1.设置断点,debug,看varibables,run-->stepover,右上角点java退出debug

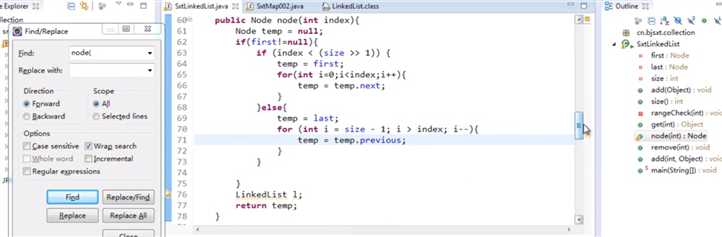
package one.eight; public class ImplementLinkedList { private Node first; private Node last; private int size; //往链表末尾插新的节点 public void add(Object obj){ Node n = new Node(); if(first==null){ n.setPrevious(null); n.setObj(obj); n.setNext(null); first = n; last = n; }else{ //直接往last节点后增加新的节点 n.setPrevious(last); n.setObj(obj); n.setNext(null); last.setNext(n); last = n; } size++; } public int size(){ return size; } private void rangeCheck(int index){ if(index<0||index>=size){ try { throw new Exception(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public Object get(int index){ //2 数组直接就可以找到index,但链表不行 rangeCheck(index); //index越界处理,index<0或者index>=size就抛出一个异常 /* // 0 1 2 3 4 Node temp = node(index); if(temp!=null){ return temp.obj; } return null; */ Node temp = null; if(first!=null){ temp = first; for(int i=0;i<index;i++){ temp = temp.next; } } return temp.obj; } //遍历节点 public Node node(int index){ Node temp = null; if(first!=null){ if (index < (size >> 1)) { temp = first; for(int i=0;i<index;i++){ temp = temp.next; } }else{ temp = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--){ temp = temp.previous; } } } // LinkedList l; return temp; } public void remove(int index){ Node temp = node(index); if(temp!=null){ Node up = temp.previous; Node down = temp.next; up.next = down; down.previous = up; size--; } } //往链表哦任意处插入节点 public void add(int index,Object obj){ Node temp = node(index); Node newNode = new Node(); newNode.obj = obj; if(temp!=null){ Node up = temp.previous; up.next = newNode; newNode.previous = up; newNode.next = temp; temp.previous = newNode; size++; } } public static void main(String[] args) { ImplementLinkedList list = new ImplementLinkedList(); list.add("aaa"); list.add("bbb"); // list.add(1,"BBBB"); list.add("ccc"); list.add("ddd"); list.add("eee"); // list.remove(1); System.out.println(list.get(3)); } } //用来表示一个节点 class Node { Node previous; //上一个节点,不加private访问修饰符,默认的default在同一个包下的其他类都可以访问 Object obj; Node next; //下一个节点 public Node() { } public Node(Node previous, Object obj, Node next) { super(); this.previous = previous; this.obj = obj; this.next = next; } public Node getPrevious() { return previous; } public void setPrevious(Node previous) { this.previous = previous; } public Object getObj() { return obj; } public void setObj(Object obj) { this.obj = obj; } public Node getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Node next) { this.next = next; } }

遍历数组改进版,折中查找,这样效率高。注意左移相当于乘以2,右移相当于除以2(a>>1)
2.

package one.eight; /** *自定义实现Map的功能! *暂不完美! 每次查东西都要遍历一次,效率低 *Map:存放键值对,根据键对象找对应的值对象.键不能重复! * */ public class ImplementMap { SxtEntry[] arr = new SxtEntry[990]; //SxtEntry类型的数组,长度990 int size; public void put(Object key,Object value){ SxtEntry e = new SxtEntry(key,value); //arr[size++] = e; //解决键值重复的处理 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ if(arr[i].key.equals(key)){ arr[i].value=value; return ; } } arr[size++] = e; } public Object get(Object key){ for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ if(arr[i].key.equals(key)){ return arr[i].value; } } return null; } public boolean containsKey(Object key){ for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ //遍历数组 if(arr[i].key.equals(key)){ return true; } } return false; } public boolean containsValue(Object value){ for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ if(arr[i].value.equals(value)){ return true; } } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { ImplementMap m = new ImplementMap(); m.put("高琪", new Wife("杨幂")); m.put("高琪", new Wife("李四")); Wife w = (Wife) m.get("高琪"); System.out.println(w.name); } } class SxtEntry { Object key; Object value; public SxtEntry(Object key, Object value) { //右键source中Generate Constructor using field自动生成的带参构造 super(); this.key = key; this.value = value; } }

