J2SE 5.0 - 2004年9月。Java SE 8 (LTS) - 2014年3月。Java SE 11 (18.9 LTS) - 2018年9月。
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class LambdaDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用匿名内部类存在的问题
//匿名内部类做了哪些事情
//①定义了一个没有名字的类
//②这个类实现了Runnable接口
//③创建了这个类的对象
//其实我们最关注的是run方法和里面要执行的代码。
//所以使用匿名内部类语法是很冗余的。
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程执行啦(*^▽^*)");
}
}).start();
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class LambdaDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Lambda体现的是函数式编程思想,只需要将要执行的代码放到函数中(函数就是类中的方法)
//Lambda就是一个匿名函数,我们只需要将要执行的代码放到Lambda表达式中即可
//Lambda表达式的好处:可以简化匿名内部类,让代码更加精简。
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("线程执行啦(*^▽^*)");
}).start();
}
}
(参数类型 参数名称) -> {
代码体;
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Swimmable {
/**
* 游泳
*/
void swimming();
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
/**
* Lambda表达式的标准格式:
* (参数列表)->{}
* (参数列表):参数列表
* {}:方法体
* ->:没有实际含义,起到连接的作用
*/
public class LambdaDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
goSwimming(new Swimmable() {
@Override
public void swimming() {
System.out.println("我是匿名内部类的游泳");
}
});
goSwimming(() -> {
System.out.println("我是Lambda的游泳");
});
}
/**
* 无参数无返回值的Lambda
*
* @param swimmable
*/
public static void goSwimming(Swimmable swimmable) {
swimmable.swimming();
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public interface Smokeable {
int smoking(String name);
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
/**
* Lambda表达式的标准格式:
* (参数列表)->{}
* (参数列表):参数列表
* {}:方法体
* ->:没有实际含义,起到连接的作用
*/
public class LambdaDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
goSmoking(new Smokeable() {
@Override
public int smoking(String name) {
System.out.println("匿名内部类:抽了" + name + "的烟");
return 0;
}
});
goSmoking((String name) -> {
System.out.println("Lambda:抽了" + name + "的烟");
return 0;
});
}
public static void goSmoking(Smokeable smokeable) {
smokeable.smoking("中华");
}
}
(参数列表) -> {}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Swimmable {
/**
* 游泳
*/
void swimming();
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
/**
* Lambda表达式的标准格式:
* (参数列表)->{}
* (参数列表):参数列表
* {}:方法体
* ->:没有实际含义,起到连接的作用
*/
public class LambdaDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
goSwimming(new Swimmable() {
@Override
public void swimming() {
System.out.println("我是匿名内部类的游泳");
}
});
}
/**
* 无参数无返回值的Lambda
*
* @param swimmable
*/
public static void goSwimming(Swimmable swimmable) {
swimmable.swimming();
}
}
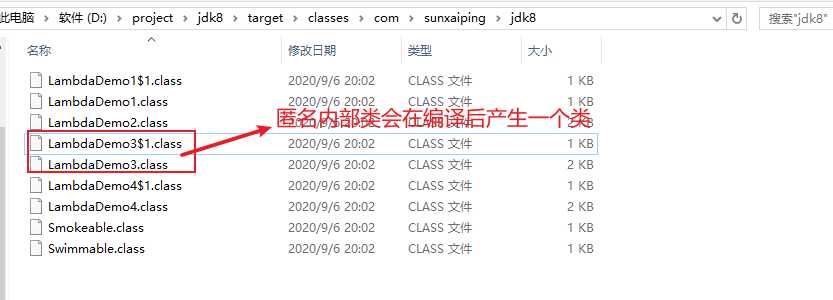
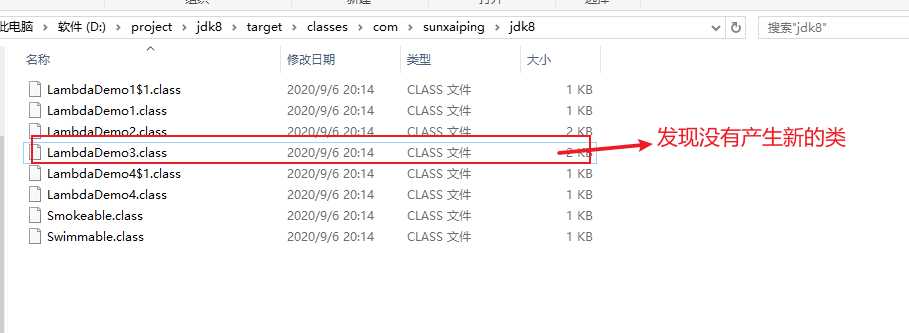
// Decompiled by Jad v1.5.8e2. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov.
// Jad home page: http://kpdus.tripod.com/jad.html
// Decompiler options: packimports(3) fieldsfirst ansi space
// Source File Name: LambdaDemo3.java
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.io.PrintStream;
// Referenced classes of package com.sunxaiping.jdk8:
// Swimmable, LambdaDemo3
static class LambdaDemo3$1
implements Swimmable
{
public void swimming()
{
System.out.println("我是匿名内部类的游泳");
}
LambdaDemo3$1()
{
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
/**
* Lambda表达式的标准格式:
* (参数列表)->{}
* (参数列表):参数列表
* {}:方法体
* ->:没有实际含义,起到连接的作用
*/
