Http代理,正向代理 和 反向代理:作为web服务器最常用的功能之一,尤其是反向代理。
正向代理:
正向代理类似一个跳板机,代理访问外部资源。
我是一个用户,我访问不了某网站,但是我能访问一个代理服务器,这个代理服务器呢,他能访问那个我不能访问的网站,于是我先连上代理服务器,告诉他我需要那个无法访问网站的内容,代理服务器去取回来,然后返回给我。从网站的角度,只在代理服务器来取内容的时候有一次记录,有时候并不知道是用户的请求,也隐藏了用户的资料,这取决于代理告不告诉网站。
正向代理 是一个位于客户端和原始服务器(origin server)之间的服务器,为了从原始服务器取得内容,客户端向代理发送一个请求并指定目标(原始服务器),然后代理向原始服务器转交请求并将获得的内容返回给客户端。客户端必须要进行一些特别的设置才能使用正向代理。
用途:
(1)访问原来无法访问的资源,如google
(2) 可以做缓存,加速访问资源
(3)对客户端访问授权,上网进行认证
(4)代理可以记录用户访问记录(上网行为管理),对外隐藏用户信息
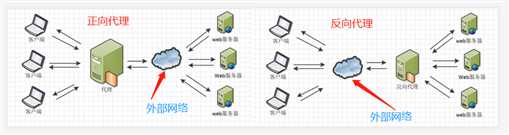
反向代理:
初次接触方向代理的感觉是,客户端是无感知代理的存在的,反向代理对外都是透明的,访问者者并不知道自己访问的是一个代理。因为客户端不需要任何配置就可以访问。
反向代理(Reverse Proxy)实际运行方式是指以代理服务器来接受internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个服务器。
作用于用途:
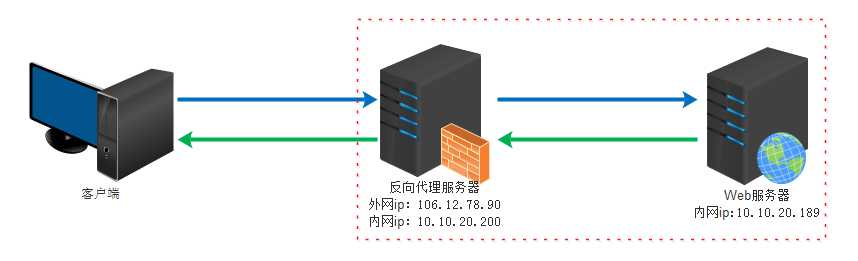
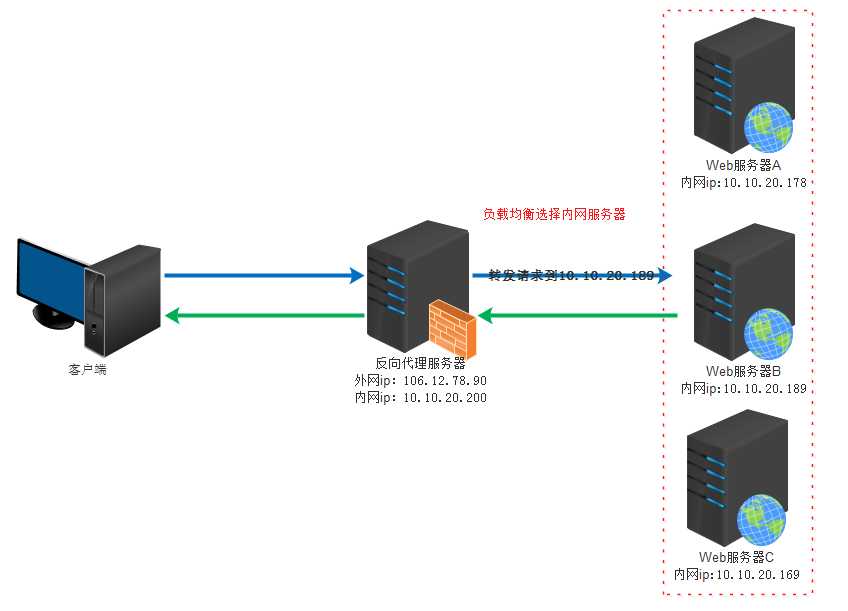
版本
nginx -v
测试配置文件格式是否正确
nginx -t
启动
nginx.exe 或者 start nginx
重启
nginx -s reload
停止
nginx -s stop
#user nobody; // 运行用户
worker_processes 1; // 启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的核心数相等
// 全局错误日志及PID文件
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
// 工作模式及连接数上限
events {
worker_connections 1024; // 单个后台worker process进程的最大并发链接数
}
// 设定http服务器,利用它的反向代理功能提供负载均衡支持
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘
# ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘
# ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘;
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65; // 连接超时时间
// 开启gzip压缩
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
// 默认请求
location / {
root html; // 定义服务器的默认网站根目录位置
index index.html index.htm; //定义首页索引文件的名称
}
// 如果请求地址是 /admin 开始的时候走这个配置代理
location /admin {
proxy_pass https:www.baidu.com;
}
// 如果location 是以api 开始的有要代理到其他地方
location /api {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
proxy_set_hearder Host $host; //将header里面的Host字段传递过去;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
# 定义错误提示页面
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache‘s document root
# concurs with nginx‘s one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/kgwei520blog/p/13673984.html