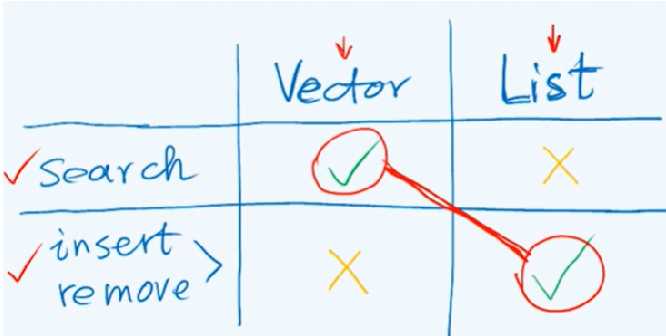
向量和列表都无法兼顾静态(如寻找)和动态(如插入)操作。而树形结构可以一定程度上结合二者的优点,可以认为树是列表的列表,是一种半线性结构。
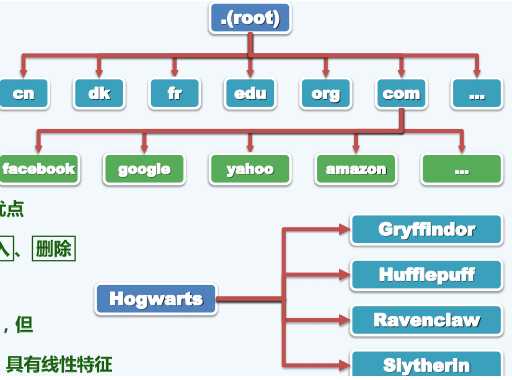
树结构的应用:层级结构表示,表达式、文件系统、URL。
什么是树结构?
树结构可以被看作是特殊的图结构 T = (V,E)。
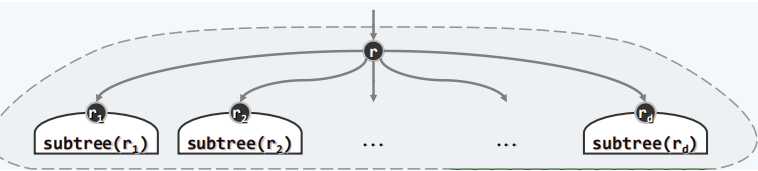
有根树:
相对于 T,Ti 称为以 ri 为根的子树,Ti = subtree(ri)。
d = degree(r) 为 r 的(出)度数,值为顶点 r 的孩子的数量。
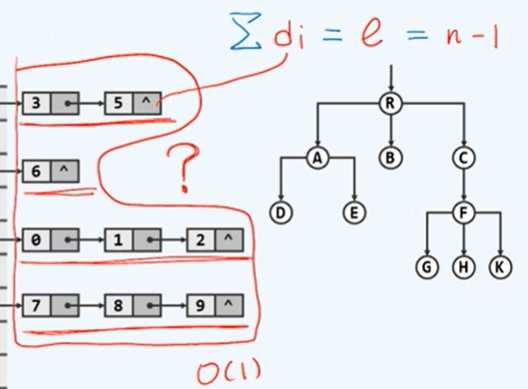
一棵树中所有顶点的度数和 ∑degree(ri) 等于树的总边数,也等于总顶点数减一,即
∑degree(ri) = e = n-1 。任何树中边数和顶点数是同阶的。
有序树:
若指定 Ti 为 T 的第 i 棵子树,ri 为 r 的第 i 个孩子,这种指定了兄弟之间明显次序的树 T 则称为有序树
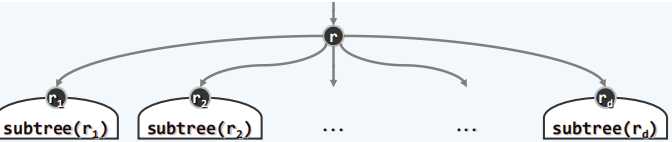
路径:
对于 V 中的 k+1 个节点,通过 E 中的 k 条边依次相连,这样就构成了一条路径
|path(v)| 。
路径的长度被定义为 边数 = k 。
环路:如果首节点 v0 和末节点 vk 为同一节点,则该路径被称为环路。
在图中,如果任意两个节点之间都路径相连,则称为连通图。
不含环路的图,称为无环图。
树实际上是一种 无环连通图,是极小连通图 和 极大无环图(满足连通条件下边数极小,满足无环条件下边数极大)
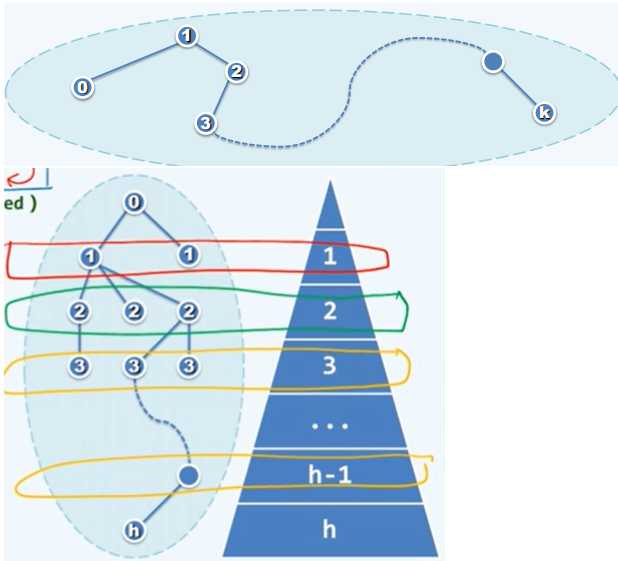
深度与层次
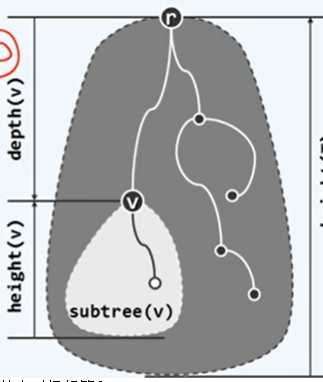
在树中,任意一个节点 v 与根之间只有唯一一条路径。
在不致歧义的情况下,路径、节点和以此节点为根的子树可相互指代。
节点的深度被定义为路径的长度:depth(v) = |path(v)| 。
path(v) 上的节点,都是 v 的祖先,v 是他们的后代。除自身外,是真 祖先/后代。
半线性:在任意深度,v 的祖先若存在则必然唯一;但 v 的后代若存在则未必唯一。
根节点是所节点的公共祖先,深度为 0 。
没后代的节点称为 叶节点/叶子。
所叶节点深度中的最大值,称为树的高度。子树的高度,就是根节点的高度。height(v) = height(subtree(v))。
任意节点 v 的深度与高度之和,不大于根节点的高度。
空树的高度取为 -1 。
树的表示
需提供的接口:

如何从逻辑上表示一个树
1) 父节点
除根外,任一节点有且仅有一个父节点。可以将节点组织为序列,各节点分别包括其本身的信息(data)和父节点的秩或位置(parent)。这样的组织形式,向上寻找父节点和根节点效率较高,但向下寻找子节点和兄弟节点效率较低。
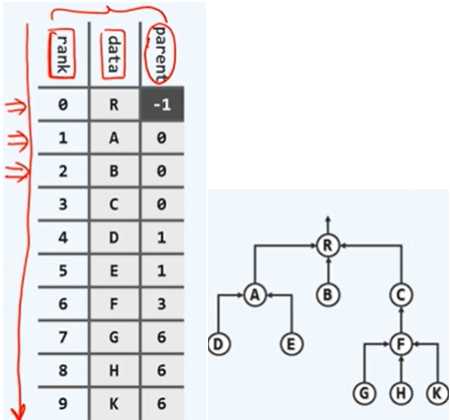
性能:

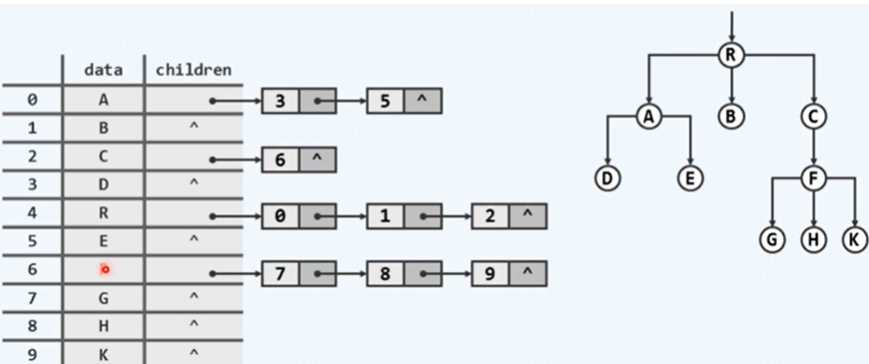
2)孩子节点
在序列中,添加孩子(children)引用,指向以此节点为父节点的孩子节点。同时,去除其指向父节点的秩或位置(parent)。这样的组织形式,向下寻找子节点和兄弟节点效率较高,但向上寻找父节点和根节点效率较低。
3)父节点+孩子节点
对于一个节点,同时包括其本身的信息(data)、父节点的秩或位置(parent)和指向其孩子的引用(children)。这样解决了向上和向下的效率不均衡的问题,但是由于每个节点的孩子数量(度数不同,导致在 children 中搜索的效率较低。
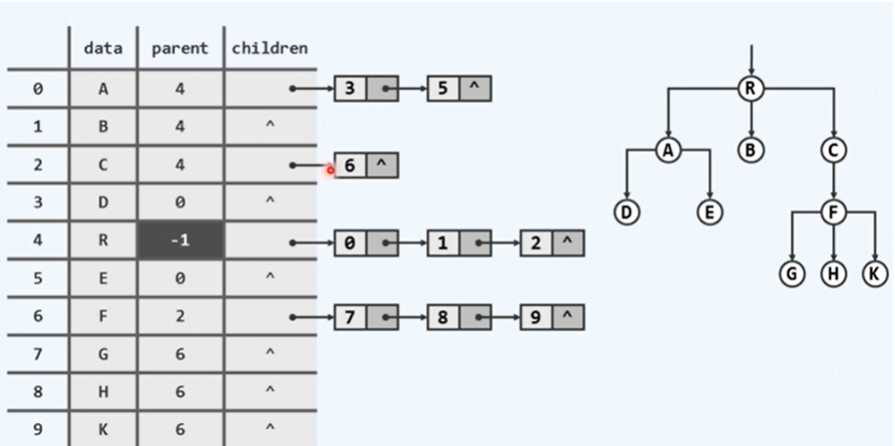
存在问题:由于父节点连着几个子节点,查询修改效率受到影响
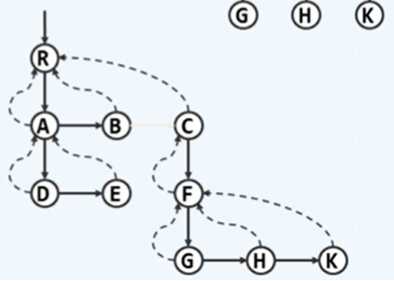
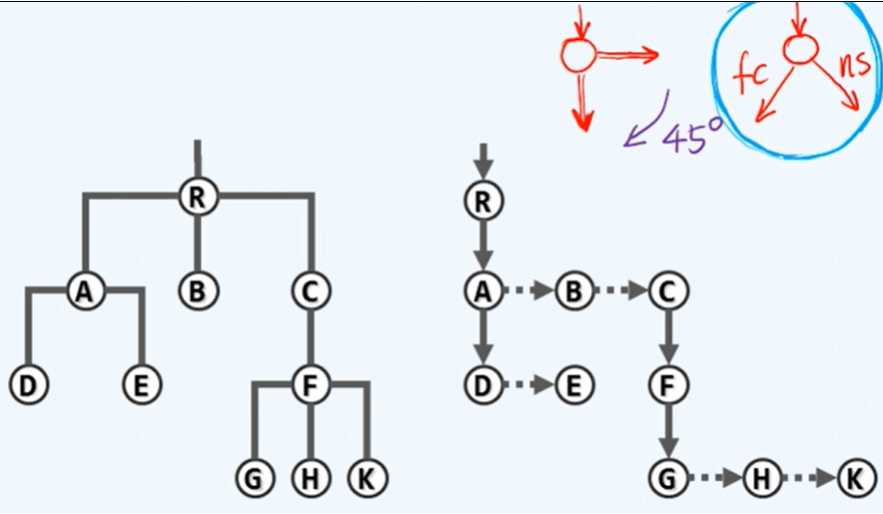
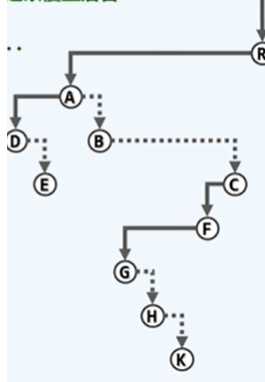
4)长子兄弟表示法
上半图为父子表示法,下半图为长子兄弟表示法。
纵向的:firstChild(),即找到以该节点为父节点的长子。
横向的:nextSibling(),即找到以该节点为最邻近的兄节点的下一个弟节点。
每个节点度数不超过2的树,称为二叉树。
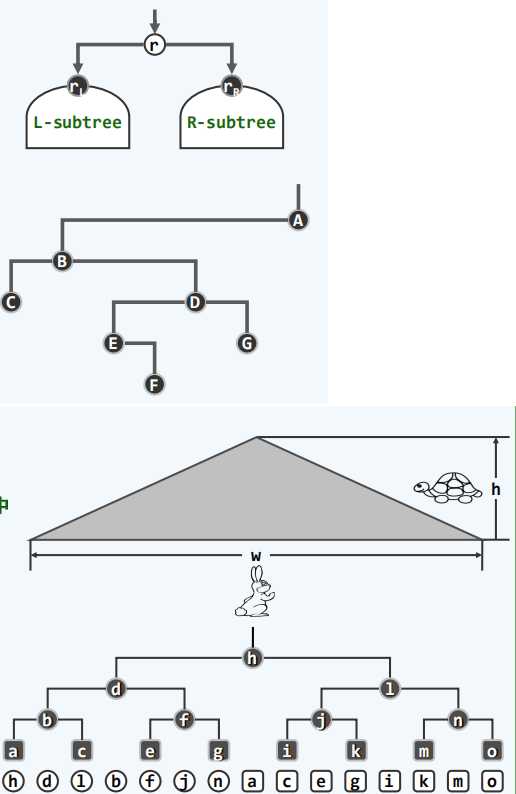
一般二叉树:
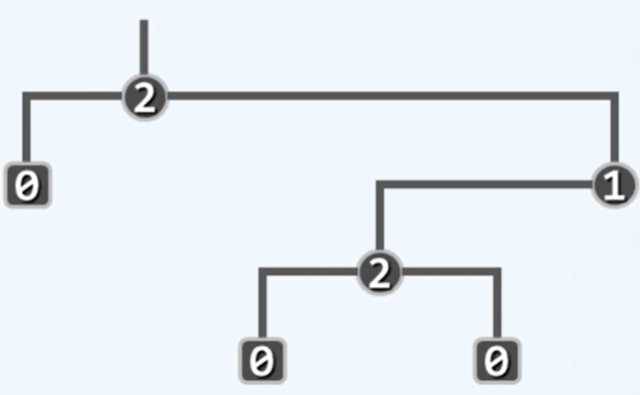
真二叉树:每个节点的度数都是偶数(2或0)。为原有的每个节点添加足够多的孩子节点(原度数为1则添加一个孩子,原度数为0则添加两个孩子)。
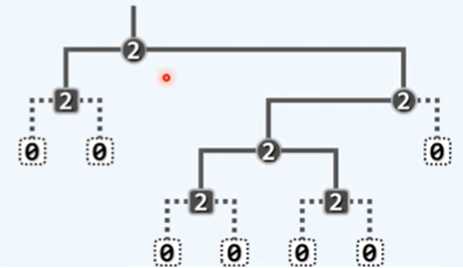
通过二叉树描述多叉树:
对于根且序的多叉树,都可以表示为二叉树。原理可以由长子兄弟表示法解释,即将长子和兄弟两条路径看作二叉树的左右子树。
BinNode类
#pragma once
#define BinNodePosi(T) BinNode<T>* //节点位置
#define stature(p) ((p) ? (p)->height: -1) //节点高度
//BinNode状态与性质的判断
#define IsRoot(x) (!((x).parent))
#define IsLeaf(x) (!((x).lc || (x).rc))
#define IsLChild(x) (!((x).parent) && (&(x) == (x).parent->lc))
#define IsRChild(x) (!((x).parent) && (&(x) == (x).parent->rc))
#define HasParent(x) ((x).parent)
#define HasLChild(x) ((x).lc)
#define HasRChild(x) ((x).rc)
#define HasChild(x) (HasLChild(x) || HasRChild(x)) //至少拥有一个孩子
#define HasBothChild(x) (HasLChild(x) && HasRChild(x)) //同时拥有两个孩子