public class LambdaDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
goSwimming(()->{
System.out.println("Lambda的游泳");
});
}
/**
* 无参数无返回值的Lambda
*
* @param swimmable
*/
public static void goSwimming(Swimmable swimmable) {
swimmable.swimming();
}
}
javap -c -p 文件名.class
-c:表示对代码进行反编译
-p:显示所有类和成员
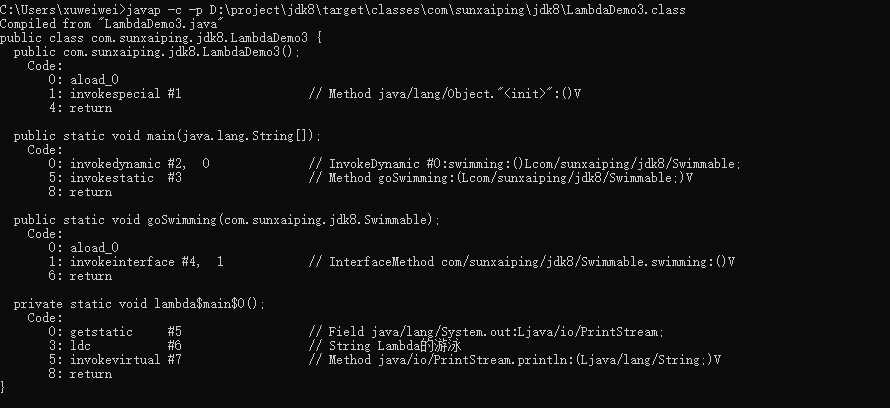
lambda$main$0。这个方法里面存放的是什么内容,我们可以通过断点调试来看看: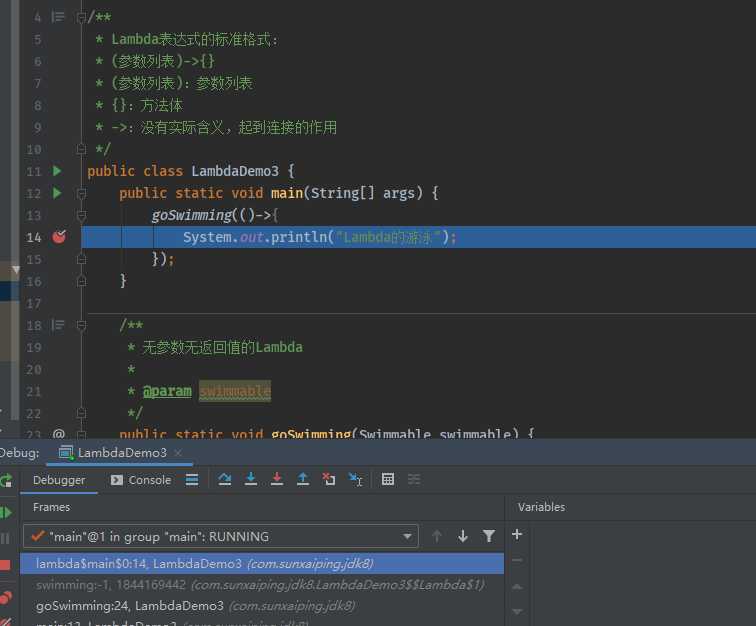
lambda$main$0里面放的就是Lambda中的内容,那么我们可以这么理解lambda$main$0方法:package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class LambdaDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
}
private static void lambda$main$0(){
System.out.println("Lambda的游泳");
}
}
lambda$main$0的命名:以lambda开头,因为是在main函数里面使用了Lambda表达式,所以带有$main表示,因为是第一个,所以$0。-Djdk.internal.lambda.dumpProxyClasses,加上这个参数后,运行时会将生成的内部class码输出到一个文件中。其命令如下:java -Djdk.internal.lambda.dumpProxyClasses 要运行的包名.类名
java -Djdk.internal.lambda.dumpProxyClasses com.sunxaiping.jdk8.LambdaDemo3
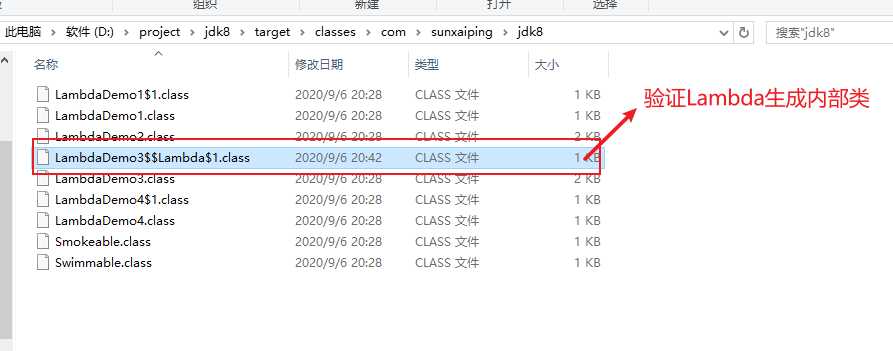
LambdaDemo3$$Lambda$1.class这个字节码文件,内容如下:// Decompiled by Jad v1.5.8e2. Copyright 2001 Pavel Kouznetsov.
// Jad home page: http://kpdus.tripod.com/jad.html
// Decompiler options: packimports(3) fieldsfirst ansi space
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
// Referenced classes of package com.sunxaiping.jdk8:
// Swimmable, LambdaDemo3
final class LambdaDemo3$$Lambda$1
implements Swimmable
{
public void swimming()
{
LambdaDemo3.lambda$main$0();
}
private LambdaDemo3$$Lambda$1()
{
}
}
LambdaDemo3.lambda$main$0(),也就是调用Lambda中的内容。最后可以将Lambda理解为:package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class LambdaDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
goSwimming(new Swimmable() {
@Override
public void swimming() {
LambdaDemo3.lambda$main$0();
}
});
}
private static void lambda$main$0(){
System.out.println("Lambda的游泳");
}
}
在Lambda标准格式的基础上,使用省略写法的规则是:
1??小括号内的参数的类型可以省略。
2??如果小括号内有且仅有一个参数,则小括号可以省略。
3??如果大括号内有且仅有一个语句,则可以同时省略大括号、return关键字以及语句的分号。
示例:
Lambda标准格式:
(int a ) -> {
return new Person();
}
a -> new Person()
Lambda的语法非常简洁,但是Lambda表达式不是随随便便就能使用的,使用时需要注意以下几个条件:
1??方法的参数或局部变量类型必须为接口才能使用Lambda。
2??接口中有且仅有一个抽象方法。
示例:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
/**
* 只有一个抽象方法的接口称为函数函数式接口。
* @FunctionalInterface 注解用来检测这个接口是不是只有一个抽象方法
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class LambdaCondition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(() -> {
System.out.println("飞");
});
//局部变量类型是接口,可以使用Lambda
Flyable flyable = () -> {
System.out.println("飞");
};
}
/**
* 方法的参数类型,可以使用Lambda
*
* @param flyable
*/
public static void test(Flyable flyable) {
flyable.fly();
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
/**
* 只有一个抽象方法的接口称为函数函数式接口。
* @FunctionalInterface 注解用来检测这个接口是不是只有一个抽象方法
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Flyable {
void fly();
}
interface 接口名{
静态常量;
抽象方法;
}
interface 接口名{
静态常量;
抽象方法;
默认方法;
静态方法;
}
interface A{
void test1();
//接口新增抽象方法,所有实现类都需要去重写这个方法,非常不利于接口的扩展
void test2();
}
interface B implements A{
@Override
public void test1(){
System.out.println("B test1");
}
//接口新增抽象方法,所有实现类都需要去重写这个方法
@Override
public void test2(){
System.out.println("B test2");
}
}
public interface Map<K,V> {
...
void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {}
}
public interface Map<K,V> {
...