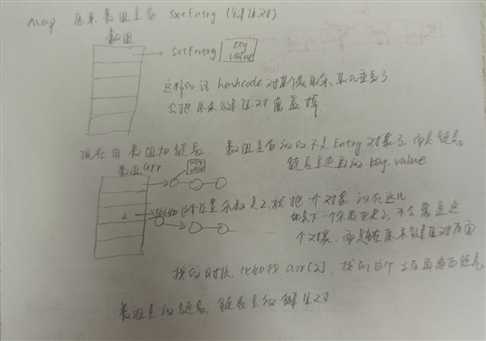
package one.eight; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * 自定义Map的升级版: * 1. 提高查询的效率 * * */ public class ImplementMapPlus { LinkedList[] arr = new LinkedList[9]; //Map的底层结构就是:数组+链表! int size; public void put(Object key,Object value){ SxtEntry e = new SxtEntry(key,value); //生成一个键值对对象,把它添加到容器里,key和value都是对象,如key="张三",value="new wife("李四")" int hash = key.hashCode();//根据对象地址生成的一个数,想办法把hashcode转成0~9的数,把它放在数组对应的index,这样就不用每次遍历了 //hash = hash<0?-hash:hash; int a = hash%arr.length; //这里arr.length=9 if(arr[a]==null){ //如果数组位置a处没有指向任何东西 LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); //新建一个链表对象,让数组位置a处指向这个链表 arr[a] = list; list.add(e); //新建的链表对象是空的,此时把键值对SxtEntry对象添加到链表对象list中 }else{ //数组a处已经指向了链表 LinkedList list = arr[a]; //取出数组a处存放的链表(实际上是引用) for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ //遍历这个数组a处指向的链表 SxtEntry e2 = (SxtEntry) list.get(i); //取出遍历到的键值对 if(e2.key.equals(key)){ e2.value = value; //键值重复直接覆盖! return; } } arr[a].add(e); //arr[a]就指向那个链表对象 } //hashcode%999,a:1000-->1 b:10000-->13,但取的这个余数有可能会重复 //int a = key.hashCode()%999; //arr[a] = e; } public Object get(Object key){ int a = key.hashCode()%arr.length; if(arr[a]!=null){ LinkedList list = arr[a]; //取出数组里存放的链表 for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ SxtEntry e = (SxtEntry) list.get(i); //取出键值对 if(e.key.equals(key)){ return e.value; } } } //return arr[key.hashCode()%999]; return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { ImplementMapPlus m = new ImplementMapPlus(); m.put("高琪", new Wife("杨幂")); m.put("高琪", new Wife("李四")); Wife w = (Wife) m.get("高琪"); System.out.println(w.name); } }
3. 重写hcode and equals方法可以借助eclipse工具,右击source----->generate hcode and equals 。Integer String Data等类都重写了hashcode and equals方法
重写hcode and equals方法可以借助eclipse工具,右击source----->generate hcode and equals 。Integer String Data等类都重写了hashcode and equals方法
4.hashset实现

package one.eight; import java.util.HashMap; /** * 自定义自己的HashSet * @author Administrator * */ public class ImplementSet { HashMap map; private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); //定义一个obj类型的常量,当做value值 public ImplementSet(){ map = new HashMap(); //无参构造 } public int size(){ return map.size(); } public void add(Object o){ map.put(o, PRESENT); //set的不可重复就是利用了map里面键对象的不可重复! } public static void main(String[] args) { ImplementSet s = new ImplementSet(); s.add("aaa"); s.add(new String("aaa")); s.add("bbb"); s.add("bbb"); System.out.println(s.size()); } }
5.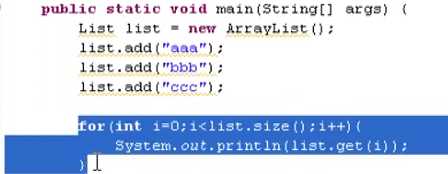 这种通过索引遍历方式只适合list,set没有(因为set没有顺序)
这种通过索引遍历方式只适合list,set没有(因为set没有顺序)
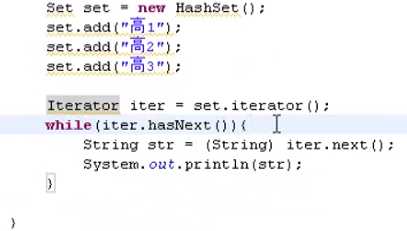 set只能通过迭代器遍历
set只能通过迭代器遍历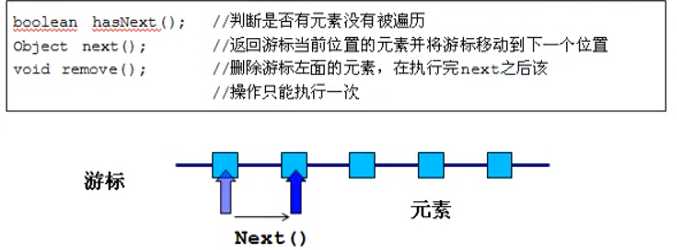
java list中迭代器的实现

