为什么需要MQ???
异步处理:
场景:
用户注册后,需要发注册邮件和注册短信,传统的做法有两种 1.串行的方式 2.并行的方式`
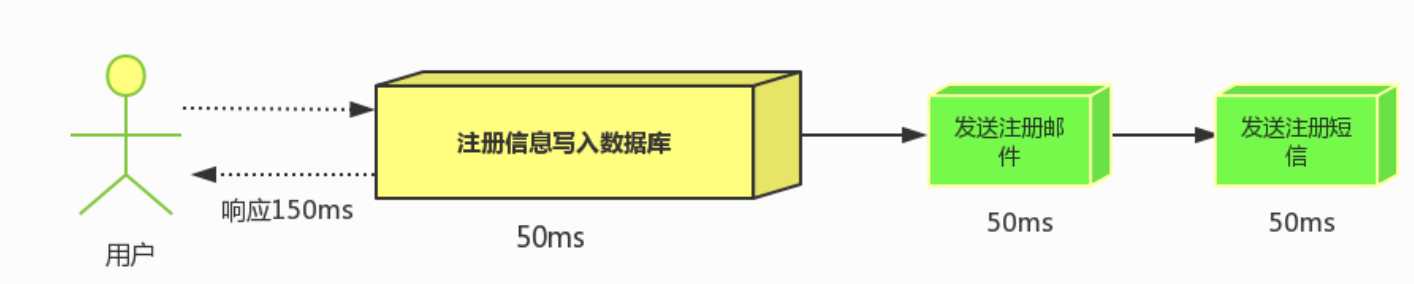
用户注册-发送注册邮箱-发送注册短信都完成之后才结束返回给客户端
邮件,短信并不是必须的,它只是一个通知,而这种做法让客户端等待没有必要等待的东西.
耗时150ms
并行:
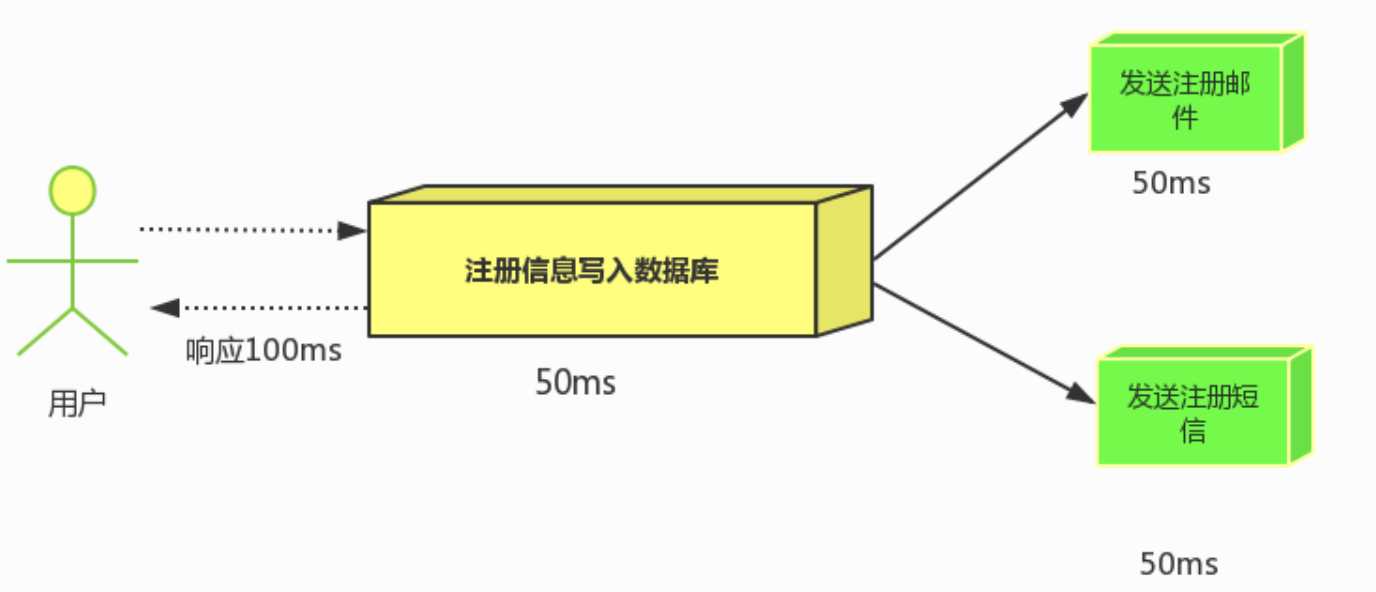
将注册信息写入数据库后,发送邮件的同时,发送短信,以上三个任务完成后,返回给客户端,并行的方式能提高处理的时间
耗时100ms
消息队列: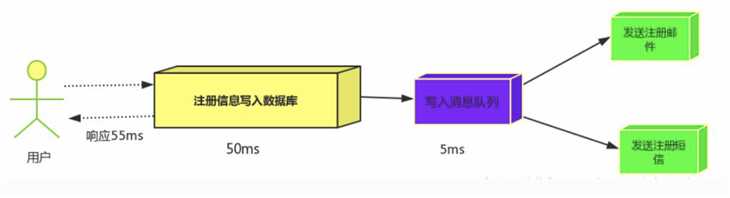
假设三个业务节点分别使用50ms,串行方式使用时间150ms,并行使用时间100ms。虽然并行已经提高的处理时间,但是,
前面说过,邮件和短信对我正常的使用网站没有任何影响,客户端没有必要等着其发送完成才显示注册成功,应该是写入
数据库后就返回.
