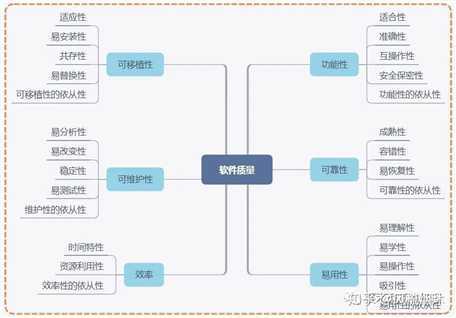
| Characteristics | Subcharacteristics | Definitions |
|---|
| |
Suitability |
This is the essential Functionality characteristic and refers to the appropriateness (to specification) of the functions of the software. |
| |
Accurateness |
This refers to the correctness of the functions, an ATM may provide a cash dispensing function but is the amount correct? |
| Functionality |
Interoperability |
A given software component or system does not typically function in isolation. This subcharacteristic concerns the ability of a software component to interact with other components or systems. |
| |
Compliance |
Where appropriate certain industry (or government) laws and guidelines need to be complied with, i.e. SOX. This subcharacteristic addresses the compliant capability of software. |
| |
Security |
This subcharacteristic relates to unauthorized access to the software functions. |
|
| |
Maturity |
This subcharacteristic concerns frequency of failure of the software. |
| Reliability |
Fault tolerance |
The ability of software to withstand (and recover) from component, or environmental, failure. |
| |
Recoverability |
Ability to bring back a failed system to full operation, including data and network connections. |
|
| |
Understandability |
Determines the ease of which the systems functions can be understood, relates to user mental models in Human Computer Interaction methods. |
Usability |
Learnability |
Learning effort for different users, i.e. novice, expert, casual etc. |
| |
Operability |
Ability of the software to be easily operated by a given user in a given environment. |
|
Efficiency |
Time behavior |
Characterizes response times for a given thru put, i.e. transaction rate. |
| |
Resource behavior |
Characterizes resources used, i.e. memory, cpu, disk and network usage. |
|
| |
Analyzability |
Characterizes the ability to identify the root cause of a failure within the software. |
| Maintainability |
Changeability |
Characterizes the amount of effort to change a system. |
| |
Stability |
Characterizes the sensitivity to change of a given system that is the negative impact that may be caused by system changes. |
| |
Testability |
Characterizes the effort needed to verify (test) a system change. |
|
| |
Adaptability |
Characterizes the ability of the system to change to new specifications or operating environments. |
| Portability |
Installability |
Characterizes the effort required to install the software. |
| |
Conformance |
Similar to compliance for functionality, but this characteristic relates to portability. One example would be Open SQL conformance which relates to portability of database used. |
| |
Replaceability |
Characterizes the plug and play aspect of software components, that is how easy is it to exchange a given software component within a specified environment. |