一、启动步骤
@SpringBootApplication public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
run方法分两个步骤进行,第一步:构造方法初始化(设置应用上下文初始化器和应用监听器);第二步:运行spring应用(创建和刷新应用上线文)。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) { return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args); }
二、构造方法
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; //资源加载器为空
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); //断言启动主类不为空
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); //第一个deduceXXX方法,判断WEB应用类型,分别为NONE(非web)、SERVLET(Servlet Web)、REACTIVE(Reactive Web)。
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); //设置应用上下文初始化器
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); //设置应用监听器
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); //第二个deduceXXX方法查找启动主类的全限名
}
如何加载应用上下文初始化器和应用监听器呢?
答:在这里扩展一下,springboot很多类不是通过注解扫描的方式,加载相关的类的;采用配置文件(META-INF/spring.factories)的方式,将需要执行的类配置在文件中,通过反射的方式进行实例化的。
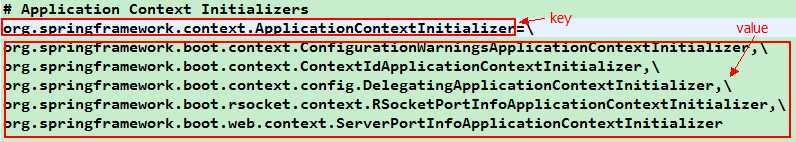
spring.factories文件已接口的全限名为key,接口的实现类的全限名为value的配置方式(可以是多个);通过扫描文件,在以key查询对应的value。我以接口org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer为例,如下图所示:
如何查询和实例化呢?
通过工具类org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(Class<?>, ClassLoader),两个参数中第1个是待加载的key(接口),第2个参数类加载器。
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) { return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {}); } //通过key(接口全限名),加载接口实现类集合并且遍历每个类采用反射方式进行实例化 private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); //加载实现类的权限路径 List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); //反射实例化实现类 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); //实例排序 return instances; } //反射实例化类 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) { List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size()); for (String name : names) { try { Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader); Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass); Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes); T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args); instances.add(instance); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex); } } return instances; }
三、运行和刷新应用上下文
启动运行容器的核心方法,包含监听器(监听生命周期不同状态)、创建应用上下文、准备应用上下文、刷新应用上下文等。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { //启动类com.springboot.demo.Application.main(String[])main方法中传递的参数,debug为空
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); //创建计时器,记录过程耗时 stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; //可配置应用上下文接口,继承ApplicationContext, Lifecycle(生命周期运行状态), Closeable(关闭释放资源) Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); //加载spring应用运行监听器,META-INF/spring.factories文件找那个配置的监听实现 listeners.starting(); //遍历启动监听器 try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); //默认应用参数类 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); //准备环境 configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); //配置忽略Bean信息 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); //打印Banner context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); //异常记录 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);//准备上下文,发布上下文准备事件(ApplicationContextInitializedEvent)
//刷新应用上线文 refreshContext(context); //调用BeanFactory工厂的后处理器实现自动boot配置;(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate) afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); //计时器结束 if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); //监听器监听上下文已启动状态 callRunners(context, applicationArguments); //启动完成,调用两个接口ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的实现类 } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); //监听器执行上下文运行中状态,发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件 } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; }
注册所有Bean后处理器:
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { super(beanFactory); this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); } public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null"); this.registry = registry; this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null); AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry); } /** * Register all relevant annotation post processors in the given registry. * @param registry the registry to operate on * @param source the configuration source element (already extracted) * that this registration was triggered from. May be {@code null}. * @return a Set of BeanDefinitionHolders, containing all bean definitions * that have actually been registered by this call */ public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors( BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry); if (beanFactory != null) { if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) { beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); } if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) { beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver()); } } Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8); if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } // Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } // Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(); try { def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader())); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex); } def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)); } return beanDefs; }
1、创建可配置应用上线文
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) { try { switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); //org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); //org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext break; default: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); //org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); } } return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