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
action.accept(k, v);
}
}
}
interface 接口名{
default 返回值类型 方法名(){
//代码;
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class DefaultFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BB bb = new BB();
bb.show();
}
}
interface AA{
default void show(){
System.out.println("我是AA接口中的默认方法");
}
}
//默认方法的使用方式一:实现类可以直接使用
class BB implements AA{
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class DefaultFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BB bb = new BB();
bb.show();
CC cc = new CC();
cc.show();
}
}
interface AA{
default void show(){
System.out.println("我是AA接口中的默认方法");
}
}
//默认方法的使用方式一:实现类可以直接使用
class BB implements AA{
}
//默认方法的使用方式二:实现类可以重写默认方法
class CC implements AA{
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("我是CC类重写的默认方法");
}
}
interface 接口名{
static 返回值类型 方法名(){
//代码
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class DefaultFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AA.show();
}
}
interface AA{
static void show(){
System.out.println("我是接口的静态方法");
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class LambdaDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test((a1, a2) -> {
System.out.println(a1 + a2);
});
}
public static void test(Operation operation) {
operation.getSum(1, 2);
}
}
interface Operation {
void getSum(int a, int b);
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {
/**
* Gets a result.
*
* @return a result
*/
T get();
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {
/**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
/**
* Applies this function to the given argument.
*
* @param t the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
R apply(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed function that first applies the {@code before}
* function to its input, and then applies this function to the result.
* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to
* the caller of the composed function.
*
* @param <V> the type of input to the {@code before} function, and to the
* composed function
* @param before the function to apply before this function is applied
* @return a composed function that first applies the {@code before}
* function and then applies this function
* @throws NullPointerException if before is null
*
* @see #andThen(Function)
*/
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
/**
* Returns a composed function that first applies this function to
* its input, and then applies the {@code after} function to the result.
* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to
* the caller of the composed function.
*
* @param <V> the type of output of the {@code after} function, and of the
* composed function
* @param after the function to apply after this function is applied
* @return a composed function that first applies this function and then
* applies the {@code after} function
* @throws NullPointerException if after is null
*
* @see #compose(Function)
*/
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
/**
* Returns a function that always returns its input argument.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input and output objects to the function
* @return a function that always returns its input argument
*/
static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> {
/**
* Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
* @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate,
* otherwise {@code false}
*/
boolean test(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate.
*
* @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate
*/
default Predicate<T> negate() {
return (t) -> !test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate
* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,
* which may be {@code null}
* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}
*/
static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return (null == targetRef)
? Objects::isNull
: object -> targetRef.equals(object);
}
}
java.util.function.Supplier<T>接口,它意味着“供给”,对应的Lambda表达式需要对外提供一个符合泛型类型的对象数据。@FunctionalInterface
public interface Supplier<T> {
/**
* Gets a result.
*
* @return a result
*/
T get();
}
供给型接口,通过Supplier接口中的get方法可以得到一个值,无参有返回值的接口。
示例:使用Lambda表达式返回数组元素的最大值。
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class LambdaDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printMax(() -> {
int[] arr = {11, 99, 100, -7};
Arrays.sort(arr);
return arr[arr.length-1];
});
}
public static void printMax(Supplier<Integer> supplier) {
Integer max = supplier.get();
System.out.println("max = " + max);
}
}
java.util.function.Consumer<T>接口正好相反,它不是生产一个数据,而是消费一个数据,其数据类型由泛型参数决定。@FunctionalInterface
public interface Consumer<T> {
/**
* Performs this operation on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
*/
void accept(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either
* operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the
* composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception,
* the {@code after} operation will not be performed.
*
* @param after the operation to perform after this operation
* @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this
* operation followed by the {@code after} operation
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null
*/
default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); };
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class LambdaDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test((s)->{
String lowerCase = s.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(lowerCase);
String upperCase = s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(upperCase);
});
}
public static void test(Consumer<String> consumer){
consumer.accept("hello world");
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class LambdaDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式先将一个字符串转成小写,再转成大写
test((s) -> {
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
}, (s) -> {
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
});
}
public static void test(Consumer<String> c1, Consumer<String> c2) {
c1.andThen(c2).accept("hello world");
}
}
java.util.function.Function<T, R>接口用来根据一个类型的数据得到另一个类型的数据,前者称为前置条件,后者称为后置条件。有参数有返回值。@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
/**
* Applies this function to the given argument.
*
* @param t the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
R apply(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed function that first applies the {@code before}
* function to its input, and then applies this function to the result.
* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to
* the caller of the composed function.
*
* @param <V> the type of input to the {@code before} function, and to the
* composed function
* @param before the function to apply before this function is applied
* @return a composed function that first applies the {@code before}
* function and then applies this function
* @throws NullPointerException if before is null
*
* @see #andThen(Function)
*/
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
/**
* Returns a composed function that first applies this function to
* its input, and then applies the {@code after} function to the result.
* If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to
* the caller of the composed function.
*
* @param <V> the type of output of the {@code after} function, and of the
* composed function
* @param after the function to apply after this function is applied
* @return a composed function that first applies this function and then
* applies the {@code after} function
* @throws NullPointerException if after is null
*
* @see #compose(Function)
*/
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
/**
* Returns a function that always returns its input argument.
*
* @param <T> the type of the input and output objects to the function
* @return a function that always returns its input argument
*/
static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Function;
public class LambdaDemo1 {
//使用Lambda表达式将字符串转成数字
public static void main(String[] args) {
getNumber((s) -> {
int num = Integer.parseInt(s);
return num;
});
}
public static void getNumber(Function<String, Integer> function) {
Integer num = function.apply("10");
System.out.println("num = " + num);
}
}
java.util.function.Predicate<T>接口。@FunctionalInterface
public interface Predicate<T> {
/**
* Evaluates this predicate on the given argument.
*
* @param t the input argument
* @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate,
* otherwise {@code false}
*/
boolean test(T t);
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate.
*
* @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this
* predicate
*/
default Predicate<T> negate() {
return (t) -> !test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed
* predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other}
* predicate is not evaluated.
*
* <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed
* to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the
* {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated.
*
* @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this
* predicate
* @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical
* OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate
* @throws NullPointerException if other is null
*/
default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) {
Objects.requireNonNull(other);
return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t);
}
/**
* Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}.
