1.引用的基本使用
作用:给变量起别名
语法:数据类型&别名 = 原名
代码示例:
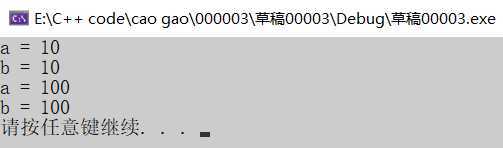
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 6 int a = 10; 7 int &b = a; 8 9 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 10 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 11 12 b = 100; 13 14 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 15 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 16 17 system("pause"); 18 19 return 0; 20 }
运行结果:
2.引用注意事项
(1)引用必须初始化
(2)引用在初始化后,不可以改变
代码示例:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int main() 4 { 5 6 int a = 10; 7 int b = 20; 8 //int &c; //错误,引用必须初始化 9 int& c = a; //一旦初始化后,就不可以更改 10 c = b; //这是赋值操作,不是更改引用 11 12 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 13 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 14 cout << "c = " << c << endl; 15 16 system("pause"); 17 18 return 0; 19 }
运行结果:

3.引用做函数参数
作用:函数传参时,可以利用引用的技术让形参修饰实参
优点:可以简化指针修改实参
代码示例:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //1. 值传递 4 void mySwap01(int a, int b) 5 { 6 int temp = a; 7 a = b; 8 b = temp; 9 } 10 11 //2. 地址传递 12 void mySwap02(int* a, int* b) 13 { 14 int temp = *a; 15 *a = *b; 16 *b = temp; 17 } 18 19 //3. 引用传递 20 void mySwap03(int& a, int& b) 21 { 22 int temp = a; 23 a = b; 24 b = temp; 25 } 26 27 int main() 28 { 29 30 int a = 10; 31 int b = 20; 32 33 mySwap01(a, b); 34 cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl; 35 36 mySwap02(&a, &b); 37 cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl; 38 39 mySwap03(a, b); 40 cout << "a:" << a << " b:" << b << endl; 41 42 system("pause"); 43 44 return 0; 45 }
运行结果:

总结:通过引用参数产生的效果同按地址传递是一样的。引用的语法更清楚简单
4.引用做函数返回值
作用:引用是可以作为函数的返回值存在的
注意:不要返回局部变量引用
用法:函数调用作为左值
代码示例:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //返回局部变量引用 4 int& test01() 5 { 6 int a = 10; //局部变量 7 return a; 8 } 9 10 //返回静态变量引用 11 int& test02() 12 { 13 static int a = 20; 14 return a; 15 } 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 20 //不能返回局部变量的引用 21 int& ref = test01(); 22 cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; 23 cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; 24 25 //如果函数做左值,那么必须返回引用 26 int& ref2 = test02(); 27 cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; 28 cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; 29 30 test02() = 1000; 31 32 cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; 33 cout << "ref2 = " << ref2 << endl; 34 35 system("pause"); 36 37 return 0; 38 }
运行结果:

5.引用的本质
本质:引用的本质在c++内部实现是一个指针常量
代码示例:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //发现是引用,转换为 int* const ref = &a; 4 void func(int& ref) 5 { 6 ref = 100; // ref是引用,转换为*ref = 100 7 } 8 int main() 9 { 10 int a = 10; 11 12 //自动转换为 int* const ref = &a; 指针常量是指针指向不可改,也说明为什么引用不可更改 13 int& ref = a; 14 ref = 20; //内部发现ref是引用,自动帮我们转换为: *ref = 20; 15 16 cout << "a:" << a << endl; 17 cout << "ref:" << ref << endl; 18 19 func(a); 20 return 0; 21 }
运行结果:
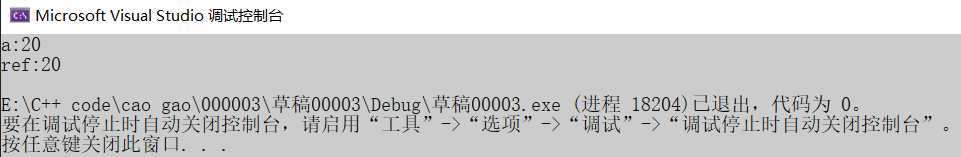
结论:C++推荐用引用技术,因为语法方便,引用本质是指针常量,但是所有的指针操作编译器都帮我们做了
6.常量引用
作用:常量引用主要用来修饰形参,防止误操作
在函数形参列表中,可以加const修饰形参,防止形参改变实参
代码示例:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //引用使用的场景,通常用来修饰形参 4 void showValue(const int& v) 5 { 6 //v += 10; 7 cout << v << endl; 8 } 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 13 //int& ref = 10; 引用本身需要一个合法的内存空间,因此这行错误 14 //加入const就可以了,编译器优化代码,int temp = 10; const int& ref = temp; 15 const int& ref = 10; 16 17 //ref = 100; //加入const后不可以修改变量 18 cout << ref << endl; 19 20 //函数中利用常量引用防止误操作修改实参 21 int a = 10; 22 showValue(a); 23 24 system("pause"); 25 26 return 0; 27 }
运行结果:

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanrongda-KaguraSakura/p/13380991.html