
经过读写分离的优化后,小王可算是轻松了一段时间,读写分离具体的方案请查看这篇文章:Sharding-JDBC:查询量大如何优化?
可是好景不长,业务发展是在太快了。数据库中的数据量猛增,由于所有表都在一个数据库中,导致服务器本地存储快满了。
从上图我们可以看的出来,由于表的数量较多,每个表的数据量也较大,但是还没到水平拆分的地步。目前遇到的问题是服务器的存储不够了,短期内还不用水平拆分,那么方案呼之欲出了:垂直拆分。
解释下什么是垂直拆分?
我们都知道,一个数据库它是由N张表构成,每个表存储的数据都不一样,都对应着各自的业务。
所谓的垂直切分其实就是分类存储,大部分都是按业务类型进行分类。相同的类型存储在相同的库上,不同的类型存储在不同的库上,这样也就将数据或者说压力分担到不同的库上面 。
比如我们可以将用户相关的放一起,订单相关的放一起,行为日志相关的放一起,依次来推下去。
优点:
拆分之后业务规划清晰,数据维护简单,分担了数据集中存储的压力。
缺点:
缺点也很明显,多表join查询无法实现,只能通过接口方式解决,提高了系统复杂度等问题。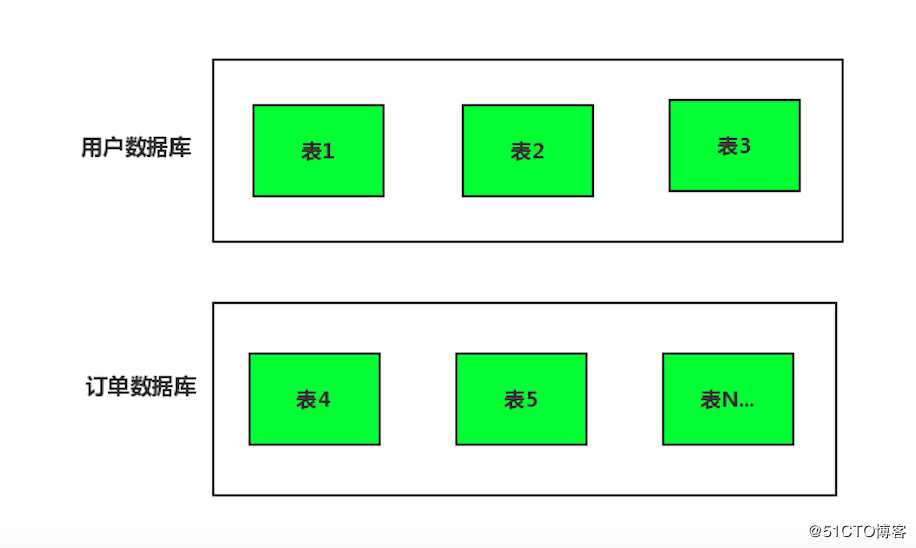
做垂直拆分其实跟读写分离是一样的,本质上还是多数据源的问题,本文中先考虑最简单的垂直拆分方式,垂直拆分+读写分离我们下篇文章进行讲解。
垂直拆分步骤
至于怎么整合Sharding-JDBC就不在讲解了,上篇文章有讲解过,直接开始和兴步骤。
假设我们拆分成了2个库,分别是ds0和ds1,每个库中的表不同,ds_0中放了user表,SQL脚本如下:
CREATE DATABASE
`ds_0`
CHARACTER SET
‘utf8‘
COLLATE
‘utf8_general_ci‘
;
CREATE TABLE
`user`
(
id bigint
(
64
)
not
null
,
city varchar
(
20
)
not
null
,
name varchar
(
20
)
not
null
,
PRIMARY KEY
(
`id`
)
)
ENGINE
=
InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARSET
=
utf8
;ds_1中放了loudong表,SQL脚本如下:
CREATE DATABASE
`ds_1`
CHARACTER SET
‘utf8‘
COLLATE
‘utf8_general_ci‘
;
CREATE TABLE
`loudong`
(
`id`
varchar
(
20
)
NOT NULL
,
`city`
varchar
(
20
)
NOT NULL
,
`region`
varchar
(
20
)
NOT NULL
,
`name`
varchar
(
20
)
NOT NULL
,
`ld_num`
varchar
(
10
)
NOT NULL
,
`unit_num`
varchar
(
10
)
NOT NULL
,
PRIMARY KEY
(
`id`
)
)
ENGINE
=
InnoDB
DEFAULT CHARSET
=
utf8最核心的还是数据源的配置以及绑定:
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
names
=
ds0
,
ds1
# ds0数据源
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
type
=
com
.
alibaba
.
druid
.
pool
.
DruidDataSource
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
driver
-
class
-
name
=
com
.
mysql
.
jdbc
.