*
* @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate
* @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality,
* which may be {@code null}
* @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according
* to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}
*/
static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) {
return (null == targetRef)
? Objects::isNull
: object -> targetRef.equals(object);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class LambdaDemo2 {
//使用Lambda判断一个名称,如果名称超过3个字就认为是很长的名称
public static void main(String[] args) {
test((name) -> {
return name.length() > 3;
}, "迪丽热巴");
}
public static void test(Predicate<String> predicate, String name) {
boolean test = predicate.test(name);
if (test) {
System.out.println(name + "的名称很长");
} else {
System.out.println(name + "的名称不长");
}
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
public class LambdaDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串即包含W也包含H
testAnd(s1 -> s1.contains("W"), s2 -> s2.contains("H"), "Hello World");
//使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串包含W或包含H
testOr(s1 -> s1.contains("W"), s2 -> s2.contains("H"), "Hello World");
//使用Lambda表达式判断一个字符串不包含W
testNegate(s1 -> s1.contains("W"), "Hello world");
}
public static void testAnd(Predicate<String> p1, Predicate<String> p2, String str) {
boolean test = p1.and(p2).test(str);
if (test) {
System.out.println(str + "既包含W也包含H");
}
}
public static void testOr(Predicate<String> p1, Predicate<String> p2, String str) {
boolean test = p1.or(p2).test(str);
if (test) {
System.out.println(str + "包含W或包含H");
}
}
public static void testNegate(Predicate<String> p1, String str) {
boolean test = p1.negate().test(str);
if (test) {
System.out.println(str + "不包含W");
}
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class LambdaDemo4 {
/**
* 获取一个数组的和
*
* @param arr
*/
public static void getSum(int[] arr) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i : arr) {
sum += i;
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arrs = {10, 19, -10, 0};
//使用方法引用:让这个指定的方法去重写接口的抽象方法,到时候调用接口的抽象方法就是调用传递过去的这个方法
printSum(LambdaDemo4::getSum,arrs);
Consumer<int[]> consumer = LambdaDemo4::getSum;
consumer.accept(arrs);
}
public static void printSum(Consumer<int[]> consumer, int[] arr) {
consumer.accept(arr);
}
}
::写法,这被称为"方法引用",是一种新的语法。方法引用的前提:
- 1??方法引用所引用的方法的参数列表必须要和函数式接口中抽象方法的参数列表相同(完全一致)。
- 2??方法引用所引用的方法的的返回值类型必须要和函数式接口中抽象方法的返回值类型相同(完全一致)。
::。方法引用。package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* 方法引用: 实例名::方法名
*/
public class LambdaDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式获取当前秒数
Date date = new Date();
Supplier<Long> supplier = () -> {
return date.getTime();
};
System.out.println(supplier.get());
//使用方法引用简化上述代码
supplier = date::getTime;
System.out.println(supplier.get());
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* 方法引用: 类名::静态方法名
*/
public class LambdaDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式获取当前的毫秒值
Supplier<Long> supplier = ()->{
return System.currentTimeMillis();
};
System.out.println("supplier = " + supplier.get());
//使用方法引用简化上面的代码
supplier = System::currentTimeMillis;
System.out.println("supplier = " + supplier.get());
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Function;
/**
* 方法引用 类名::方法名
*/
public class LambdaDemo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式将字符串转换为Long类型
Function<String, Long> function = (s) -> {
return Long.parseLong(s);
};
Long apply = function.apply("5");
System.out.println("apply = " + apply);
//使用Lambda简化上面的代码
function = Long::parseLong;
apply = function.apply("5");
System.out.println("apply = " + apply);
}
}
类名::new的格式表示。package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* 方法引用 类名::new
*/
public class LambdaDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式获取Person类对象
Supplier<Person> supplier = () -> {
return new Person();
};
Person person = supplier.get();
System.out.println("person = " + person);
supplier = Person::new;
person = supplier.get();
System.out.println("person = " + person);
BiFunction<String, Integer, Person> function = (name, age) -> {
return new Person(name, age);
};
person = function.apply("李四", 20);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
function = Person::new;
person = function.apply("张三", 25);
System.out.println("person = " + person);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.function.Function;
/**
* 方法引用 数据类型[]::new
*/
public class LambdaDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用Lambda表达式创建指定长度的String数组
Function<Integer, String[]> function = (length) -> {
return new String[length];
};
String[] str = function.apply(2);
System.out.println("str.length = " + str.length);
//使用方法引用简化上面的代码
function = String[]::new;
str = function.apply(5);
System.out.println("str.length = " + str.length);
}
}
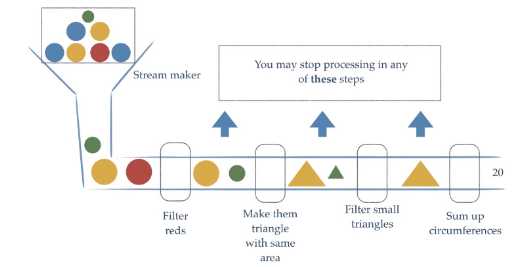
引用已经存在的方法。一个ArrayList集合中存储有以下数据:张无忌、周芷若、赵敏、张强、张三丰
需求:①拿到所有姓张的 ②拿到名字长度为3个字的 ③打印这些数据
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class StreamIntroDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "张无忌", "周芷若", "赵敏", "张强", "张三丰");
//拿到所有姓张的
List<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : list) {
if (s.startsWith("张")) {
zhangList.add(s);
}
}
//拿到名字长度=3的
List<String> threeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : zhangList) {
if (s.length() == 3) {
threeList.add(s);
}
}
//对结果进行打印
for (String name : threeList) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class LambdaDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "张无忌", "周芷若", "赵敏", "张强", "张三丰");
list.stream().filter(name->name.startsWith("张")).filter((name)->name.length()==3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
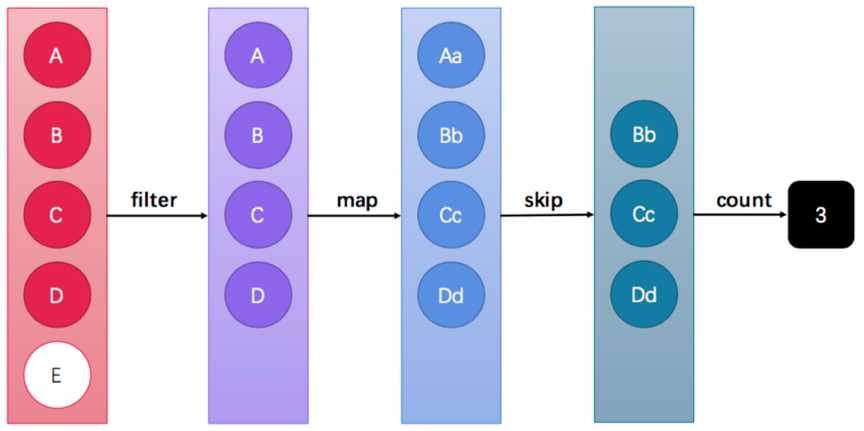
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {
default Stream<E> stream() {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);
}
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 获取Stream流的方式
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
/**
* Returns a sequential {@code Stream} containing a single element.
*
* @param t the single element
* @param <T> the type of stream elements
* @return a singleton sequential stream
*/
public static<T> Stream<T> of(T t) {
return StreamSupport.stream(new Streams.StreamBuilderImpl<>(t), false);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential ordered stream whose elements are the specified values.