#define sibling(p) (IsLChild(*(p)) ? (x).parent.rc: (x).parent.lc) //兄弟
#define uncle(p) (sibling((p).parent)) //叔叔
#define FromParentTo(x) ( IsRoot(x) ? _root : ( IsLChild(x) ? (x).parent->lc : (x).parent->rc ) ) //来自父亲的引用
typedef enum { RB_RED, RB_BLACK } RBColor; //节点颜色
template <typename T> struct BinNode{
BinNodePosi(T) parent;
BinNodePosi(T) lc;
BinNodePosi(T) rc; //父亲、孩子
int npl;
RBColor color;
T data; int height; //高度、子树规模
//构造函数
BinNode():
parent( nullptr ), lc( nullptr ),rc( nullptr ),height ( 0 ),npl( 1 ),color ( RB_RED ) {}
BinNode( T e, BinNodePosi(T) p = nullptr, BinNodePosi(T) lc = nullptr, BinNodePosi(T) rc = nullptr, int h = 0, int l = 1, RBColor c = RB_RED):
data( e ), parent( p ), lc( lc ), rc( rc ),height ( h ),npl( 1 ),color ( c ) {}
//操作接口
int size();
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsLC( T const & ); //作为左孩子插入新节点
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRC( T const & ); //作为右孩子插入新节点
BinNodePosi(T) succ(); //(中序遍历意义下)当前节点的直接后继
template <typename VST> void travLevel(VST &); //子树层次遍历
template <typename VST> void travPre(VST &); //子树先序遍历
template <typename VST> void travIn(VST &); //子树中序遍历
template <typename VST> void travPost(VST &); //子树后序遍历
};
//作为左孩子插入
template <typename T> BinNodePosi(T) BinNode<T>::insertAsLC(T const &e)
{return lc = new BinNode( e, this);}
//作为右孩子插入
template <typename T> BinNodePosi(T) BinNode<T>::insertAsRC(T const &e)
{return rc = new BinNode( e, this);}
//size()
template <typename T> int BinNode<T>::size(){//后代总数,以其为根的子树的规模
int s = 1; //计入本身
if (lc) s += lc->size(); //递归计入左子树规模
if (rc) s += rc->size(); //递归计入右子树规模
return s;
}//O(n=|size|)
Bintree类
#include "binnode.h"
#include "release.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include "../dsa_queue_20200717/queue.h"
#define max(a,b) ( a > b ? a : b)
template <typename T> class BinTree{
protected:
int _size;//规模
virtual int updateHeight( BinNodePosi(T) x); //更新节点x的高度
void updateHeightAbove( BinNodePosi(T) x); //更新x及祖先的高度
public:
BinNodePosi(T) _root; //根节点
//构造函数
BinTree():_size( 0 ), _root ( nullptr ) {}
//~BinTree(){ if ( 0 < _size ) remove( _root );}
//函数接口
int size() const { return _size; } //规模
bool empty() const { return !_root;} //判空
BinNodePosi(T) root() const {return _root; } //树根
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRoot(T const& e); //作为根节点插入
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x, T const& e);//作为左孩子节点接入
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x, T const& e);//作为右孩子节点接入
BinNodePosi(T) attachAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x, BinTree<T>* &S);//作为左子树接入
BinNodePosi(T) attachAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x, BinTree<T>* &S);//作为右子树接入
int remove(BinNodePosi(T) x);//删除以节点x为根的子树
