ApplicationContext具有发布事件的能力。这是因为该接口继承了ApplicationEventPublisher接口。Spring中与事件有关的接口和类主要包括ApplicationEvent、ApplicationListener。
定义一个事件的类需要继承ApplicationEvent或者ApplicationContextEvent抽象类,该抽象类中只有一个构造函数,并 且带有一个Object类型的参数作为事件源,并且该事件源不能为null,因此我们需要在自己的构造函数中执行super(Object)。
针对一种事件,可能需要特定的监听器,因此,监听器需要实现ApplicationListener接口。当监听器接收到一个事件的时候,就会执行它的 onApplicationEvent()方法。由于Spring IoC中的事件模型是一种简单的、粗粒度的监听模型,当有一个事件到达时,所有的监听器都会接收到,并且作出响应,如果希望只针对某些类型进行监听,需要 在代码中进行控制。
至此便完成了事件的发布,当ApplicationContext接收到事件后,事件的广播是Spring内部给我们做的,不需要了解具体的细节。其实在 Spring读取配置文件之后,利用反射,将所有实现ApplicationListener的Bean找出来,注册为容器的事件监听器。当接收到事件的 时候,Spring会逐个调用事件监听器。剩下要做的就是在配置文件中配置监听器
一.基于xml方式
1.ApplicationEvent类的子类
public class UserEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private int age; private String name; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public UserEvent(Object source, int age, String name) { super(source); this.age = age; this.name = name; } }
2.监听器类
public class UserListener implements ApplicationListener { public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if(event instanceof UserEvent) { UserEvent userEvent = (UserEvent)event; Integer age = userEvent.getAge(); String name = userEvent.getName(); System.out.println("age " +age +" name " +name); } } }
3.配置文件中注册
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id = "userListener" class="com.itheima.test.UserListener"></bean> </beans>
4.测试类
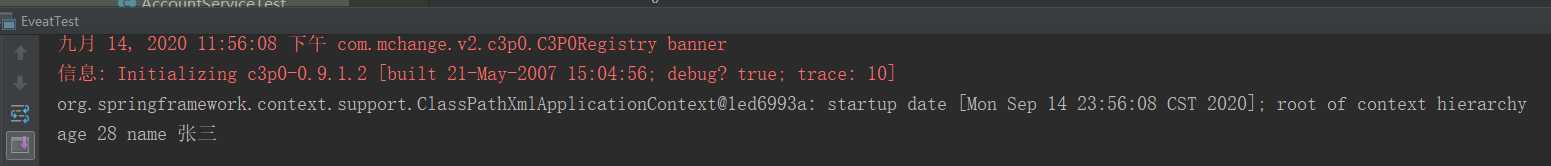
public class EveatTest { public static void main(String []args) { ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); // ApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(EventConfig.class); System.out.println(context); UserEvent userEvent = new UserEvent("object",28,"张三"); context.publishEvent(userEvent); } }
二.基本注解方式
1.ApplicationEvent类的子类
public class UserEvent extends ApplicationEvent
{
private int age;
private String name;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public UserEvent(Object source, int age, String name) {
super(source);
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
2.监听器类
@Component
public class UserListener implements ApplicationListener {
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if(event instanceof UserEvent) {
UserEvent userEvent = (UserEvent)event;
Integer age = userEvent.getAge();
String name = userEvent.getName();
System.out.println("age " +age +" name " +name);
}
}
}
3.配置文件
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima.test") public class EventConfig { }
4.测试类
public class EveatTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
// ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
ApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(EventConfig.class);
System.out.println(context);
UserEvent userEvent = new UserEvent("object",28,"张三");
context.publishEvent(userEvent);
}
}

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/liuyi13535496566/p/13670284.html