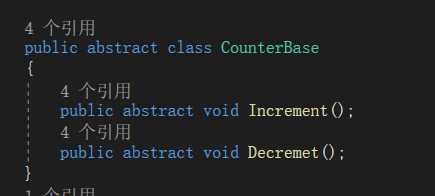
1.我们先定义一个抽象类,定义两个抽象方法用于实现加减,如下:
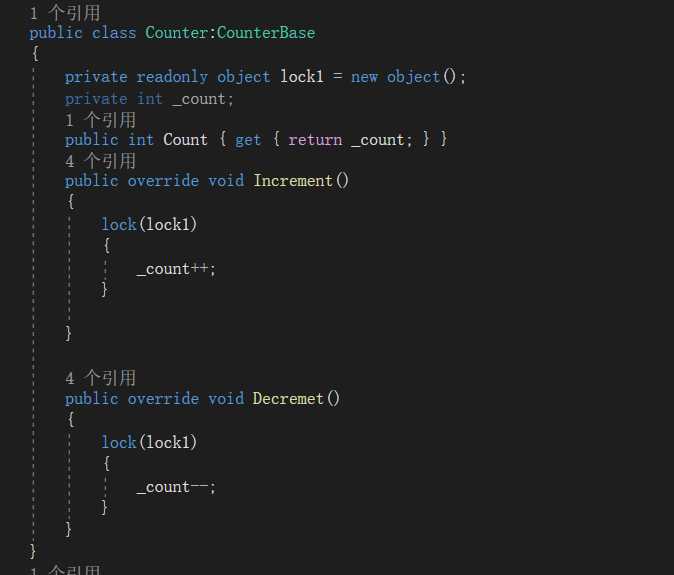
2.然后新建两个类继承抽象类并实现抽象方法:
1>定义的类实现的方法使用lock锁定一次只能有一个线程操作,其它线程则等待。
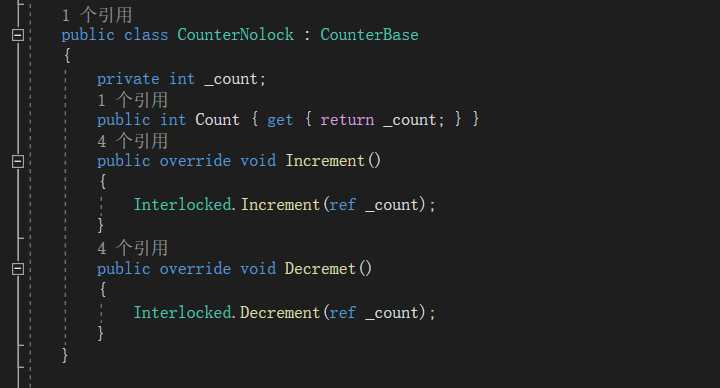
2>定义的类实线的方法使用Interlocked如下:
3.最后在Main方法中编写如下代码:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var c = new Counter();
var t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter1(c));
var t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter1(c));
var t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter1(c));
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
t3.Start();
t1.Join();
t2.Join();
t3.Join();
Console.WriteLine("total1 count{0}", c.Count);
var c1 = new CounterNolock();
var m1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1));
var m2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1));
var m3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1));
m1.Start();
m2.Start();
m3.Start();
m1.Join();
m2.Join();
m3.Join();
Console.WriteLine("total2 count{0}", c1.Count);
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void TestCounter(CounterBase c)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
c.Increment();
c.Decremet();
}
}
static void TestCounter1(CounterBase c)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
c.Increment();
c.Decremet();
}
}
当程序启动时会创建三个线程,由于Counter不是线程安全的,会有相互竞争的情况,所以计算的结果值不是确定的。而CounterNoLock借助Interlocked类,我们无需锁定即可得到正确的结果。
借助Interlocked 类不用阻塞线程即可避免竞争条件——执行基本的原子操作
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/a2502971/p/13681916.html