template <typename VST> void travPre(BinNodePosi(T) x, VST& visit) { if (_root) _root->travPre(visit); }//先序遍历
template <typename VST> void travPost(const VST& visit) { if (_root) _root->travPost(visit); }//后序遍历
template <typename VST> void travLevel(const VST& visit) { if (_root) _root->travLevel(visit); }//层次遍历
template <typename VST> void travIn( const VST& visit) { if (_root) _root->travIn(visit); }//中序遍历
void traverse (BinNodePosi(T) x, void (*)(T&) );
};
template <typename T> void BinTree<T>::traverse ( BinNodePosi(T) x, void (*visit )( T& ))
{
if( !x ) return;
visit( x->data );
traverse( x->lc, visit );
traverse( x->rc, visit );
}
//先序遍历
template <typename T, typename VST> void travPre(BinNodePosi(T) x, VST& visit) {
if( !x ) return;
//BinNodePosi(T) x = root();
visit( x->data );
travPre( x->lc, visit );
travPre( x->rc, visit );
}
//后序遍历
template <typename T, typename VST> void travPost(BinNodePosi(T) x, VST& visit) {
if( !x ) return;
travPost( x->lc, visit );
travPost( x->rc, visit );
visit( x->data );
}
//中序遍历
template <typename T, typename VST> void travIn(BinNodePosi(T) x, VST& visit) {
if( !x ) return;
travIn( x->lc, visit );
visit( x->data );
travIn( x->rc, visit );
}
//层次遍历
template <typename T> template <typename VST> void BinNode<T>::travLevel ( VST& visit){
Queue<BinNodePosi(T)> Q;
Q.enqueue( this );
while( !Q.empty()){
BinNodePosi(T) x = Q.dequeue();visit( x->data);
if( HasLChild(*x )) Q.enqueue( x->lc);
if( HasRChild(*x )) Q.enqueue( x->rc);
}
}
//更新节点x的高度
template <typename T>
int BinTree<T>::updateHeight(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
return x->height = 1 + max(stature(x->lc), stature(x->rc));
}
//更新树的高度
template <typename T>
void BinTree<T>::updateHeightAbove(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
while (x) { updateHeight(x); x = x->parent; }
}
//空树插入根节点
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BinTree<T>::insertAsRoot(T const& e)
{
_size = 1; return _root = new BinNode<T> (e);
}
//作为节点x的左孩子插入
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BinTree<T>::insertAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x,T const& e)
{
_size++; x->insertAsLC(e); updateHeightAbove(x); return x->lc;
}
//作为节点x的右孩子插入
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BinTree<T>::insertAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x,T const& e)
{
_size++; x->insertAsRC(e); updateHeightAbove(x); return x->rc;
}
//S作为节点x的左子树插入
//S本身被置空
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BinTree<T>::attachAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x, BinTree<T>* &S)
{
x->lc = S->_root;
x->lc->parent = x;
_size += S->_size;
updateHeightAbove(x);
S->_root =nullptr;
S->size = 0; dtl::release(S); S = nullptr; return x;
}
//S作为节点x的右子树插入
//S本身被置空