*
* @param <T> the type of stream elements
* @param values the elements of the new stream
* @return the new stream
*/
@SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs") // Creating a stream from an array is safe
public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values) {
return Arrays.stream(values);
}
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 获取Stream流的方式
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public class Arrays {
public static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array) {
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link Stream} with the specified range of the
* specified array as its source.
*
* @param <T> the type of the array elements
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @param startInclusive the first index to cover, inclusive
* @param endExclusive index immediately past the last index to cover
* @return a {@code Stream} for the array range
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code startInclusive} is
* negative, {@code endExclusive} is less than
* {@code startInclusive}, or {@code endExclusive} is greater than
* the array size
* @since 1.8
*/
public static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link IntStream} with the specified array as its
* source.
*
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @return an {@code IntStream} for the array
* @since 1.8
*/
public static IntStream stream(int[] array) {
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link IntStream} with the specified range of the
* specified array as its source.
*
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @param startInclusive the first index to cover, inclusive
* @param endExclusive index immediately past the last index to cover
* @return an {@code IntStream} for the array range
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code startInclusive} is
* negative, {@code endExclusive} is less than
* {@code startInclusive}, or {@code endExclusive} is greater than
* the array size
* @since 1.8
*/
public static IntStream stream(int[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {
return StreamSupport.intStream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link LongStream} with the specified array as its
* source.
*
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @return a {@code LongStream} for the array
* @since 1.8
*/
public static LongStream stream(long[] array) {
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link LongStream} with the specified range of the
* specified array as its source.
*
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @param startInclusive the first index to cover, inclusive
* @param endExclusive index immediately past the last index to cover
* @return a {@code LongStream} for the array range
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code startInclusive} is
* negative, {@code endExclusive} is less than
* {@code startInclusive}, or {@code endExclusive} is greater than
* the array size
* @since 1.8
*/
public static LongStream stream(long[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {
return StreamSupport.longStream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link DoubleStream} with the specified array as its
* source.
*
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @return a {@code DoubleStream} for the array
* @since 1.8
*/
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array) {
return stream(array, 0, array.length);
}
/**
* Returns a sequential {@link DoubleStream} with the specified range of the
* specified array as its source.
*
* @param array the array, assumed to be unmodified during use
* @param startInclusive the first index to cover, inclusive
* @param endExclusive index immediately past the last index to cover
* @return a {@code DoubleStream} for the array range
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if {@code startInclusive} is
* negative, {@code endExclusive} is less than
* {@code startInclusive}, or {@code endExclusive} is greater than
* the array size
* @since 1.8
*/
public static DoubleStream stream(double[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) {
return StreamSupport.doubleStream(spliterator(array, startInclusive, endExclusive), false);
}
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 获取Stream流的方式
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Arrays.stream(new Integer[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5});
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
| 方法名 | 方法作用 | 返回值类型 | 方法种类 |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 统计个数 | long | 终结 |
| forEach | 逐一处理 | void | 终结 |
| filter | 过滤 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| limit | 取前几个 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| skip | 跳过前几个 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| map | 映射 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| concat | 组合 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action);
//略
}
public interface Map<K,V> {
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
action.accept(k, v);
}
}
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* forEach
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, "张三", "李四", "王五");
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* forEach
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("aa","aaa");
map.put("bb","bbb");
map.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println("k = " + k);
System.out.println("v = " + v);
});
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
long count();
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* count
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
long count = stream.count();
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
//略
}
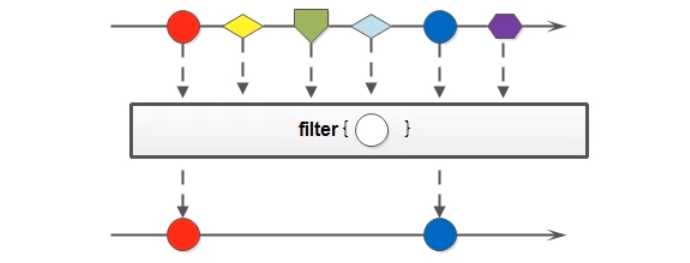
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* filter
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七", "王八");
stream.filter(s -> s.contains("张")).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize);
//略
}
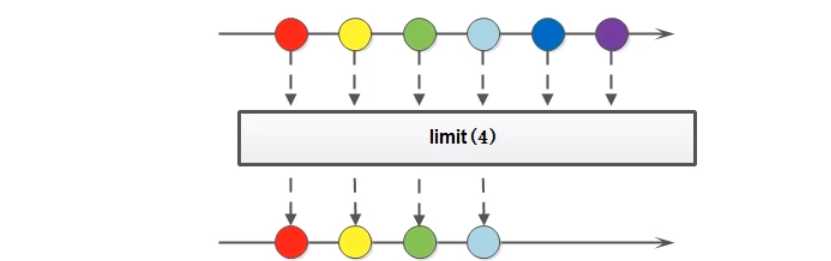
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* limit
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七", "王八");
stream.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
Stream<T> skip(long n);
//略
}
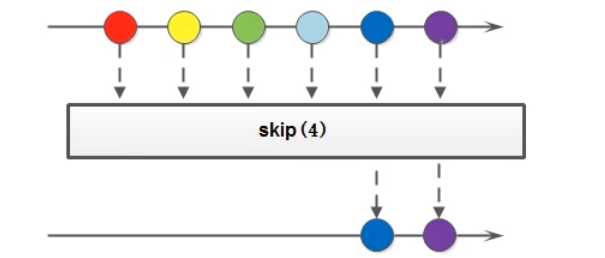
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* skip
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六", "田七", "王八");
stream.skip(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
<R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);
//略
}
该接口需要一个Function函数式接口参数,可以将当前流中的T类型转换为另一种R类型的流。
使用场景:
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* map
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6");
stream.map(Integer::parseInt).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
<R> Stream<R> flatMap(Function<? super T, ? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper);
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* flatMap
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("Hello", "World");
stream.map(s -> s.split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
Stream<T> sorted();
Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
//略
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1, -1, 10, 0, 100, 55);
//自然排序
list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
//逆序
list.stream().sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
Stream<T> distinct();
//略
}