 游标
游标
 刚刚访问的那个元素
刚刚访问的那个元素
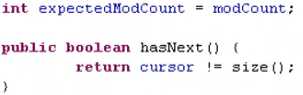
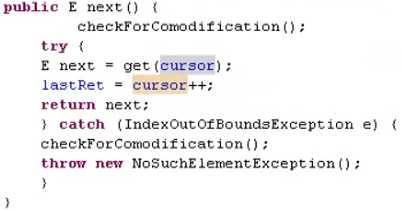
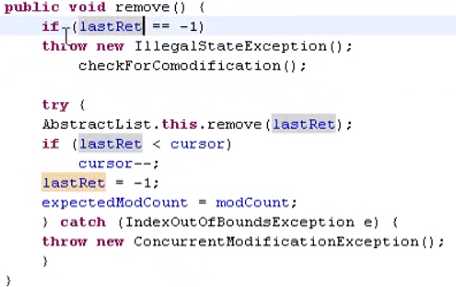 只能删刚刚遍历到的对象,不能连续remove,因为remove会把lastret置为-1,再次调用remove时,代码刚开始lastret=-1抛出异常
只能删刚刚遍历到的对象,不能连续remove,因为remove会把lastret置为-1,再次调用remove时,代码刚开始lastret=-1抛出异常

package cn.bjsxt.iterator; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new ArrayList(); list.add("aaa"); list.add("bbb"); list.add("ccc"); //通过索引遍历List for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ System.out.println(list.get(i)); } //通过迭代器遍历List for(Iterator iter2 = list.iterator();iter2.hasNext();){ String str = (String) iter2.next(); System.out.println(str); iter2.remove(); iter2.remove(); //这里会抛出异常 } System.out.println(list.size()+"******"); Set set = new HashSet(); set.add("高1"); set.add("高2"); set.add("高3"); //通过迭代器遍历Set // Iterator iter = set.iterator(); // while(iter.hasNext()){ for(Iterator iter = set.iterator();iter.hasNext();){ String str = (String) iter.next(); System.out.println(str); } } }
6.右击一个工程
7.泛型
7.1
 子类
子类
 重写方法类型随父类而定
重写方法类型随父类而定
7.2擦除

7.3类型通配符
 编译时看左边,所以即使stu=new studentn<Fruit>,还是编译错误,因为stu编译时类型不确定
编译时看左边,所以即使stu=new studentn<Fruit>,还是编译错误,因为stu编译时类型不确定

7.4 泛型嵌套
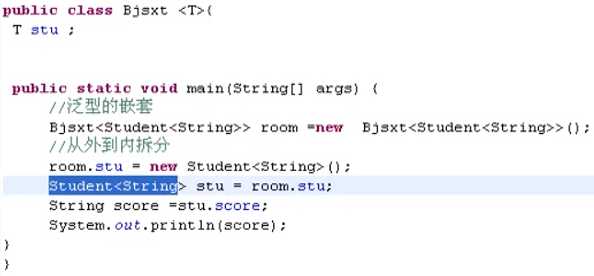
7.5泛型与数组


 这样就是错的,声明时没有问题,但使用时出错,都不知道是什么类型的数组怎么开辟空间呢
这样就是错的,声明时没有问题,但使用时出错,都不知道是什么类型的数组怎么开辟空间呢
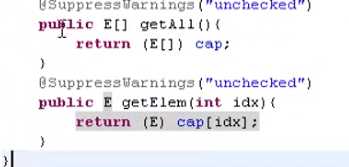
// 获取数组中所有的值和获取某个索引处的值
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/fenglivoong/p/13432436.html