`消息队列`: 引入消息队列后,把发送邮件,短信不是必须的业务逻辑异步处理
应用解耦:
场景:
双11是购物狂节,用户下单后,订单系统需要通知库存系统,传统的做法就是订单系统调用库存系统的接口
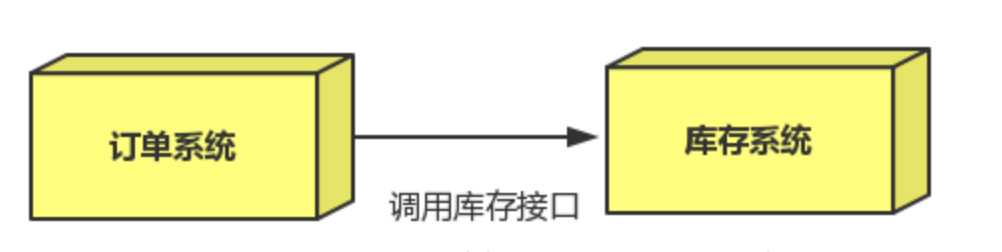
注意:当库存系统出现故障时,订单就会失败。订单系统和库存系统高耦合
引入消息队列
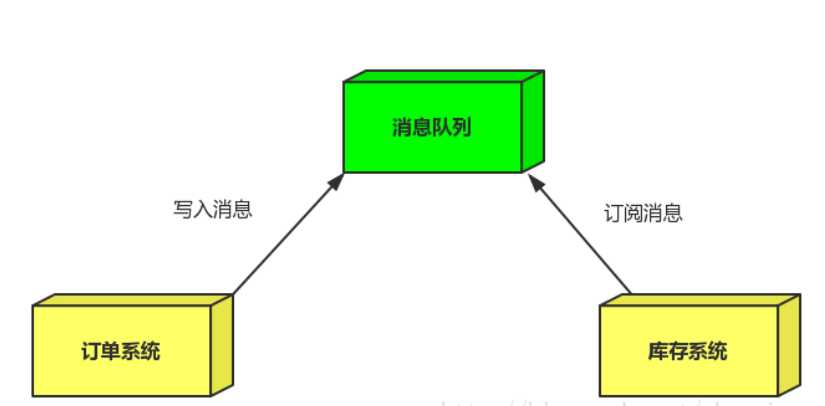
`订单系统:`用户下单后,订单系统完成持久化处理,将消息写入消息队列,返回用户订单下单成功。
库存系统:`订阅下单的消息,获取下单消息,进行库操作。 就算库存系统出现故障,消息队列也能保证消息的可靠投递,
不会导致消息丢失.
流量削峰:
场景:
秒杀活动,一般会因为流量过大,导致应用挂掉,为了解决这个问题,一般在应用前端加入消息队列。
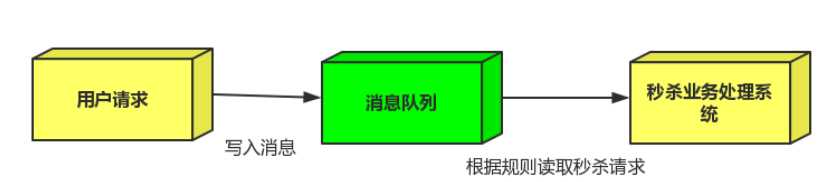
2.秒杀业务根据消息队列中的请求信息,再做后续处理.
