String表示字符串类型,是引用数据类型,不是基本数据类型。"abc"、"def"、"hello world",这是3个String对象。"abc"自出生到死亡,不可变,不能变成"abcd",也不能变成"ab"。public class StringTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这两行代码表示底层创建了3个字符串对象,都是在字符串常量池中
String s1 = "abcdef";
String s2 = "abcdef" + "xy";
// 分析:这是使用new方式创建的字符串对象。这个代码中的“xy”是从哪里来的?
// 凡是双引号括起来的都在字符串常量池中有一份。
// new对象的时候一定在堆内存当中开辟空间
String s3 = new String("xy");
}
}
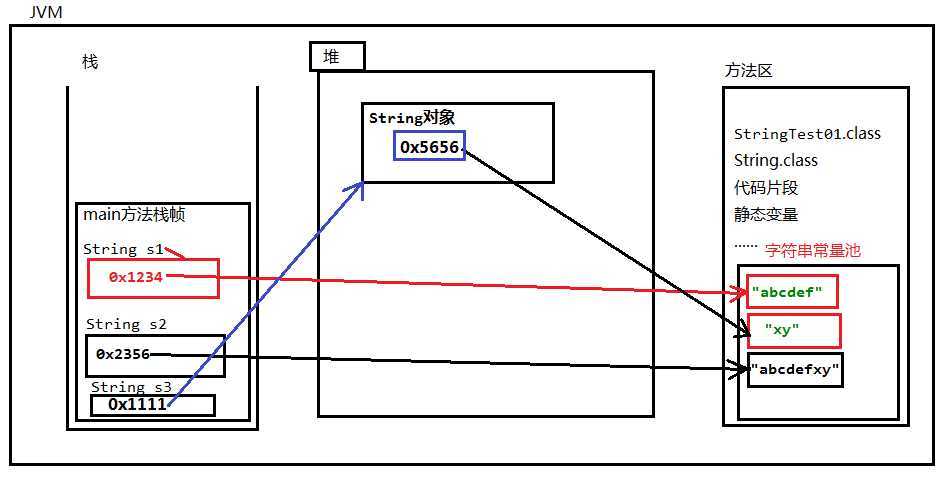
String类型的引用中存储的同样是对象的内存地址
public class UserTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User(110, "张三");
}
}
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
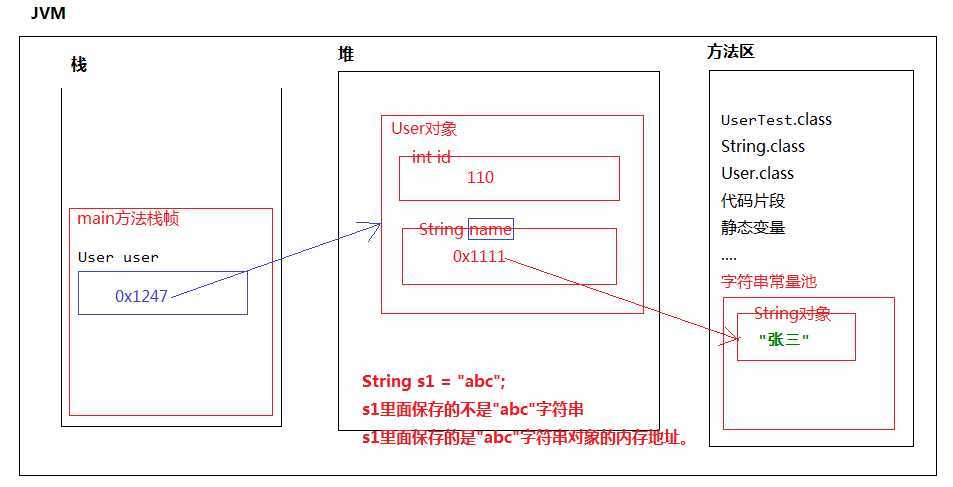
字符串对象之间的比较不能使用==,==不保险,应该调用String类的equals()方法.
