 的行数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(rows) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) lines = sheet1.ncols print(‘sheet1 的列数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(lines) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # 遍历Sheet1的数据 # print(‘sheet1 的数据如下‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # for row in range(rows): # for line in range(lines): # data = sheet1.cell(row, line).value # print(data) # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # for row in range(rows): # row_data = sheet1.row_values(row) # print(row_data) # 一行一行遍历 for line in range(lines): line_data = sheet1.col_values(line) print(line_data) # 一列一列遍历
运行结果
D:\Python37_64\python.exe D:/B_CODE/Python/读取CSV文件/ReadXLSX.py --------------------sheet1 表名--------------------- Sheet1 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的行数-------------------- 21 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的列数-------------------- 3 -------------------------------------------------- [‘height‘, 160.0, 165.0, 166.0, 170.0, 180.0, 175.0, 167.0, 177.0, 185.0, 178.0, 166.0, 156.0, 157.0, 165.0, 170.0, 175.0, 178.0, 169.0, 164.0, 170.0] [‘weight‘, 95.0, 100.0, 95.0, 150.0, 150.0, 95.0, 96.0, 105.0, 130.0, 98.0, 95.0, 85.0, 89.0, 90.0, 89.0, 90.0, 95.0, 90.0, 90.0, 90.0] [‘sex‘, 1.0, ‘‘, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0] Process finished with exit code 0
3、读取日期类型(读取生日)
我们直接读取表格,会发现生日读出来不是datatime类型,而是float类型,例如:
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*- import xlrd if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: pass filename = ‘data1.xlsx‘ f = xlrd.open_workbook(filename) # 打开Excel all_sheets = f.sheets() # 找到所有的表 # print(‘表的数量‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(len(all_sheets)) # 打印表的数量 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for sheet in all_sheets: name = sheet.name # print(‘每个表的名字‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(name) # 遍历打印表的名字 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) if len(all_sheets) >= 2: sheet1 = all_sheets[1] print(‘sheet1 表名‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(sheet1.name) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) rows = sheet1.nrows print(‘sheet1 的行数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(rows) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) lines = sheet1.ncols print(‘sheet1 的列数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(lines) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # 遍历Sheet1的数据 # print(‘sheet1 的数据如下‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # for row in range(rows): # for line in range(lines): # data = sheet1.cell(row, line).value # print(data) # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for row in range(rows): row_data = sheet1.row_values(row) print(row_data) # 一行一行遍历 # for line in range(lines): # line_data = sheet1.col_values(line) # print(line_data) # 一列一列遍历
运行结果
D:\Python37_64\python.exe D:/B_CODE/Python/读取CSV文件/ReadXLSX.py --------------------sheet1 表名--------------------- 表格2 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的行数-------------------- 21 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的列数-------------------- 3 -------------------------------------------------- [‘姓名‘, ‘年龄‘, ‘生日‘] [‘李华1‘, 20.0, 43831.0] [‘李华2‘, 21.0, 43832.0] [‘李华3‘, 22.0, 43833.0] [‘李华4‘, 23.0, 43834.0] [‘李华5‘, 24.0, 43835.0] [‘李华6‘, 25.0, 43836.0] [‘李华7‘, 26.0, 43837.0] [‘李华8‘, 27.0, 43838.0] [‘李华9‘, 28.0, 43839.0] [‘李华10‘, 29.0, 43840.0] [‘李华11‘, 30.0, 43841.0] [‘李华12‘, 31.0, 43842.0] [‘李华13‘, 32.0, 43843.0] [‘李华14‘, 33.0, 43844.0] [‘李华15‘, 34.0, 43845.0] [‘李华16‘, 35.0, 43846.0] [‘李华17‘, 36.0, 43847.0] [‘李华18‘, 37.0, 43848.0] [‘李华19‘, 38.0, 43849.0] [‘李华20‘, 39.0, 43850.0] Process finished with exit code 0
可以采用这种读取方式(先判断读出类型是什么,再进行转换)
类型有 0 代表empty,1代表 string, 2代表 number, 3代表 date, 4 代表boolean, 5 代表error
读取返回类型sheet1.cell(row, line).ctype
判断如果类型ctype等于3,则使用datetime(*xldate_as_tuple(val, 0))进行转换
需要import的模块
from datetime import datetime
import xlrd
from xlrd import xldate_as_tuple
# -*- encoding=utf-8 -*- from datetime import datetime import xlrd from xlrd import xldate_as_tuple if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: pass filename = ‘data1.xlsx‘ f = xlrd.open_workbook(filename) # 打开Excel all_sheets = f.sheets() # 找到所有的表 # print(‘表的数量‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(len(all_sheets)) # 打印表的数量 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for sheet in all_sheets: name = sheet.name # print(‘每个表的名字‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # print(name) # 遍历打印表的名字 # print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) if len(all_sheets) >= 2: sheet1 = all_sheets[1] print(‘sheet1 表名‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(sheet1.name) # 打印表1的名字 print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) rows = sheet1.nrows print(‘sheet1 的行数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(rows) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) lines = sheet1.ncols print(‘sheet1 的列数‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) print(lines) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # 遍历Sheet1的数据 # print(‘sheet1 的数据如下‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) for row in range(rows): for line in range(lines): data_type = sheet1.cell(row, line).ctype if data_type == 3: print(‘日期类型‘) val = sheet1.cell(row, line).value data = datetime(*xldate_as_tuple(val, 0)) else: data = sheet1.cell(row, line).value print(data) print(‘‘.center(50, ‘-‘)) # for row in range(rows): # row_data = sheet1.row_values(row) # print(row_data) # 一行一行遍历 # for line in range(lines): # line_data = sheet1.col_values(line) # print(line_data) # 一列一列遍历
运行结果
D:\Python37_64\python.exe D:/B_CODE/Python/读取CSV文件/ReadXLSX.py --------------------sheet1 表名--------------------- 表格2 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的行数-------------------- 21 -------------------------------------------------- --------------------sheet1 的列数-------------------- 3 -------------------------------------------------- 姓名 年龄 生日 李华1 20.0 日期类型 2020-01-01 00:00:00 李华2 21.0 日期类型 2020-01-02 00:00:00 李华3 22.0 日期类型 2020-01-03 00:00:00 李华4 23.0 日期类型 2020-01-04 00:00:00 李华5 24.0 日期类型 2020-01-05 00:00:00 李华6 25.0 日期类型 2020-01-06 00:00:00 李华7 26.0 日期类型 2020-01-07 00:00:00 李华8 27.0 日期类型 2020-01-08 00:00:00 李华9 28.0 日期类型 2020-01-09 00:00:00 李华10 29.0 日期类型 2020-01-10 00:00:00 李华11 30.0 日期类型 2020-01-11 00:00:00 李华12 31.0 日期类型 2020-01-12 00:00:00 李华13 32.0 日期类型 2020-01-13 00:00:00 李华14 33.0 日期类型 2020-01-14 00:00:00 李华15 34.0 日期类型 2020-01-15 00:00:00 李华16 35.0 日期类型 2020-01-16 00:00:00 李华17 36.0 日期类型 2020-01-17 00:00:00 李华18 37.0 日期类型 2020-01-18 00:00:00 李华19 38.0 日期类型 2020-01-19 00:00:00 李华20 39.0 日期类型 2020-01-20 00:00:00 -------------------------------------------------- Process finished with exit code 0
4、写入(后续追加)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/rainbow-tan/p/13224847.html