起到的作用就是:
1.可以控制活动人数,超过此一定阀值的订单直接丢弃 2.可以缓解短时间的高流量压垮应用(应用程序按自己的最大处理能力获取订单)
springboot- 配置文件:
spring.application.name=springboot_rabbitmq spring.rabbitmq.host=localhost spring.rabbitmq.port=5672 spring.rabbitmq.username=quan spring.rabbitmq.password=admin spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=quan server.port=9898
RabbitMQ介绍
https://www.cnblogs.com/java-quan/p/13560266.html
第一种模型:直连
生产者:
@Autowired RabbitTemplate template; @Test void producer1() { template.convertAndSend("hello","hello-rabbit"); }
消费者:
@Component @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("hello")) public class Customer { @RabbitHandler public void remsg(String msg){ System.out.println("message== "+msg); } }
第二种模型:任务模型(
producer;
@Autowired RabbitTemplate template; @Test void producer2() { for (int i = 0;i<10;i++){ template.convertAndSend("work",i+"hello-rabbit"); System.out.println(i); }
customer:
@Component public class Customer2 { @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("work")) public void receive1(String msg){ System.out.println("work-msg1= " +msg); } @RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue("work")) public void receive2(String msg){ System.out.println("work-msg2= " +msg); } }
结果:
* work-msg1= 1hello-rabbit * work-msg2= 0hello-rabbit * work-msg1= 5hello-rabbit * work-msg2= 4hello-rabbit * work-msg1= 9hello-rabbit * work-msg2= 8hello-rabbit
默认在Spring AMQP实现中Work这种方式就是公平调度,如果需要实现能者多劳需要额外配置`
第三种模型--广播
producer:
@Autowired RabbitTemplate template; @Test void producer3() { template.convertAndSend("logs2","","广播广播"); }
customer:
@Component public class Customer3 { @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, exchange = @Exchange(name = "logs2",type = "fanout") ) ) public void receive1(String msg){ System.out.println("msg1= " +msg); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue,//c创造临时队列 exchange = @Exchange(name = "logs2",type = "fanout")//绑定交换机类型 ) ) public void receive2(String msg){ System.out.println("msg2= " +msg); } }
结果:
// msg2= 广播广播
// msg1= 广播广播
第四种模式:Routing-订阅模式中的-直连(direct)
producer:
@Autowired RabbitTemplate template; @Test void producer4() { template.convertAndSend("directs","error","广播广播"); template.convertAndSend("directs","info","广播广播"); template.convertAndSend("directs","debug","广播广播"); }
customer:
@Component public class Customer4 { @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, key = {"info","error","debug"}, exchange = @Exchange(name = "directs",type = "direct") ) ) public void receive1(String msg){ System.out.println("msg1-info-error-debug= " +msg); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue,//c创造临时队列 key = {"info"}, exchange = @Exchange(name = "directs",type = "direct")//绑定交换机类型 ) ) public void receive2(String msg){ System.out.println("msg2-info= " +msg); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue,//c创造临时队列 key = {"error"}, exchange = @Exchange(name = "directs",type = "direct")//绑定交换机类型 ) ) public void receive3(String msg){ System.out.println("msg3-error= " +msg); } }
结果:
/** * msg3-error= 广播广播 * msg2-info= 广播广播 * msg1-info-error-debug= 广播广播 * msg1-info-error-debug= 广播广播 * msg1-info-error-debug= 广播广播 */
Routing的订阅模式--topic:
producer
@Test void producer5() { template.convertAndSend("topics", "user.quan", "user.quan广播广播"); template.convertAndSend("topics", "user.quan.all", "user.quan.all广播广播"); }
customer
@Component public class Customer5 { @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue, key = {"user.*"}, exchange = @Exchange(name = "topics",type = "topic") ) ) public void receive1(String msg){ System.out.println("msg1-info-error-debug= " +msg); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue,//c创造临时队列 key = {"user.#"}, exchange = @Exchange(name = "topics",type = "topic")//绑定交换机类型 ) ) public void receive2(String msg){ System.out.println("msg2-info= " +msg); } }
结果:
/** * msg2-info= user.quan广播广播 * msg1-info-error-debug= user.quan广播广播 * msg2-info= user.quan.all广播广播 */
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/java-quan/p/13560571.html