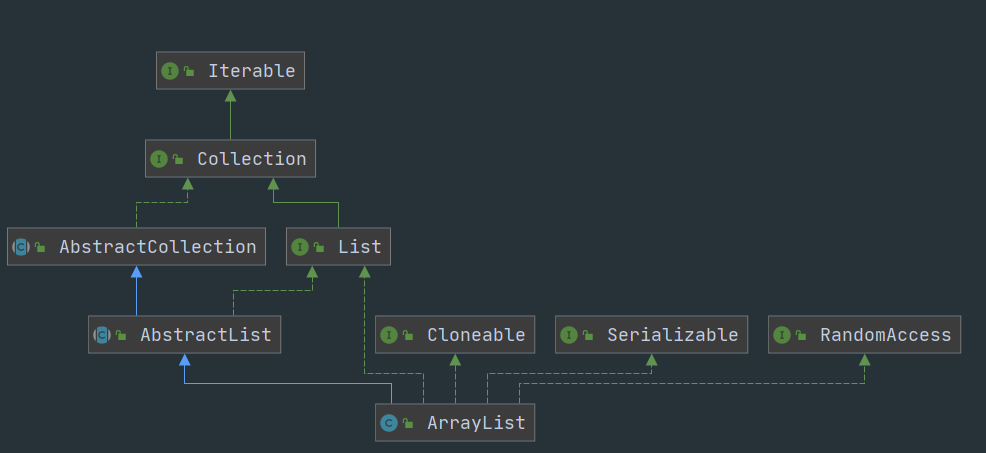
首先,来看ArrayList集合的属性
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
根据ArrayList开头部分源码可以知道:ArrayList底层是一个数组,ArrayList中有扩容的概念,可以实现动态增长。
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
可以看出,如果指定了容量,那么数组就初始化为对应的容量
否则返回的是DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
步骤:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return true (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
我们发现,与扩容相关ArrayList的add方法底层其实都是arraycopy()来实现的
看到arraycopy(),我们可以发现:该方法是由C/C++来编写的,并不是由Java实现:
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
步骤:
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
步骤:
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
/**
* Trims the capacity of this <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to be the
* list‘s current size. An application can use this operation to minimize
* the storage of an <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance.
*/
public void trimToSize() {
modCount++;
if (size < elementData.length) {
elementData = (size == 0)
? EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
: Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size);
}
}
Vector是jdk1.2的类了,比较老旧的一个集合类。
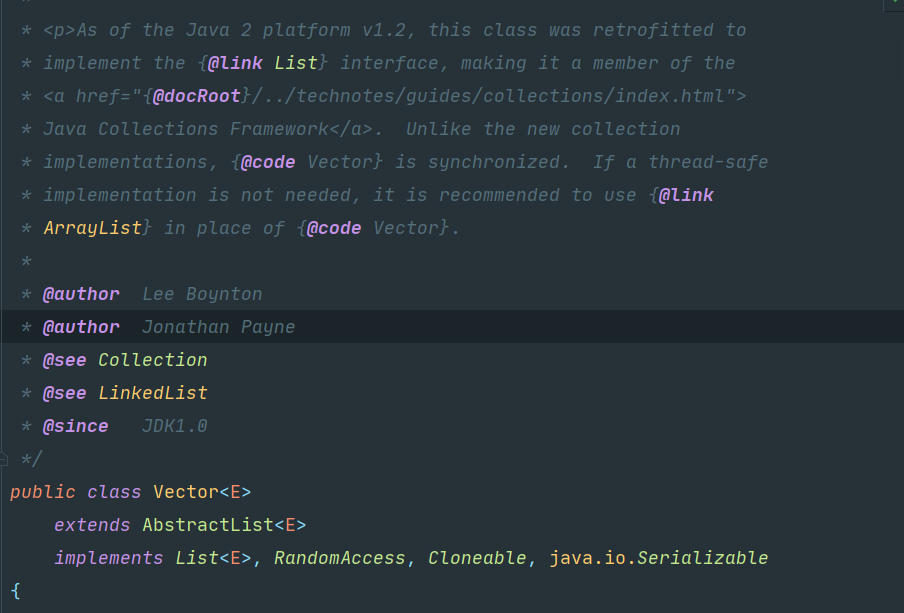
Vector底层也是数组,与ArrayList最大的区别是:同步(线程安全)
Vector是同步的,我们可以从方法上就可以看出来~
在要求非同步的情况下,我们一般都是使用ArrayList来替代Vector
如果想让ArrayList实现同步,可以使用Collections的方法:List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList(...));, 就可以实现同步了
还有一个区别:
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
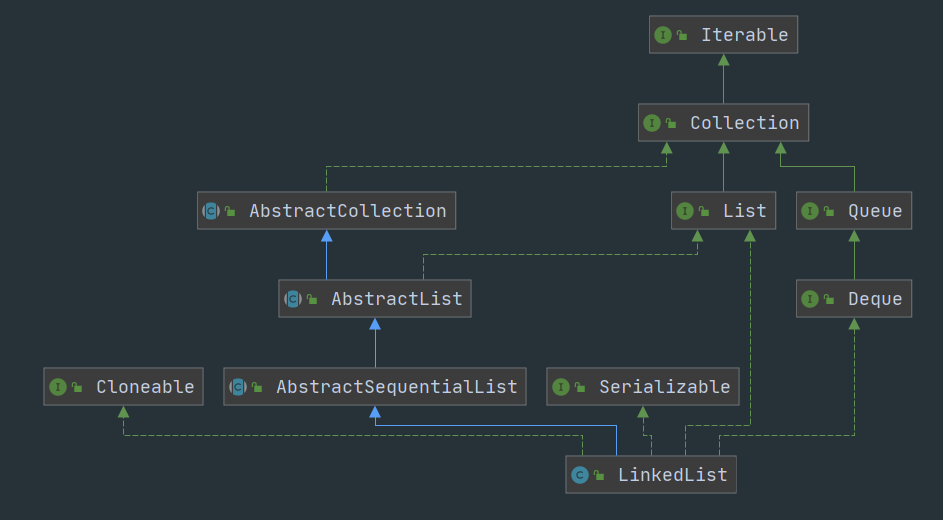
LinkedList底层是双向链表
从结构上,我们还看到了LinkedList实现了Deque接口,因此,我们可以操作LinkedList像操作队列和栈一样~
LinkedList变量就这么几个,因为我们操作单向链表的时候也发现了:有了头结点,其他的数据我们都可以获取得到了。(双向链表也同理)
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
LinkedList的构造方法有两个:
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection‘s
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
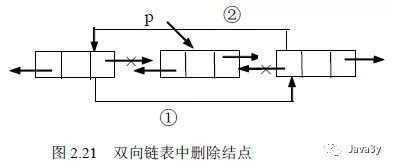
删除节点调用unlink方法
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
实际操作如图
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
进入到?Node node(int index)?方法看具体实现方式
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector算是在面试题中比较常见的的知识点了。下面我就来做一个简单的总结:
ArrayList:?
LinkedList:
Vector:?
总的来说:查询多用ArrayList,增删多用LinkedList。
ArrayList增删慢不是绝对的(在数量大的情况下,已测试):
add()(增加到末尾)的话,那是ArrayList要快但一般来说:增删多还是用LinkedList,因为上面的情况是极端的~
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/bwangblog/p/13632829.html