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BinTree<T>::attachAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x, BinTree<T>* &S)
{
x->rc = S->_root;
x->rc->parent = x;
_size += S->_size;
updateHeightAbove(x);
S->_root = nullptr;
S->size = 0; dtl::release(S); S = nullptr; return x;
}
template <typename T>//二叉树删除x节点及其后代
int BinTree<T>::remove(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
FromParentTo( *x ) = nullptr;
updateHeightAbove ( x->parent );
int n = removeAt( x ); _size -=n;
return n;
}
template <typename T>//删除x节点及其后代,返回删除节点数
static int removeAt(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
if (!x)return 0;//递归基
int n = 1 + removeAt(x->lc) + removeAt(x->rc);
dtl::release(x->data); dtl::release(x); return n;
}
测试
/*
* The program aims to test BinTree class
* author@Ripples
* 20200723
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "bintree.h"
#include "../dsa_vector_200622/dsa_vector.h"
using namespace std;
template<typename T> void returnValue(T& a)
{
cout << "return_value: " << a << endl;
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
//构造树
BinTree<char> bt_test;
bt_test.insertAsRoot(‘b‘);
bt_test.insertAsLC(bt_test.root(), ‘a‘);
bt_test.insertAsRC(bt_test.root(), ‘f‘);
bt_test.insertAsLC(bt_test.root()->rc, ‘d‘);
bt_test.insertAsRC(bt_test.root()->rc, ‘g‘);
bt_test.insertAsLC(bt_test.root()->rc->lc, ‘c‘);
bt_test.insertAsRC(bt_test.root()->rc->lc, ‘e‘);
/*
b
a f
d g
c e
*/
//前序遍历:b,a,f,d,c,e,g
//后序遍历:a,c,e,d,g,f,b
//中序遍历:a,b,c,d,e,f,g
void (* visit)(char& ) = &returnValue;
bt_test.traverse(bt_test.root(),visit);
//删除右子树之后遍历
cout << "modifed:" << endl;
bt_test.remove(bt_test.root()->rc);
bt_test.traverse(bt_test.root(),visit);//b,a
return 0;
}
Binnode
package com.atguigu.Dao;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-02 20:55
*/
public class BinNode<T> implements BinNodeImpl<T>{
//成员
public Boolean color;
// 颜色
public T data;
// 关键字(键值)
public BinNode<T> rc;
// 右孩子
public BinNode<T> lc;
// 左孩子
public BinNode<T> parent;
// 父亲
public int height;
public int npl;
//构造函数
public BinNode() {
}
public BinNode(T data, BinNode<T> parent) {
this.data = data;
this.parent = parent;
}
public BinNode(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public BinNode(Boolean color, T data, BinNode<T> rc, BinNode<T> lc, BinNode<T> parent, int height, int npl) {
this.color = color;
this.data = data;
this.rc = rc;
this.lc = lc;
this.parent = parent;
this.height = height;
this.npl = npl;
}
//操作方法的实现
@Override
public int size() {
int s = 1;
if (lc != null){
s += lc.size();
}
if (rc != null){
s += rc.size();
}
return s;
}
@Override
public BinNode insertAsLC(T e) {
return lc = new BinNode<>(e,this);
}
@Override
public BinNode insertAsRC(T e) {
return rc = new BinNode<>(e,this);
}
@Override
public BinNode succ() {
BinNode<T> s = this;