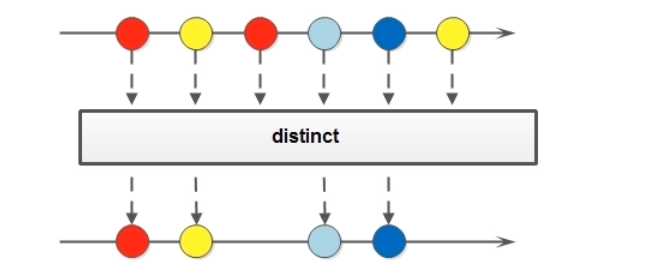
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1, -1, 10, 0, 10, 55);
list.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//元素是否全部满足条件
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
//元素是否满足任意一个条件
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
//元素是否全部不满足条件
boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
//略
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1, -1, 10, 0, 10, 55);
boolean b = list.stream().allMatch((e) -> e > 5);
if (b) {
System.out.println("元素是否满足都>5");
}
b = list.stream().anyMatch((e) -> e > 5);
if (b) {
System.out.println("元素是否满足任意元素>5");
}
b = list.stream().noneMatch(e -> e > 5);
if (b) {
System.out.println("元素是否全部不小于5");
}
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//获取Stream流中的第一个元素
Optional<T> findFirst();
//获取Stream流中的第一个元素
Optional<T> findAny();
//略
}
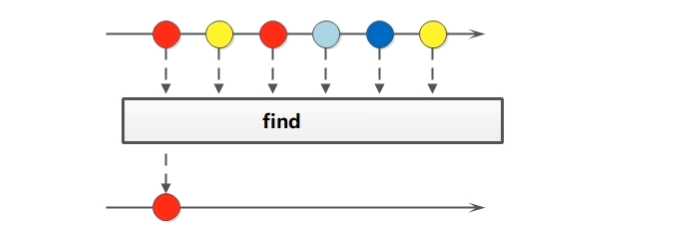
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1, -1, 10, 0, 10, 55);
Optional<Integer> first = list.stream().findFirst();
System.out.println("first = " + first.get());
Optional<Integer> any = list.stream().findAny();
System.out.println("any = " + any.get());
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//获取Stream流中的最大值
Optional<T> max(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
//获取Stream流中的最小值
Optional<T> min(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
//略
}
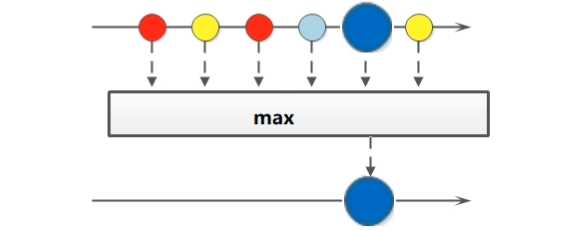
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1, -1, 10, 0, 10, 55);
Optional<Integer> max = list.stream().max(Integer::compareTo);
System.out.println("max = " + max.get());
Optional<Integer> min = list.stream().min(Integer::compareTo);
System.out.println("min = " + min.get());
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//获取Stream流中的最大值
T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
//获取Stream流中的最小值
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
//略
}

package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, -5, 9, 100, 0);
//第一个参数是默认值
//第二个参数:对数据进行处理的方式
Integer reduce = stream.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println("reduce = " + reduce);
}
}
Stream<Integer>中的Integer类型转成int类型,可以使用mapToInt方法。public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//获取Stream流中的最大值
IntStream mapToInt(ToIntFunction<? super T> mapper);
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* mapToInt
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Integer占用的内存比int多,在Stream流操作中会自动装箱和拆箱
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
//操作
stream.filter(n -> n > 3).forEach(System.out::println);
//mapToInt将Stream流中的Integer变为int
//IntStream:内部操作的是int类型的数据,节省内存,减少自动装箱和拆箱
IntStream intStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).mapToInt(Integer::intValue);
intStream.filter(n -> n > 3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//将两个流合并成一个流
public static <T> Stream<T> concat(Stream<? extends T> a, Stream<? extends T> b) {
Objects.requireNonNull(a);
Objects.requireNonNull(b);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Spliterator<T> split = new Streams.ConcatSpliterator.OfRef<>(
(Spliterator<T>) a.spliterator(), (Spliterator<T>) b.spliterator());
Stream<T> stream = StreamSupport.stream(split, a.isParallel() || b.isParallel());
return stream.onClose(Streams.composedClose(a, b));
}
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* concat
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3);
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.of(4, 5, 6);
//两个流合并之后,不能操作之前的流
Stream<Integer> concat = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2);
concat.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
java.util.stream.Collector<T, A, R> 接口对象来指定收集到那种集合中。java.util.stream.Collectors类提供一些方法,可以作为Collector接口的实例。public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//Stream流中的结果保存到集合中
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流中的结果保存到集合中
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
//将Stream流中的结果保存到List集合中
List<Integer> list = stream1.collect(Collectors.toList());
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//将Stream流中的结果保存到Set集合中
Stream<Integer> stream2 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Set<Integer> set = stream2.collect(Collectors.toSet());
set.forEach(System.out::println);
//将Stream流中的结果保存到ArrayList集合中
Stream<Integer> stream3 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = stream3.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
arrayList.forEach(System.out::println);
//将Stream流中的结果保存到HashSet集合中
Stream<Integer> stream4 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = stream4.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
hashSet.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
public interface Stream<T> extends BaseStream<T, Stream<T>> {
//Stream流中的结果保存到数组中
Object[] toArray();
<A> A[] toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator);
//略
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Stream流中的数据转换成Object数组
Stream<Integer> stream1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Object[] array = stream1.toArray();
System.out.println("Stream流转换为Object数组:" + Arrays.toString(array));
//Stream流中的数据转换成String数组
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "0");
String[] strings = stream2.toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println("Stream流转换为String数组 = " + Arrays.asList(strings));
}
}
当我们使用Stream流处理数据的时候,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作。比如获取最大值、获取最小值、求和、平均值、统计数量。
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Stream流中数据的总数
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
long count = stream.count();
System.out.println("count = " + count);
//获取Stream流中的最大值
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Optional<Integer> max = stream.max(Integer::compareTo);
System.out.println("max = " + max.get());
//获取Stream流中的最小值
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Optional<Integer> min = stream.min(Integer::compareTo);
System.out.println("min = " + min.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Optional<Integer> maxOptional = stream.collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println("max = " + maxOptional.get());
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Optional<Integer> minOptional = stream.collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println("min = " + minOptional.get());
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
count = stream.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("count = " + count);
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Double avg = stream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Integer::intValue));
System.out.println("avg = " + avg);
stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
Integer sum = stream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Integer::intValue));
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性进行数据分组。
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer score;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Integer score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Integer score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Stream.of(
new Person("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Person("杨颖", 56, 86),
new Person("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Person("柳岩", 52, 77));
//根据年龄分组
Map<Integer, List<Person>> map = stream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge));
