关于知识点,JUC的最后一篇文章。更加深的时候,再在这个之后进行书写。
1.大纲
Runnable的不足
CallAble的接口
Future类
1.不足
不能返回返回值
run方法不能抛出异常,因为大部分可以处理异常的不是我们写的,所以,要想处理,还是要在run里进行自己处理异常
2.程序
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object‘s
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}
1.说明
实现call
2.程序
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
1.作用
不要要等待,需要的时候,到future获取数据
2.Callable与Future的关系
可以使用Future.get来获取Callable接口返回的执行结果
可以通过Future.isDone来判断任务是否已经执行完成,
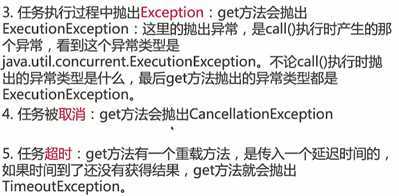
如果call()还没有执行完成,调用get的线程将会被阻塞,只有等运行完成,才能获取到结果,然后主线程才回切换到runnable的状态
3.总结
Future是一个存储器,存储了call这个任务的结果
4.主要方法
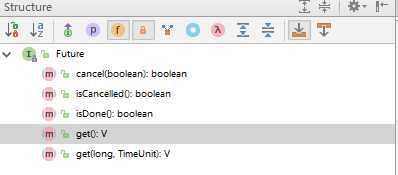
5.get方法
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;

6.get(timeout,unit)
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
超时很常见
超时不获取,任务需要取消
7.cancel方法
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
8.isDone
boolean isDone();
是否完毕,不一定是成功的,抛出异常也是执行完毕
9.isCancel
boolean isCancelled();
1.基础的用法
线程池的submit方法返回Future对象

public class OneFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(new CallableTask());
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
static class CallableTask implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
return new Random(10).nextInt();
}
}
}
效果:
Connected to the target VM, address: ‘127.0.0.1:49767‘, transport: ‘socket‘ -1157793070 Disconnected from the target VM, address: ‘127.0.0.1:49767‘, transport: ‘socket‘ Process finished with exit code 0
2.lambda方式
public class TwoFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
Callable<Integer> callable = ()->{
Thread.sleep(3000);
return new Random(10).nextInt();
};
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(callable);
try {
System.out.println(future.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
3.多个任务,使用Future数组来获取结果
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/juncaoit/p/13237428.html