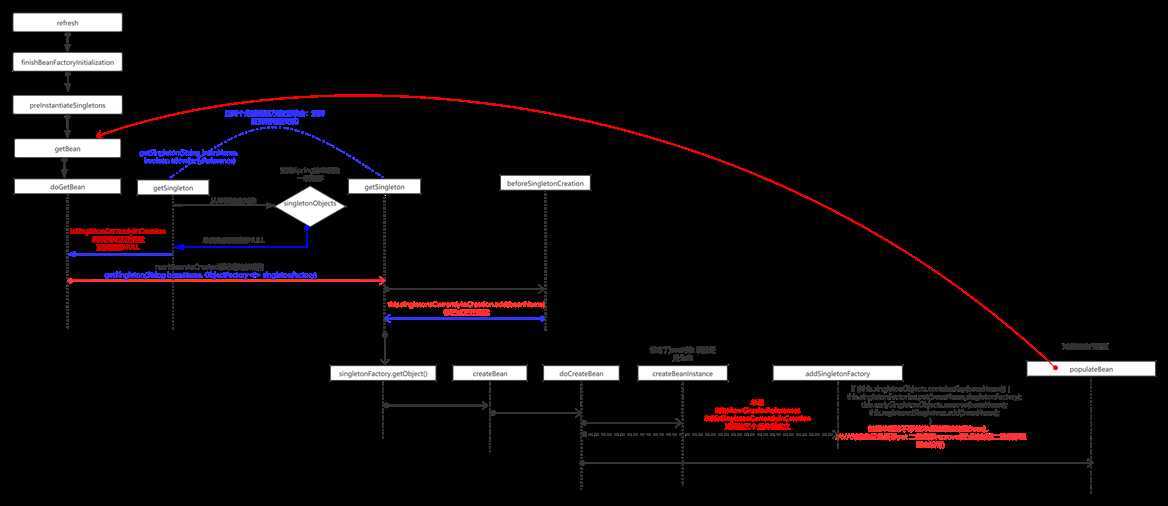
比如A引用B,B也引用A Spring创建对象的流程:
/** * Add the given singleton factory for building the specified singleton * if necessary. * <p>To be called for eager registration of singletons, e.g. to be able to * resolve circular references. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param singletonFactory the factory for the singleton object */ protected void addSingletonFactory(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) { Assert.notNull(singletonFactory, "Singleton factory must not be null"); synchronized (this.singletonObjects) { if (!this.singletonObjects.containsKey(beanName)) { this.singletonFactories.put(beanName, singletonFactory); this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName); this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName); } } }
以上是通过populateBean给属性赋值
我们知道,创建好的对象,并不是一个完整的对象,里面的属性还没有被赋值。
所以这个方法就是为创建好的Bean为它的属性赋值。并且调用了我们实现的的XXXAware接口进行回调初始化,。然后调用我们实现的Bean的后置处理器,给我们最后一次机会去修改Bean的属性。其他的地方我不做过多的介绍,
我只讲一个重点就是,在populateBean里面他会解析你的属性,并且赋值,当发现,A对象里面依赖了B,此时又会走getBean方法,
但这个时候,你去缓存中是可以拿的到的。因为我们在对createBeanInstance对象创建完成以后已经放入了缓存当中,
所以创建B的时候发现依赖A,直接就从缓存中去拿,此时B创建完,A也创建完,一共执行了4次。至此Bean的创建完成,最后将创建好的Bean放入单例缓存池中addSingleton();
至此Ioc创建Bean的整个生命周期已经介绍完毕。下面附加一张流程脑图。
参考文章:简书:https://www.jianshu.com/p/55e433434b32
后序在解释这个流程图吧,暂时跟着源码走了一遍 自己都迷迷糊糊的 哈哈,,,
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/ssskkk/p/13375298.html