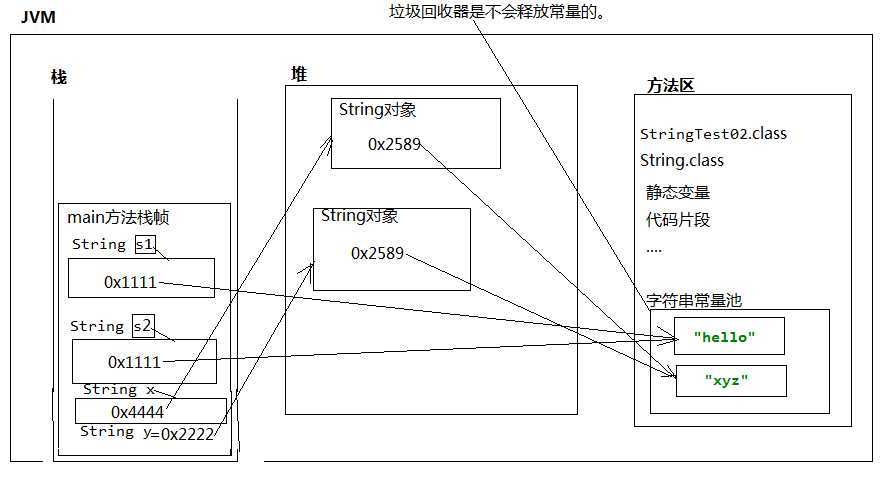
public class StringTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// “hello”是存储在方法区的字符串常量池中
// 所以这个“hello”不会新建
String s1 = "hello";
// 双引号比较的是变量中保存的内存地址
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
String x = new String("xyz");
String y = new String("xyz");
System.out.println(x == y);
// 通过这个案例的学习,我们知道了,字符串对象之间的比较不能使用“==”
// “==”不保险,应该调用String类的equals()方法
// String类已经重写了equals()方法,以下的equals()方法调用的是String重写之后的equals()方法。
System.out.println(x.equals(y));//true
String k = new String("testString");
// 为什么"testString"这个字符串后面可以加"."呢?
// 因为"testString"是一个String字符串对象,只要是对象都能调用方法。
System.out.println("testString".equals(k));//建议使用这种方式,因为这个可以避免空指针异常
System.out.println(k.equals("testString"));//存在空指针异常的风险,不建议这样写。
}
}
变量和引用存储内容的区别
int i = 100; //i变量中保存的是100这个值
String s = "abc";
/*
s变量中保存的是字符串对象的内存地址
s引用中保存的不是“abc”,而是0x111
而0x1111是“abc”字符串对象在字符串常量池当中的内存地址
*/
分析以下程序,一共创建了几个对象。
public class StringTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
一共3个对象
方法区字符串常量池中有1个"hello"
堆内存中有两个String对象
一共3个对象
*/
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
}
}
第一个:String s = new String("");
第二个:String s = "";
第三个:String s = new String(char数组);
第四个:String s = new String(char数组,起始下标,长度);
第五个:String s = new String(byte数组);
第六个:String s = new String(byte数组,起始下标,长度);
public class StringTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建字符串对象最常用的一种方式
String s1 = "hello world";
// s1这个变量中存储的是一个内存地址
// 按照以前应该输出一个地址
// 但是实际输出的是一个字符串,说明String类已经重写了toString()方法
System.out.println(s1);
// 这里只掌握最常用的构造方法
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99};//97是a,98是b,99是c
String s2 = new String(bytes);
// 输出一个引用的时候,会自动调用toString()方法,默认Object的话,会自动输出对象的地址
// 通过输出一个结果我们得出一个结论:String类已经重写了toString()方法。
// 输出字符串对象的话,输出的不是对象的内存地址,而是字符串本身。
System.out.println(s2);//abc
System.out.println(s2.toString());//abc
// String(字节数组,数组元素下标的起始位置,长度)
// 将bytes数组中的一部分转换成字符串
String s3 = new String(bytes, 1, 2);
System.out.println(s3);//bc
// 将char数组全部转换程字符串
char[] chars={‘我‘,‘是‘,‘中‘,‘国‘,‘人‘};
// 将char数组的一部分转换成字符串
String s4 = new String(chars);
System.out.println(s4);//我是中国人
}
}
1.char charAt(int index);
// 1.char charAt(int index);
char c = "中国人".charAt(1);//"中国人"是一个字符串String对象,只要是对象就能"."
