继上一章 Netty之ByteBuf 之后,我们继续来谈 ByteBuf 的 API
因为 TCP 底层可能粘包,几百个整包消息被 TCP 粘包后作为一个整包发送。这样,通过 discardReadBytes 操作可以重用之前已经解码过的缓冲区,从而防止接收缓冲区因为容量不足导致的扩张。
需要指出的是,调用 discardReadBytes 会发生字节数组的内存复制,所以频繁调用将会导致性能下降,因此在调用它之前要确认你确实需要这样做,例如牺牲性能来换取更多的可用内存。
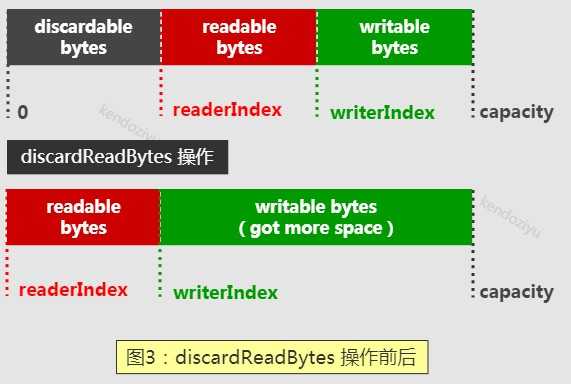
如图所示,capacity 保持不变,reaerIndex = 0,writerIndex -= readerIndex,红色部分的数据发生拷贝。
clear 操作主要用来操作位置指针,并不会清空缓冲区内容本身。
mark 操作针对之前的操作进行回滚
查找操作的返回值特点:找到了符合条件的,返回索引,否则返回-1
查找操作的参数特点 :可以指定起始坐标和查找长度,但是起始坐标+查找长度不能超过可读字节数。
indexOf(fromIndex:int, toIndex:int, value:byte) // 起始索引 fromIndex,终点 toIndex
bytesBefore(value:byte) // 起始索引 readerIndex,终点 writerIndex
bytesBefore(length:int, value:byte) // 起始索引 readerIndex,终点 readerIndex+length <= writerIndex
bytesBefore(index:int, length:int, value:byte) // 起始索引 index,终点 index+length <= writerIndex
forEachByte(processor:ByteBufProcessor) // 起始索引 readerIndex,终点 writerIndex
forEachByte(index:int, length:int, processor:ByteBufProcessor) // 起始索引 index,终点 index+length
forEachByteDesc(processor:ByteBufProcessor) // 起始索引 writerIndex-1,直到 readerIndex
forEachByteDesc(index:int, length:int, processor:ByteBufProcessor) // 起始索引 index,直到 index+length
ByteBufProcessor
FIND_NOT_ 为前缀类似于数据库的视图,ByteBuf 提供了多个接口用于创建某个 ByteBuf 的视图或者复制 ByteBuf,具体方法如下:
duplicate():ByteBuf
copy():ByteBuf
copy(int index, int length):ByteBuf
创建缓冲区可读字节的切片
slice():ByteBuf // 起始位置从 readerIndex 到 writerIndex
slice(int index, int length) // 起始位置从 index 到 index + length
nioBuffer():ByteBuffer
nioBuffer(int index, int length):ByteBuffer
两者共享同一个缓冲区内容引用。对 ByteBuffer 的读写操作不会改变 ByteBuf 的读写索引。
需要注意的是,返回后的 ByteBuffer 无法感知原 ByteBuf 的动态拓展操作。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/kendoziyu/p/io-netty-buffer_2.html