a)创建数据库
create database my_db ; 可跟charactor set 编码格式
b)删除数据库
drop database my_db;
数据库的数据类型可以分为三大类:数字、字符串、日期和时间。
1.数字有整型和浮点数
如果类型前加unsigned修饰,代表的是无符号数,最大取值翻倍。m指的是查询结果集中显示的宽度
| 数据类型 | 取值 |
| tinyint(m) | 1个字节 范围(-128~127) |
| smallint(m) | 2个字节 范围(-32768~32767) |
| mediumint(m) | 3个字节 范围(-8388608~8388607) |
| int(m) | 4个字节 范围(-2147483648~2147483647) |
| bigint(m) | 8个字节 范围(+-9.22*10的18次方) |
m总个数,d指的是精度,如果整数位+精度d大于m,总个数以实际为准。定点数decimal(m,d)(m<65,d<30)在数据库中存放的是近似值,而定点类型存放的是精确值。
| MySQL数据类型 | 含义 |
| float(m,d) | 单精度浮点型 8位精度(4字节) m总个数,d小数位 |
| double(m,d) | 双精度浮点型 16位精度(8字节) m总个数,d小数位 |
2.字符串
n指的是字符串长度,如果字符串长度小于n,则在后面补上空格,如果字符串长度>n,会报错。text类型不能有默认值。字符串还包括了二进制数据。
| MySQL数据类型 | 含义 |
| char(n) | 固定长度,最多255个字符 |
| varchar(n) | 固定长度,最多65535个字符 |
| tinytext | 可变长度,最多255个字符 |
| text | 可变长度,最多65535个字符 |
| mediumtext | 可变长度,最多2的24次方-1个字符 |
| longtext | 可变长度,最多2的32次方-1个字符 |
3.日期和时间
如果定义一个字段为timestamp,这个字段里的时间数据会随其他字段修改的时候自动刷新。
| MySQL数据类型 | 含义 |
| date | 日期 ‘2008-12-2‘ |
| time | 时间 ‘12:25:36‘ |
| datetime | 日期时间 ‘2008-12-2 22:06:44‘ |
| timestamp | 自动存储记录修改时间 |
create table stu(id int unsigned auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(10),
sex int);
a)增加列
alter table stu add address text null after sex;
在列sex后面增加列 address
b)修改列
alter table stu change sex sex0 varchar(4);
修改列sex为新列名 sex0,数据类型 varchar(4)
c)删除列
alter table stu drop address;
d)修改表名
alter table stu rename students;
1)插入数据
insert into stu values(1,"张三",20);
insert into stu(name,sex) values("王五",30);
2)更新数据
update students set name="cc" where id=1; # 更新id=1的name列,新值="cc"
3)删除数据
delete from students where id=1; # 删除id=1的列
4)查询数据
select * from students; * 表示所有列 ,查询students的所有行和列
eg. extract(year from now()) 2020
常用unit: 年 YEAR 月 month 日 day
时 HOUR 分 MINUTE 秒 SECOND
查询select和更新 update、删除delete数据时,都可以设置条件。以我这里的表student和sc为例演示条件查询。
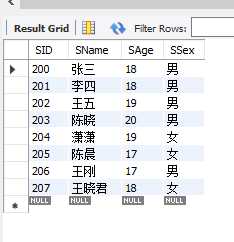
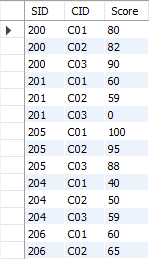
1.where 按照一定条件查询、更新、删除数据
eg. select 列名1,... from table where 列名 运算符 值
2.运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| = | 等于 |