System.out.println(c);//国
2.(了解)int compareTo(String anotherString);
// 2.(了解)int compareTo(String anotherString);
int result = "abc".compareTo("abc");
System.out.println(result);//0(等于0) 前后一致 10-10=0
// 拿着字符串第一个字母和后面的字符串的第一个字母进行比较。能分出胜负就不再比较了。
int result1 = "abcd".compareTo("abce");
System.out.println(result1);//-1(小于0) 前小后大 8-9=-1
int result2 = "abce".compareTo("abcd");
System.out.println(result2);//1(大于0) 前大后小 9-8=1
3.(掌握)boolean contains(CharSequence s);
// 3.(掌握)boolean contains(CharSequence s);
// 判断前面的字符串中是否包含后面的字符串
System.out.println("helloworld.java".contains(".java"));//true
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".contains("https://"));//false
4.(掌握)boolean endWith(String suffix);
// 4.(掌握)boolean endWith(String suffix);
// 判断当前的字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
System.out.println("test.txt".endsWith(".txt"));//true
System.out.println("test.txt".endsWith(".java"));//false
5.(掌握)boolean equals(Object anObject);
// 5.(掌握)boolean equals(Object anObject);
// equals()方法只能看出是否相等。compareTo()方法不仅可以看出是否相等还可以看出谁大谁小
// 比较两个字符串必须使用equals()方法,不能使用"=="
System.out.println("abc".equals("abc"));//true
6.(掌握)boolean equals equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString);
// 6.(掌握)boolean equals equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString);
// 判断两个字符串是否相等,并且同时忽略大小写
System.out.println("ABc".equalsIgnoreCase("abC"));//true
7.(掌握)byte[] getBytes();
// 7.(掌握)byte[] getBytes();
// 将字符串对象转换成字符数组
byte[] bytes = "abcdef".getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
8.(掌握)int indexOf(String str);
// 8.(掌握)int indexOf(String str);
// 判断某个子字符串在当前字符串第一次出现处的索引
System.out.println("oraclejavac++.netc#phppythonjavaoraclec++".indexOf("java"));//6
9.(掌握)boolean isEmpty();
// 9.(掌握)boolean isEmpty();
// 判断某个字符串是否为"空字符串"
String s = "a";
System.out.println(s.isEmpty());//false
10.(掌握)int lenght();
// 10.(掌握)int lenght();
/*
判断数组长度和判断字符串长度不一样
判断数组长度是lenght属性;判断字符串长度是lenght()方法。
*/
System.out.println("abc".length());//3
System.out.println("".length());//0
11.(掌握)int lastIndexOf(String str);
// 11.(掌握)int lastIndexOf(String str);
// 判断某个子字符串在当前字符串中最后一次出现的索引(下标)
System.out.println("oraclejavac++.netc#phppythonjavaoraclec++".lastIndexOf("java"));//28
12.(掌握)String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement);
// 12.(掌握)String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement);
// String的父类接口就是:CharSequence
String newString = "http://www.baidu.com".replace("http://", "https://");
System.out.println(newString);//https://www.baidu.com
13.(掌握)String[] split(String regex);
// 13.(掌握)String[] split(String regex);
// 拆分字符串
String[] ymd = "1980-10-11".split("-");//"1980-10-11"以"-"分隔符进行拆分
for (int i = 0; i < ymd.length; i++) {
System.out.println(ymd[i]);
}
14.(掌握)boolean startWith(String prefix);
// 14.(掌握)boolean startWith(String prefix);
// 判断某个字符串是否以某个子字符串开始
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".startsWith("http"));//true
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".startsWith("https"));//false
15.(掌握)String substring(int beginIndex);
// 15.(掌握)String substring(int beginIndex);
// 截取字符串,参数是起始下标
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".substring(7));// www.baidu.com
16.(掌握)String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex);
// 16.(掌握)String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex);
// beginIndex起始位置(包括);endIndex结束位置(不包括)
System.out.println("http://www.baidu.com".substring(7, 10));//www
17.(掌握)char[] toCharArray();
// 17.(掌握)char[] toCharArray();
// 将字符串转换成char数组
char[] chars = "我是中国人".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.println(chars[i]);
}
18.(掌握)String toLowerCase();
// 18.(掌握)String toLowerCase();
// 转换为小写
System.out.println("AFHDSaddfjeSFNF".toLowerCase());//afhdsaddfjesfnf
19.(掌握)String toUpperCase();
// 19.(掌握)String toUpperCase();
System.out.println("AFHDSaddfjeSFNF".toUpperCase());//AFHDSADDFJESFNF
20.(掌握)String trim();
// 20.(掌握)String trim();
// 去除字符串前后空白
System.out.println(" hello world ".trim());//hello world
21.(掌握)String 中只有一个方法是静态的,不需要new 对象这个方法叫valueOf,作用:将"非字符串"转换成"字符串"
public class StringTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
// 21.(掌握)String 中只有一个方法是静态的,不需要new 对象这个方法叫valueOf
// 作用:将"非字符串"转换成"字符串"
String s1 = String.valueOf(true);
System.out.println(s1);//true
String s2 = String.valueOf(new Customer1());
// 没有重写toString()方法之前输出的是对象的内存地址
// System.out.println(s2);//Customer1@f5f2bb7
// 重写toString()方法后的输出内容如下:
System.out.println(s2);//我是一个努力学习的人!
}
}
class Customer1 {
// 重写toString()方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "我是一个努力学习的人!";
}
}
关于printn()方法
// 关于printn()方法
Object obj = new Object();
// 为什么输出一个引用的时候,会调用toString()方法
// 本质上System.out.println()这个方法在输出任何数据的时候都是先转换成字符串,再输出。
System.out.println(obj);
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yxc-160206/p/13235604.html