Driver
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
url
=
jdbc
:
mysql
:
//localhost:3306/ds_0?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
username
=
root
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
password
=
123456
# ds1数据源
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
type
=
com
.
alibaba
.
druid
.
pool
.
DruidDataSource
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
driver
-
class
-
name
=
com
.
mysql
.
jdbc
.
Driver
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
url
=
jdbc
:
mysql
:
//localhost:3306/ds_1?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
username
=
root
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
password
=
123456
# 绑定loudong表所在节点
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
loudong
.
actual
-
data
-
nodes
=
ds1
.
loudong
# 绑定user表所在节点
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
user
.
actual
-
data
-
nodes
=
ds0
.
user
# 设置自增ID
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
user
.
key
-
generator
.
column
=
id
# 设置自增ID算法
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
user
.
key
-
generator
.
type
=
SNOWFLAKE配置完之后该怎么用还是怎么用,完全不用改变一行代码。sharding-jdbc底层会对数据源进行接管。
如果我们不用sharding-jdbc的话,你同样需要配置2个数据源,这个其实差不多,最复杂的就是你在操作数据库的时候需要知道当前的操作是哪个数据源,因为每个数据源中的表都不一样,通过sharding-jdbc框架屏蔽了这些复杂的操作。
垂直拆分下的读写分离步骤
从最开始的单库多表,到读写分离,再到垂直拆分多个库。
循序渐进的为大家讲解高并发,大数据量下的数据库解决方案。并引入开源的Sharding-JDBC来实现具体的方案。
垂直拆分后进一步提升性能的方式就是垂直拆分多库的读写分离,如下图:
要实习这个功能,我们只需要在上面的基础上,为每个库增加一个从节点的配置就可以了,然后用master-slave-rules将主从数据源进行绑定,如下:
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
names
=
ds0
,
ds0slave
,
ds1
,
ds1slave
# ds0主数据源
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
type
=
com
.
alibaba
.
druid
.
pool
.
DruidDataSource
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
driver
-
class
-
name
=
com
.
mysql
.
jdbc
.
Driver
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
url
=
jdbc
:
mysql
:
//localhost:3306/ds_0?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
username
=
root
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0
.
password
=
123456
# ds0从数据源
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0slave
.
type
=
com
.
alibaba
.
druid
.
pool
.
DruidDataSource
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0slave
.
driver
-
class
-
name
=
com
.
mysql
.
jdbc
.
Driver
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0slave
.
url
=
jdbc
:
mysql
:
//localhost:3306/ds0slave?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0slave
.
username
=
root
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds0slave
.
password
=
123456
# ds1主数据源
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
type
=
com
.
alibaba
.
druid
.
pool
.
DruidDataSource
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
driver
-
class
-
name
=
com
.
mysql
.
jdbc
.
Driver
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
url
=
jdbc
:
mysql
:
//localhost:3306/ds_1?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
username
=
root
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1
.
password
=
123456
# ds1从数据源
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1slave
.
type
=
com
.
alibaba
.
druid
.
pool
.
DruidDataSource
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1slave
.
driver
-
class
-
name
=
com
.
mysql
.
jdbc
.
Driver
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1slave
.
url
=
jdbc
:
mysql
:
//localhost:3306/ds1slave?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1slave
.
username
=
root
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
datasource
.
ds1slave
.
password
=
123456
# 绑定loudong表所在节点
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
loudong
.
actual
-
data
-
nodes
=
ds1
.
loudong
# 绑定user表所在节点
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
user
.
actual
-
data
-
nodes
=
ds0
.
user
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
user
.
key
-
generator
.
column
=
id
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
tables
.
user
.
key
-
generator
.
type
=
SNOWFLAKE
# 读写分离
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
master
-
slave
-
rules
.
ds0
.
master
-
data
-
source
-
name
=
ds0
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
master
-
slave
-
rules
.
ds0
.
slave
-
data
-
source
-
names
=
ds0slave
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
master
-
slave
-
rules
.
ds1
.
master
-
data
-
source
-
name
=
ds1
spring
.
shardingsphere
.
sharding
.
master
-
slave
-
rules
.
ds1
.
slave
-
data
-
source
-
names
=
ds1slave源码参考:https://github.com/yinjihuan/sharding-jdbc
觉得不错的记得关注下哦,给个Star吧!
加入星球特权
1、从前端到后端玩转Spring Cloud
2、实战分库分表中间件Sharding-JDBC
3、实战分布式任务调度框架Elastic Job
4、配置中心Apollo实战
5、高并发解决方案之缓存
6、更多课程等你来解锁,20+课程

尹吉欢
我不差钱啊
喜欢作者
原文:https://blog.51cto.com/14888386/2515770