if (rc != null){
s = rc;
while (s.lc != null){
s = s.parent;
}
} else {
while (!(s.parent != null) && (s == s.parent.rc)){
s = s.parent;
}
}
return s;
}
public int stature(){
if (this == null){
return 0;
} else {
return this.height;
}
}
}
BinTree
package com.atguigu.Dao;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-02 20:49
*/
public class BinTree<T> implements BinTreeImpl<T>{
protected int _size;
public BinNode<T> _root;
// 根结点
//构造函数
public BinTree() {
_size = 0;
_root = null;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return _size;
}
@Override
public Boolean empty() {
return (_root != null);
}
//更新节点的高度
@Override
public int updateHeight(BinNode<T> x) {
int m1 = 0;
int m2 = 0;
if (x.lc != null){
m1 = x.lc.height;
}
if (x.rc != null){
m2 = x.rc.height;
}
return x.height = 1 + Math.max(m1,m2);
}
//更新树的高度
@Override
public void updateHeightAbove(BinNode<T> x) {
while (x != null){
updateHeight(x);
x = x.parent;
}
}
//空树插入根节点
@Override
public BinNode<T> insertAsRoot(T e) {
_size = 1;
return _root = new BinNode<T>(e);
}
//作为节点x的左孩子插入
@Override
public BinNode<T> insertAsLc(BinNode<T> x, T e) {
_size++;
x.insertAsLC(e);
updateHeightAbove(x);
return x.lc;
}
//作为节点x的右孩子插入
@Override
public BinNode<T> insertAsRc(BinNode<T> x, T e) {
_size++;
x.insertAsRC(e);
updateHeightAbove(x);
return x.rc;
}
@Override
public BinNode<T> attachAsLc(BinNode<T> x, BinTree<T> s) {
x.lc = s._root;
x.lc.parent = x;
_size += s._size;
updateHeightAbove(x);
s._root = null;
s._size = 0;
return x;
}
@Override
public BinNode<T> attachAsRc(BinNode<T> x, BinTree<T> s) {
x.rc = s._root;
x.rc.parent = x;
_size += s._size;
updateHeightAbove(x);
s._root = null;
s._size = 0;
return x;
}
@Override
public int remove(BinNode<T> x) {
/*IsRoot(x) ? _root : ( IsLChild(x) ? x.parent.lc : x.parent.rc )
BinNode<T> s = FromParentTo(x);
s = null;*/
if (IsRoot(x)){
_root = null;
} else {
if (IsLChild(x)){
x.parent.lc = null;
} else {
x.parent.rc = null;
}
}
updateHeightAbove(x.parent);
int n = removeAt(x);
_size -= n;
return n;
}
public int removeAt(BinNode<T> x){
if (x == null) return 0;
int n = 1 + removeAt(x.lc) + removeAt(x.rc);
x.lc = null;
x.rc = null;
return n;
}
//先序遍历
/*@Override
public void travPre(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
visit(x);
travPre(x.lc);
travPre(x.rc);
}*/
//改进1
/*@Override
public void travPre(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
if (x != null){
s.push(x);
}
while (!s.empty()){
x = s.pop();
visit(x);
if (HasRChild(x)){
s.push(x.rc);
}
if (HasLChild(x)){
s.push(x.lc);
}
}
}*/
//改进2
@Override
public void travPre(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
while (true){
visitAlongLeftBranch(x,s);
if (s.empty()) break;
x = s.pop();
}
}
public void visitAlongLeftBranch(BinNode<T> x, Stack<BinNode<T>> s){
while (x != null){