map.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println("年龄 = " + k);
List<Person> personList = v;
System.out.println("person = " + personList);
});
}
}
还可以对流中的数据进行多级分组。
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer score;
private String sex;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Integer score, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
this.sex = sex;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Integer score) {
this.score = score;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
", sex=‘" + sex + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Stream.of(
new Person("赵丽颖", 52, 95, "女"),
new Person("杨颖", 56, 86, "女"),
new Person("迪丽热巴", 56, 99, "女"),
new Person("黄晓明", 52, 77, "男"));
//先根据性别分组,性别相同再按照年龄分组
Map<String, Map<Integer, List<Person>>> map = stream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getSex, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge)));
map.forEach((sex, v1) -> {
System.out.println("sex = " + sex);
Map<Integer, List<Person>> map1 = v1;
map1.forEach((age, v2) -> {
System.out.print(age + "---->");
System.out.println("personList = " + v2);
});
});
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer score;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Integer score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Integer score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Stream.of(
new Person("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Person("杨颖", 56, 86),
new Person("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Person("黄晓明", 52, 77));
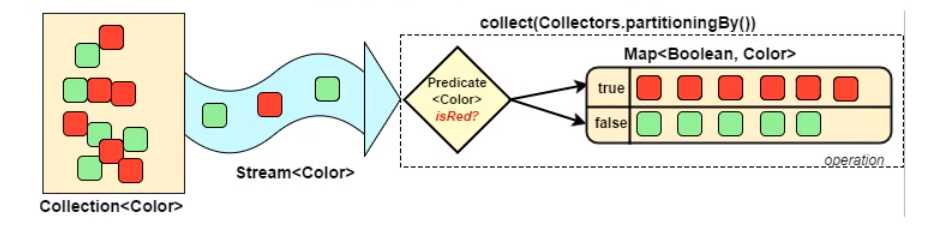
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> map = stream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(p -> p.getScore() > 90));
map.forEach((k,v)->{
System.out.println("k = " + k);
System.out.println("v = " + v);
});
}
}
Collectors的joining方法会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer score;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Integer score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(Integer score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> stream = Stream.of(
new Person("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Person("杨颖", 56, 86),
new Person("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Person("黄晓明", 52, 77));
String str = stream.map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("><", "(#^.^#)", "^_^"));
System.out.println("str = " + str);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0);
long count = stream.filter(s -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---" + s);
return true;
}).count();
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//直接获取并行的Stream流
Stream<String> parallelStream = list.parallelStream();
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* Stream流一旦调用终止方法,就不可以再操作。
*/
public class LambdaDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//串行流转成并行流
Stream<String> parallel = list.stream().parallel();
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
public class OptionalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = null;
if(null != username){
System.out.println("username = " + username);
}
}
}

//创建一个Optional实例
public static <T> Optional<T> of(T value);
//创建一个空的Optional实例
public static<T> Optional<T> empty();
//如果value不为null,则创建Optional实例,否则创建空的Optional实例
public static <T> Optional<T> ofNullable(T value);
//判断是否包含值,如果包含值返回true,否则返回false
public boolean isPresent();
//如果Optional有值则将其抛出NoSuchElementException异常
public T get();
//如果存在包含值,返回包含值,否则返回参数other
public T orElse(T other) ;
//如果存在包含值,返回包含值,否则返回other获取的值
public T orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> other);
//如果存在包含值,对其处理,并返回处理后的Optional,否则返回Optional.empty()
public<U> Optional<U> map(Function<? super T, ? extends U> mapper);
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class OptionalDemo {
/**
* 创建Optional实例
* Optional.of(T value):不能传null,否则报错
*/
@Test
public void testCreateOptional1() {
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("凤姐");
System.out.println("optional.get() = " + optional.get());
}
/**
* 创建Optional实例
* Optional.empty() 创建一个空的Optional
*/
@Test
public void testCreateOptional2() {
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.empty();
System.out.println("empty = " + empty);
}
/**
* 创建Optional实例
* Optional.ofNullable(T value):如果value是null,则返回Optional.empty();如果value有值,则返回Optional.of(T value)
*/
@Test
public void testCreateOptional3() {
Optional<Object> optional = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println("optional = " + optional);
optional = Optional.ofNullable("你好啊");
System.out.println("optional = " + optional);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class OptionalDemo {
/**
* 判断Optional类中是否有值
*/
@Test
public void test() {
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.empty();
if (empty.isPresent()) {
System.out.println("Optional类中有值");
} else {
System.out.println("Optional类中没有值");
}
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class OptionalDemo {
/**
* 获取Optional类中的值
*/
@Test
public void test() {
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable("你好,世界");
if (optional.isPresent()) {
//get()方法,可以用来获取Optional类中的值,如果有值就返回具体值,否则就报错。
//一般get()方法配置isPresent()方法使用
String str = optional.get();
System.out.println("str = " + str);
}
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class OptionalDemo {
/**
* 获取Optional类中的值
*/
@Test
public void test() {
Optional<Object> optional = Optional.empty();
//orElse:如果Optional中有值,就返回Optional中的值。否则返回orElse方法中参数指定的值
Object obj = optional.orElse("如花");
System.out.println("obj = " + obj);
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class OptionalDemo {
/**
* 获取Optional类中的值
*/
@Test
public void test() {
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("凤姐");
//ifPresent:如果有值,就调用参数
optional.ifPresent((s) -> {
System.out.println("有值:" + s);
});
//ifPresentOrElse在JDK9以后才有
//ifPresentOrElse第一个参数表示如果有值,做什么
//ifPresentOrElse第二个参数表示如果没有值,做什么
optional.ifPresentOrElse(s -> {
System.out.println("s = " + s);
}, () -> {
System.out.println("没有值");
});
}
}
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class OptionalDemo {
/**
* 获取Optional类中的值
*/
@Test
public void test() {
//将Person中的用户名转成大写返回
Person person = null;
person = new Person("hello world", 18, 99);
String name = getTraditionUpperName(person);
System.out.println("name = " + name);
name = getOptionalUpperName(person);
System.out.println("name = " + name);
}
public String getOptionalUpperName(Person person) {
return Optional.ofNullable(person).map(Person::getName).map(String::toUpperCase).orElse(null);
}
/**
* 传统方式 实现需求
*
* @param person
* @return
*/
public String getTraditionUpperName(Person person) {
if (null != person) {
String name = person.getName();
if (null != name) {
return name.toUpperCase();
}
}
return null;
}
}
JDK8中增加了一套全新的日期时间API,这套API设计合理,是线程安全的。
新的日期和时间API位于java.time包中,下面是一些管件类。
Java中使用的历法是ISO 8601日历系统,它是世界民用历法,也就是我们所说的公历。平年有365天,闰年有366天。此外Java8还提供了4条其他历法,分别是:
LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime类的实例是不可变的对象,分别表示ISO 8601日历系统的日期、时间、日期和时间。它们提供了简单的日期或时间,并不包含当前的时间信息,也不包含和时区相关的信息。
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
public class DateTimeDemo {
@Test
public void testLocalDate() {
//LocalDate:表示日期,有年、月、日
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2011, 11, 11);
System.out.println("date = " + date);
int year = now.getYear();
System.out.println("year = " + year);
int month = now.getMonth().getValue();
System.out.println("month = " + month);