| <> | 不等于 |
| > | 大于 |
| < | 小于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
| and | 与 |
| or | 或 |
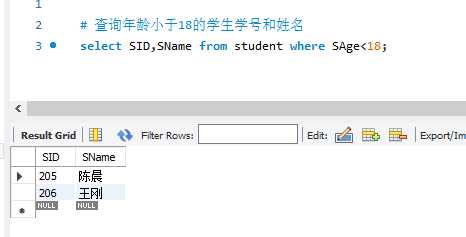
eg.查询student中年龄小于18的学生姓名和学号
3.between 列的取值在A和B之间
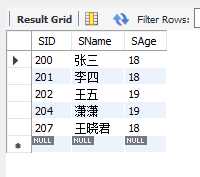
eg.查询年龄大于18,小于19的学生姓名和学号
select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge between 18 and 19;
4.like 模糊查询
% 表示一个或者多个字符
_表示一个字符
select SID,SName from student where SName like "王%";eg.查询姓王的学生姓名和学号
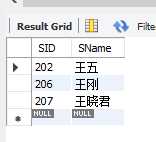
5.in 取值为集合中的某个值
eg.查询年龄为18、17、或者19的学生姓名和年龄
select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge in (18,17,19);
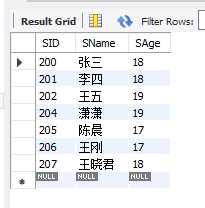
6.not 表示否定
eg.查询年龄不是18或者17的学生姓名、年龄
select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge not in (18,17);
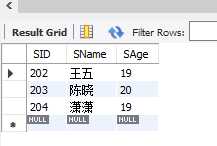
7.order by 将查询到的结果集排序,可以指定一列或者多列,默认升序ASC,降序可以用desc
eg.查询学生所有的数据,按年龄的大小降序排序,年龄相同的按学号升序排序
select * from student order by SAge desc,SID;
8.limit 取查询结果的某几列
eg.将学生表按年龄的大小降序排序,年龄相同的按学号升序排序,取第2到5列
select * from student order by SAge desc,SID limit 1,5;
limit 后跟起始下标和列数
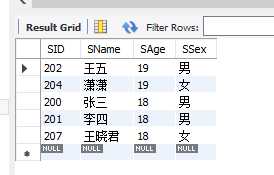
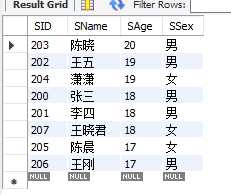
9.as 别名
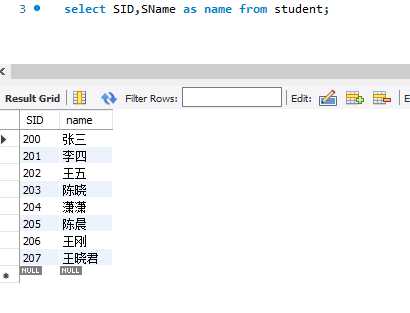
eg.查询学生学号和姓名,[姓名]这一列别名name输出
10.distinct 忽略重复的值
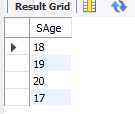
eg.查询学生年龄,排除重复的年龄
select distinct(SAge) from student;
11.group by 根据一个或者多个列,对结果集进行分组
12.count 根据某一列,计算结果集的总行数
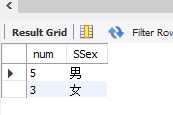
eg.查询女生人数、男生人数
select count(SID) as num,SSex from student group by SSex;
13.max/min 根据某一列,计算最大值/最小值,如果有多行值相同的,只会返回一行。
eg.查询年龄最大的学生学号、姓名、年龄
select SID,SName,max(SAge) from student;
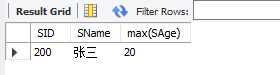
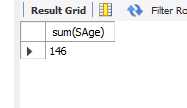
14.sum 根据某一列,计算所有行的总和
eg.计算所有学生的年龄总和
select sum(SAge) from student;
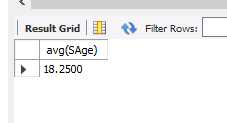
15.avg 根据某一列,计算结果行的平均值
eg.计算学生的平均年龄
select avg(SAge) from student;
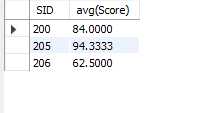
16.having 合计函数无法与where一起使用,用having替代where
eg.查询平均分数超过60的学生学号以及平均成绩