visit(x);
s.push(x.rc);
x = x.lc;
}
}
//后序遍历
/*@Override
public void travPost(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
travPost(x.lc);
travPost(x.rc);
visit(x);
}*/
//改进
@Override
public void travPost(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
if (x != null){
s.push(x);
}
while (!s.empty()){
if (s.peek() != x.parent){
gotoHLVFL(s);
}
x = s.pop();
visit(x);
}
}
public void gotoHLVFL(Stack<BinNode<T>> s){
BinNode<T> x = new BinNode<>();
x = s.peek();
while (x != null ){
if (HasLChild(x)){
if (HasRChild(x)){
s.push(x.rc);
}
s.push(x.lc);
} else {
s.push(x.rc);
}
x = s.peek();
}
s.pop();
}
//中序遍历
/*@Override
public void travIn(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
travIn(x.lc);
visit(x);
travIn(x.rc);
}*/
//改进1
@Override
public void travIn(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
while (true){
goAlongLeftBranch(x,s);
if (s.empty()) break;
x = s.pop();
visit(x);
x = x.rc;
}
}
public void goAlongLeftBranch(BinNode<T> x, Stack<BinNode<T>> s){
while (x != null){
s.push(x);
x = x.lc;
}
}
//层次遍历
@Override
public void travLevel() {
Queue<BinNode<T>> Q = new LinkedList<BinNode<T>>();
Q.add(this._root);
while ((Q.peek() != null)){
BinNode<T> x = Q.poll();
visit(x);
if (x.lc != null){
Q.offer(x.lc);
}
if (x.rc != null){
Q.offer(x.rc);
}
}
}
//感觉和先序遍历没什么区别
@Override
public void traverse(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
visit(x);
traverse(x.lc);
traverse(x.rc);
}
//一个二叉树中的处理函数以及判断的函数
void visit(BinNode<T> x){
System.out.print(x.data);
}
Boolean IsRoot(BinNode<T> x) {
return x.parent == null;
}
Boolean IsLeaf(BinNode<T> x) {
return !(x.lc != null || x.rc != null);
}
Boolean IsLChild(BinNode<T> x){
return ((x.parent != null) && (x == x.parent.lc));
}
Boolean IsRChild(BinNode<T> x){
return ((x.parent != null) && (x == x.parent.rc));
}
Boolean HasParent(BinNode<T> x){
return (x.parent != null);
}
Boolean HasLChild(BinNode<T> x){
return (x.lc != null);
}
Boolean HasRChild(BinNode<T> x){
return (x.lc != null);
}
Boolean HasChild(BinNode<T> x) {
return (HasLChild(x) || HasRChild(x) );
}
//至少拥有一个孩子
Boolean HasBothChild(BinNode<T> x) {
return (HasLChild(x) && HasRChild(x) );
}
//同时拥有两个孩子
BinNode<T> FromParentTo(BinNode<T> x){
return ( IsRoot(x) ? _root : ( IsLChild(x) ? x.parent.lc : x.parent.rc ) );
}
//来自父亲的引用
}
测试
package com.atguigu.Test;
import com.atguigu.Dao.BinTree;
/**
* @anthor shkstart
* @create 2020-08-04 10:56
*/
public class bintreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinTree<Character> bt_test = new BinTree<>();
bt_test.insertAsRoot(‘b‘);
bt_test.insertAsLc(bt_test._root,‘a‘);
bt_test.insertAsRc(bt_test._root,‘f‘);
bt_test.insertAsLc(bt_test._root.rc,‘d‘);
bt_test.insertAsRc(bt_test._root.rc,‘g‘);
bt_test.insertAsLc(bt_test._root.rc.lc,‘c‘);