month = now.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("month = " + month);
int day = now.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("day = " + day);
}
@Test
public void testLocalTime() {
//LocalTime:表示时间,有时、分、秒
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(15, 30, 11);
System.out.println("time = " + time);
int hour = now.getHour();
System.out.println("hour = " + hour);
int minute = now.getMinute();
System.out.println("minute = " + minute);
int second = now.getSecond();
System.out.println("second = " + second);
int nano = now.getNano();
System.out.println("nano = " + nano);
}
@Test
public void testLocalDateTime() {
//LocalDateTime:表示日期时间,有年、月、日、时、分、秒
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2011, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11);
System.out.println("dateTime = " + dateTime);
int year = now.getYear();
System.out.println("year = " + year);
int month = now.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("month = " + month);
month = now.getMonth().getValue();
System.out.println("month = " + month);
int day = now.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("day = " + day);
int hour = now.getHour();
System.out.println("hour = " + hour);
int minute = now.getMinute();
System.out.println("minute = " + minute);
int second = now.getSecond();
System.out.println("second = " + second);
int nano = now.getNano();
System.out.println("nano = " + nano);
}
/**
* 修改时间
*/
@Test
public void testLocalDateTime2() {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = now.withYear(2021).withMinute(5);
System.out.println("now = " + now);
System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = now.plusYears(1);
System.out.println("localDateTime1 = " + localDateTime1);
}
/**
* 比较时间
*/
@Test
public void testLocalDateTime3() {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now().plusYears(1);
boolean before = now.isBefore(localDateTime);
System.out.println("before = " + before);
}
}
通过java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter类可以进行日期时间解析和格式化。
示例:
package com.sunxiaping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class DateTimeFormatterDemo {
@Test
public void test() {
DateTimeFormatter df = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//格式化 调用LocalDateTime
String format = now.format(df);
System.out.println("format = " + format);
//解析 调用LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse(format, df);
System.out.println("parse = " + parse);
//格式化
format = df.format(now);
System.out.println("format = " + format);
//解析
parse = df.parse(format, LocalDateTime::from);
System.out.println("parse = " + parse);
}
}
Instant时间戳/时间线,内部保存了从1970年1月1日 00:00:00 以来的秒和纳秒。
示例:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.Instant;
public class DateTimeDemo {
@Test
public void test() {
//Instance内部保存了秒和纳秒,一般不是给用户使用的,而是方便我们程序做一些统计
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println("now = " + now);
Instant instant = now.plusSeconds(20);
System.out.println("instant = " + instant);
long epochSecond = now.getEpochSecond();
System.out.println("epochSecond = " + epochSecond);
int nano = now.getNano();
System.out.println("nano = " + nano);
}
}
Duration:用于计算2个时间(LocalTime,Instant等)的距离。
Period:用于计算2个日期(LocalDate)的距离。
示例:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.Period;
public class DateTimeDemo {
@Test
public void test() {
Duration duration = Duration.between(LocalTime.now(), LocalTime.now().plusSeconds(60));
System.out.println("相差天 = " + duration.toDays());
System.out.println("相差小时 = " + duration.toHours());
System.out.println("相差分钟 = " + duration.toMinutes());
System.out.println("相差毫秒 = " + duration.toNanos());
System.out.println("相差秒 = " + duration.getSeconds());
Period period = Period.between(LocalDate.now(), LocalDate.now().plusDays(2).plusMonths(2));
System.out.println("相差年 = " + period.getYears());
System.out.println("相差月 = " + period.getMonths());
System.out.println("相差日 = " + period.getDays());
}
}
有时我们可能需要获取例如:将日期调整到下一个月的第一天等操作。可以通过时间校正器来进行。
TemporalAdjuster:时间校正器。
TemporalAdjusters:该类通过静态方法提供了大量的常用TemporalAdjuster的实现。
示例:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters;
public class DateTimeDemo {
@Test
public void test() {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//将日期和时间调整到"下一个月的第一天"
LocalDateTime localDateTime = now.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfNextMonth());
System.out.println("localDateTime = " + localDateTime);
}
}
JDK8中加入了对时区的支持,LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTIme是不带时区的,带时区的日期时间类分别是ZonedDate、ZonedTime、ZonedDateTime。
其中每个时区都对应的ID,ID的格式是“区域/城市”,比如:Asia/Shanghai等。
ZoneId:该类中包含了所有的时区信息。
示例:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.time.Clock;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class DateTimeDemo {
@Test
public void test() {
//获取所有的时区信息
ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds().forEach(System.out::println);
//获取当前默认的时区
String id = ZoneId.systemDefault().getId();
System.out.println("默认的时区id = " + id);
//不带时区,获取计算机的当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("不带时区的当前时间 = " + now);
//操作带时区的类
ZonedDateTime bz = ZonedDateTime.now(Clock.systemUTC());
System.out.println("世界标准时间 = " + bz);
ZonedDateTime time = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println("带时区的当前时间 = " + time);
//修改时区
ZonedDateTime dateTime = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("America/Los_Angeles"));
//withZoneSameInstant既改时区,也改时间
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = dateTime.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.systemDefault());
//withZoneSameLocal只改时区
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1 = dateTime.withZoneSameLocal(ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println("修改时区和时间 = " + zonedDateTime);
System.out.println("只改时区 = " + zonedDateTime1);
}
}
自从JDK5中引入注解依赖,注解开始变得非常流行,并在各个框架和项目中被广泛使用。不过注解有一个很大的限制是:在同一个地方不能多次使用同一个注解。JDK8引入重复注解的概念,允许在同一个地方多次使用同一个注解。在JDK8中使用@Repeatable注解定义重复注解。
重复注解的使用步骤:
1??定义重复注解的容器注解:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* 定义重复注解的容器
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTests {
MyTest[] value();
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
/**
* 定义重复注解
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Repeatable(MyTests.class)
public @interface MyTest {
String value();
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.io.Serializable;
@MyTest("aa")
@MyTest("bb")
@MyTest("cc")
public class Person implements Serializable {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", age=" + age +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class RepeatableAnnotationDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//getAnnotationsByType是新增的API,用于获取重复的注解
MyTest[] myTests = Person.class.getAnnotationsByType(MyTest.class);
Arrays.stream(myTests).map(MyTest::value).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
JDK8为@Target元注解新增了两种类型:TYPE_PARAMETER和TYPE_USE。
TYPE_PARAMETER:表示该注解能写在类型参数的声明语句中。
TYPE_USE:表示注解可以在任何用到类型的地方使用。
示例:
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER)
public @interface TypeParam {
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class Demo02<@TypeParam T> {
public <@TypeParam E> void test(){
}
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE_USE)
public @interface TypeUse {
}
package com.sunxaiping.jdk8;
public class Demo02<@TypeUse T> {
public <@TypeUse E> void test(){
}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuweiweiwoaini/p/13660384.html