select SID,avg(Score) from sc group by SID having avg(Score)>60;
17.case
计算条件列表,并返回多个可能的结果表达式之一
1)简单表达式
CASE input_expression WHEN when_expression THEN result_expression [ ...n ] [ ELSE else_result_expression ] END
2)搜索表达式
CASE WHEN Boolean_expression THEN result_expression [ ...n ] [ ELSE else_result_expression ] END
查询学生信息,如果性别为男,显示1,如果性别为女,显示0,其他显示为其他
select SID,SName,CASE SSex when "男" then 0 when "女" then 1 else "其他" end as "性别" from student;
统计学生是否已经成年
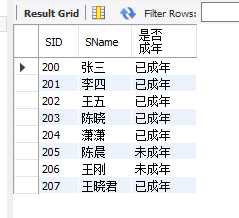
select SID,SName,CASE when Sage<18 then "未成年" else "已成年" end as "是否成年" from student;
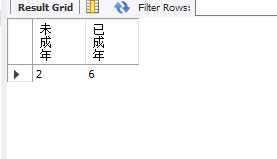
统计学生的成年人数,和未成年人数
select sum(CASE when Sage<18 then 1 else 0 end) as "未成年", sum(case when SAge>=18 then 1 else 0 end) as "已成年" from student;
连接两个结果集,列数和类型需要相同,union会消除重复的行,union all则连接所有行
查询年龄小于等于18岁和大于18岁的学生学号和姓名、年龄,并且合并两个结果集
select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge>=18 union select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge<=18;
查询年龄小于等于18岁和大于18岁的学生学号和姓名、年龄,并且合并两个结果集,保留重复的行。可以看到对比下查询结果看看。
select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge>=18 union all select SID,SName,SAge from student where SAge<=18;
根据列之间的关系,连接两个或者多个表,从这些表中查询数据,会删掉没有匹配的行。
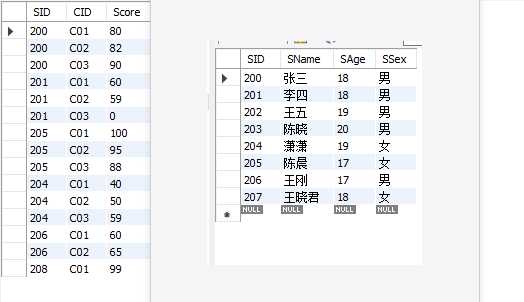
eg.查询每个学生参与考试的课程ID和成绩
select student.SID,student.SName,sc.CID,sc.score from student join sc on student.SID=sc.SID;
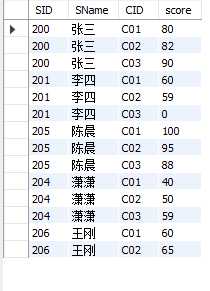
外连接分左外连接和右外连接,有些数据库还支持全外连接,mysql是不支持的。
同样是查询学生信息和学生成绩
select student.SID,student.SName,sc.CID,sc.score from student left join sc on student.SID=sc.SID; select student.SID,student.SName,sc.CID,sc.score from student right join sc on student.SID=sc.SID;
左边是左外链接的查询结果,右边是右外连接的查询结果。
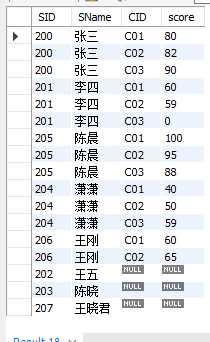
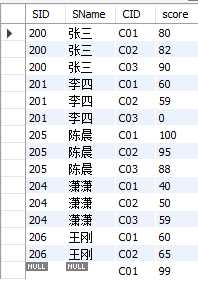
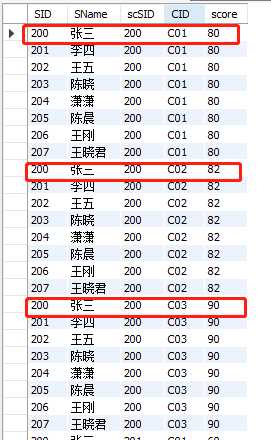
cross join,返回左表中的所有行,左表中的每一行与右表中的每一行组合。
select student.SID,student.SName,sc.SID,sc.CID,sc.score from student CROSS join sc;
查询结果比较长,只截图了一部分
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/Cc905/p/13178610.html