2、准备上下文
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { context.setEnvironment(environment); // postProcessApplicationContext(context); //后处理应用上下文 applyInitializers(context); //构造方法中添加的应用上下文初始化器,遍历逐一执行进行初始化(EventPublishingRunListener) listeners.contextPrepared(context); //监听器监听上下文准备完成状态事件(ApplicationContextInitializedEvent) if (this.logStartupInfo) { logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); logStartupProfileInfo(context); } // Add boot specific singleton beans ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); //Bean工厂(DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); //注册应用参数单例 if (printedBanner != null) { beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); //注册Banne单例 } if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) { ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); //设置是否允许Bean定义重写覆盖 } if (this.lazyInitialization) { //如果设置懒初始化True context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor()); //上下文添加Bean工厂后处理器 } // Load the sources Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); //加载上下文 listeners.contextLoaded(context); //第一步:将SpringApplication中监听器添加应用上下文中;
//第二步:SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster事件广播器,广播发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件 }
加载指定资源
/** * Load beans into the application context. * @param context the context to load beans into * @param sources the sources to load */ protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources)); } BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources); //创建Bean定义加载器 if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) { loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator); } if (this.resourceLoader != null) { loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader); } if (this.environment != null) { loader.setEnvironment(this.environment); } loader.load(); }
加载启动类Bean定义、注册到容器中。
int load() { int count = 0; for (Object source : this.sources) { count += load(source); } return count; }
//支持类、资源、包、字符序列4类加载 private int load(Object source) { Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null"); if (source instanceof Class<?>) { return load((Class<?>) source); } if (source instanceof Resource) { return load((Resource) source); } if (source instanceof Package) { return load((Package) source); } if (source instanceof CharSequence) { return load((CharSequence) source); } throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass()); } private int load(Class<?> source) { if (isGroovyPresent() && GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) { // Any GroovyLoaders added in beans{} DSL can contribute beans here GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class); load(loader); } if (isComponent(source)) { //AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader实例,读取Bean定义、Bean的ScopeMetadata属性(例如scope属性:作用范围)、AnnotationBeanNameGenerator生成容器中的BeanName //BeanDefinitionReaderUtils注册 this.annotatedReader.register(source); return 1; } return 0; }
3、刷新上下文(refreshContext(context))
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { refresh(context); if (this.registerShutdownHook) { try { context.registerShutdownHook(); } catch (AccessControlException ex) { // Not allowed in some environments. } } } /** * Refresh the underlying {@link ApplicationContext}. * @param applicationContext the application context to refresh */ protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) { Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext); ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh(); //ServletWebServerApplicationContext类的public final void refresh()方法 }
此处调用父抽象类AbstractApplicationContext定义的模板模式,在抽象类中再回调用子类的实现方法。
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //调动Bean工厂后处理器实现自动配置 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); //启动容器中间件,默认是Tomcat;ServletWebServerFactory接口作为Web容器的工厂类 // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset ‘active‘ flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring‘s core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()); // Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime // (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor) if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory)); beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader())); } }
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) { // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement // PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors. List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size()); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have // modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values... beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }
四、自动配置
从注解开始
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration //引入@Configuration注解 @EnableAutoConfiguration //开启自动配置(重点) @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) //开启组件扫码 public @interface SpringBootApplication {。。。}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {。。。}
这里要说明一下:AutoConfigurationImportSelector类实现DeferredImportSelector接口,DeferredImportSelector继承ImportSelector接口。
springboot自动配置是基于ImportSelector接口进行实现的。
属性实现自动配置:
@Conditional 依赖的条件
@ConditionalOnBean 在某个Bean存在的条件下
@ConditionalOnMissingBean 在某个Bean不存在的条件下
@ConditionalOnClass 在某个Class存在的条件下
@ConditionalOnMissingClass 在某个Class不存在的条件下
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/wangymd/p/13272031.html