bt_test.insertAsRc(bt_test._root.rc.lc,‘e‘);
//遍历
bt_test.travPre(bt_test._root);
System.out.println();
bt_test.travIn(bt_test._root);
System.out.println();
bt_test.travPost(bt_test._root);
System.out.println();
bt_test.travLevel();
System.out.println();
//删除 右子树后遍历
bt_test.remove(bt_test._root.rc);
bt_test.traverse(bt_test._root);
}
}
//先序遍历
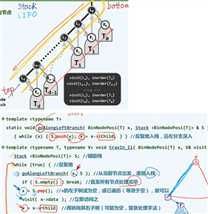
@Override
public void travPre(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
visit(x);
travPre(x.lc);
travPre(x.rc);
}
//改进1
@Override
public void travPre(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
if (x != null){
s.push(x);
}
while (!s.empty()){
x = s.pop();
visit(x);
if (HasRChild(x)){
s.push(x.rc);
}
if (HasLChild(x)){
s.push(x.lc);
}
}
}

//改进2
@Override
public void travPre(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
while (true){
visitAlongLeftBranch(x,s);
if (s.empty()) break;
x = s.pop();
}
}
public void visitAlongLeftBranch(BinNode<T> x, Stack<BinNode<T>> s){
while (x != null){
visit(x);
s.push(x.rc);
x = x.lc;
}
}
//后序遍历
@Override
public void travPost(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
travPost(x.lc);
travPost(x.rc);
visit(x);
}
//改进
@Override
public void travPost(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
if (x != null){
s.push(x);
}
while (!s.empty()){
if (s.peek() != x.parent){
gotoHLVFL(s);
}
x = s.pop();
visit(x);
}
}
public void gotoHLVFL(Stack<BinNode<T>> s){
BinNode<T> x = new BinNode<>();
x = s.peek();
while (x != null ){
if (HasLChild(x)){
if (HasRChild(x)){
s.push(x.rc);
}
s.push(x.lc);
} else {
s.push(x.rc);
}
x = s.peek();
}
s.pop();
}
//中序遍历
@Override
public void travIn(BinNode<T> x) {
if (x == null) return;
travIn(x.lc);
visit(x);
travIn(x.rc);
}
//改进1
@Override
public void travIn(BinNode<T> x) {
Stack<BinNode<T>> s = new Stack<>();
while (true){
goAlongLeftBranch(x,s);
if (s.empty()) break;
x = s.pop();
visit(x);
x = x.rc;
}
}
public void goAlongLeftBranch(BinNode<T> x, Stack<BinNode<T>> s){
while (x != null){
s.push(x);
x = x.lc;
}
}
@Override
public void travLevel() {
Queue<BinNode<T>> Q = new LinkedList<BinNode<T>>();
Q.add(this._root);
while ((Q.peek() != null)){
BinNode<T> x = Q.poll();
visit(x);
if (x.lc != null){
Q.offer(x.lc);
}
if (x.rc != null){
Q.offer(x.rc);
}
}
}
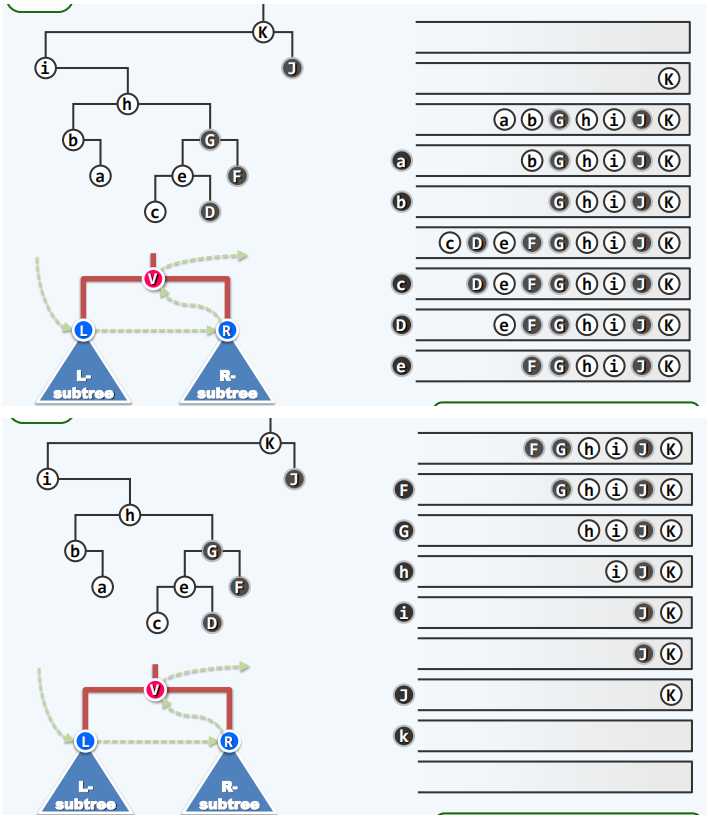
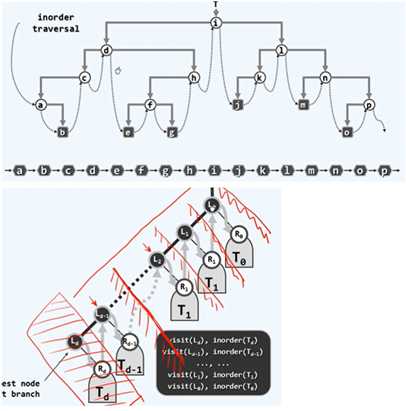
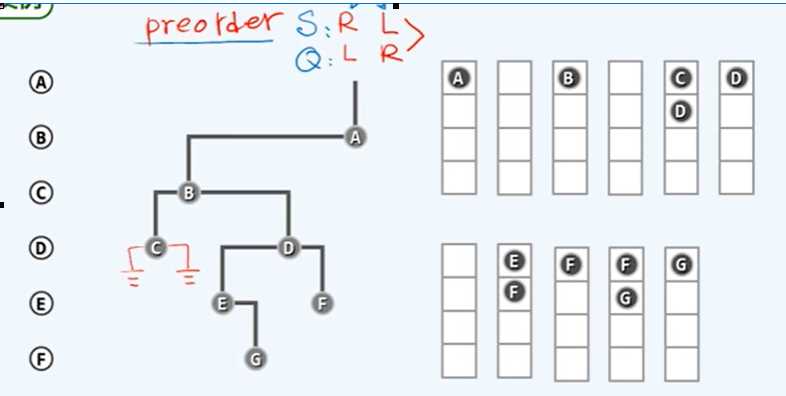
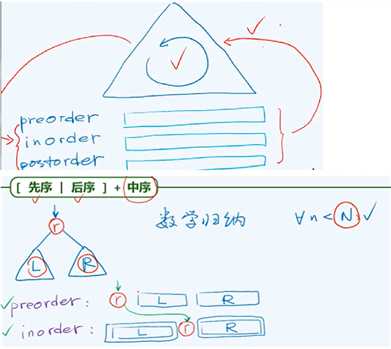
对于一棵二叉树,首先要知道其中序遍历结果,然后知道其先序或后序遍历结果其中之一,即可还原二叉树。以先序遍历和中序遍历的结果为例:可以根据根节点的位置特点,确定根节点。再用根节点(r)划分左右子树的遍历序列(L和R)。
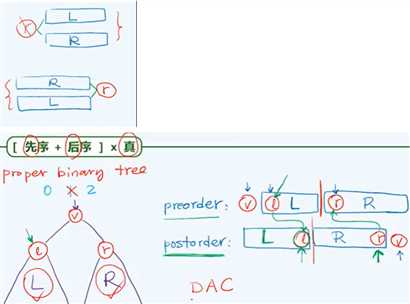
在某种情况下,先序遍历和后序遍历的结果,也可以重构二叉树。

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Node{
char letter;
int power;
Node left_son;
Node right_son;
public Node() { super();}
public Node(int power) {
this.power = power;
}
}
public class CurrDesign {
static Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<Character, String>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
List <Node>list = codingTable();//输入
Node tree_root = creatHFMtree(list);
creatTable(tree_root,"");
display();
String text = inputText();
encode(text);
String code = inputCode();
decode(code,tree_root);
}
public static String[] encode(String text) {
String []s = new String[100];
char []key = text.toCharArray();
System.out.println("编码结果为:");
for(int i=0;i<key.length;i++) {
s[i]=map.get(key[i]);
System.out.print(s[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
return s;
}
public static void decode(String s,Node tree_root) {
System.out.println("译码结果为:");
char []num = s.toCharArray();
Node node = tree_root;
for(int i=0;i<num.length;i++) {
node = check(node,num[i]);
if(node==null) {
node = check(tree_root,num[i]);
}
}
System.out.println(node.letter);
}
public static Node check(Node node,char c) {
if(node.left_son!=null && c==‘0‘)
return node.left_son;
else if(node.right_son!=null && c==‘1‘){
return node.right_son;
}
System.out.print(node.letter);
return null;
}
public static Object getKey(Object value){
for(Object key: map.keySet()){
if(map.get(key).equals(value)){
return key;
}
}
return null;
}
public static String inputText() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要编码的文本,只含大写字母:");
String text = in.next();
return text;
}
public static String inputCode() {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入编码:");
String code = in.next();
in.close();
return code;
}
public static List<Node> codingTable(){
List <Node>list = new ArrayList<Node>();
int []num = {186,64,13,22,32,103,21,15,47,57,1,2,32,20,57,63,15,1,48,51,80,23,8,18,1,16};
Node node = null;
for(int n=0;n<26;n++) {
node = new Node();
node.letter = (char)(‘A‘+n);
node.power = num[n];
list.add(node);
}
return list;
}
public static void display() {
System.out.println("The huffman coding table are:");
System.out.println(map.toString());
}
public static Node creatHFMtree(List<Node> list){
Node p = null;
int n = 0;
while(!list.isEmpty()) {
if(n!=0) {
list.add(p);
}
Node min1 = new Node(1000);
Node min2 = new Node(999);
for(Node node:list) {
if(node.power < min1.power) {
if(node.power < min2.power) {
min1 = min2;
min2 = node;
}else {
min1 = node;
}
}
}
p = new Node(min1.power+min2.power);
p.left_son = min2;
p.right_son = min1;
list.remove(min1);
list.remove(min2);
n++;
}
return p;
}
public static void creatTable(Node node,String coding){
if(node.left_son!=null) {
creatTable(node.left_son,coding+"0");
}
if(node.right_son!=null) {
creatTable(node.right_son,coding+"1");
}
if(node.left_son==null && node.right_son==null) {
map.put(node.letter, coding);
}
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/suit000001/p/13436362.html