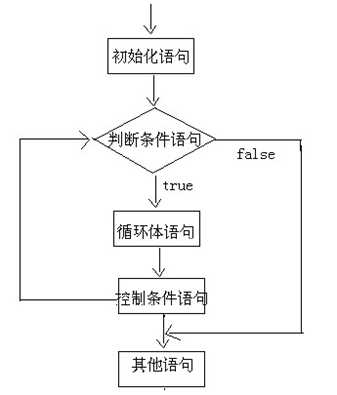
for(初始化语句;判断条件语句;控制条件语句) {
循环体语句;
}
1):执行初始化语句
2):执行判断条件语句,看其结果是true还是false
如果是false,循环结束。
如果是true,继续执行。
3):执行循环体语句
4):执行控制条件语句
5):回到B继续
package com.test.day03;
/*
* for循环语句格式:
* for(初始化语句;判断条件语句;控制条件语句) {
* 循环体语句;
* }
*
* 执行流程:
* A:执行初始化语句
* B:执行判断条件语句,看结果是true还是false
* 如果是true,就继续执行
* 如果是false,就结束循环
* C:执行循环体语句
* D:执行控制条件语句
* E:回到B继续
*
* 需求:
* 在控制台输出10次”HelloWorld”的案例。
*/
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 原始写法
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
System.out.println("-------------------------");
// 用循环改进
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
}
}
示例代码。仅供参考
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 需求:获取数据1-5和5-1
*/
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 原始做法
System.out.println(1);
System.out.println(2);
System.out.println(3);
System.out.println(4);
System.out.println(5);
System.out.println("-------------");
// 用循环改进
for (int x = 1; x <= 5; x++) {
System.out.println(x);
}
System.out.println("-------------");
// 1-5的数据我们获取到了,如何获取5-1呢?
for (int x = 5; x >= 1; x--) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
示例代码。仅供参考
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 需求:求出1-5之间数据之和
*
* 分析:
* A:定义求和变量,初始化值是0
* B:获取1-5之间的数据,用for循环实现
* C:把每一次获取到的数据,累加起来就可以了
* D:输出求和变量即可
*/
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义求和变量,初始化值是0
int sum = 0;
// 获取1-5之间的数据,用for循环实现
for (int x = 1; x <= 5; x++) {
// 把每一次获取到的数据,累加起来就可以了
// sum = sum + x;
/*
* 第一次:sum = 0 + 1 = 1 第二次:sum = 1 + 2 = 3 第三次:sum = 3 + 3 = 6 第四次:sum = 6 + 4 =
* 10 第五次:sum = 10 + 5 = 15
*/
sum += x;
}
// 输出求和结果
System.out.println("sum:" + sum);
}
}
示例代码。仅供参考
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 需求:求出1-100之间偶数和
*
* 分析:
* A:定义求和变量,初始化值是0
* B:获取1-100之间的数据,用for循环实现
* C:把获取到的数据进行判断,看是否是偶数
* 如果是,就累加
* D:输出求和结果
*/
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义求和变量,初始化值是0
int sum = 0;
// 获取1-100之间的数据,用for循环实现
for (int x = 1; x <= 100; x++) {
// 把获取到的数据进行判断,看是否是偶数
if (x % 2 == 0) {
sum += x;
}
}
// 输出求和结果
System.out.println("sum:" + sum);
}
}
示例代码。仅供参考
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 需求:在控制台输出所有的”水仙花数”
*
* 分析:
* 什么是水仙花数呢?
* 所谓的水仙花数是指一个三位数,其各位数字的立方和等于该数本身。
* 举例:153就是一个水仙花数。
* 153 = 1*1*1 + 5*5*5 + 3*3*3
*
* A:三位数其实就告诉了我们水仙花数的范围
* 100-999
* B:如何获取一个数据的每一个位上的数呢?
* 举例:我有一个数据153,请问如何获取到个位,十位,百位
* 个位:153%10 = 3;
* 十位:153/10%10 = 5;
* 百位:153/10/10%10 = 1;
* 千位:...
* 万位:...
* C:让每个位上的立方和相加,并和该数据进行比较,如果相等,就说明该数据是水仙花数,在控制台输出
*/
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 通过循环获取到每一个三位数
for (int x = 100; x < 1000; x++) {
// 获取个位,十位,百位
int ge = x % 10;
int shi = x / 10 % 10;
int bai = x / 10 / 10 % 10;
// 让每个位上的立方和相加,并和该数据进行比较,如果相等,就说明该数据是水仙花数,在控制台输出
if ((ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai * bai) == x) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
}
示例代码。仅供参考
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 需求:统计”水仙花数”共有多少个
*
* 分析:
* A:定义统计变量,初始化值是0
* B:获取三位数,用for循环实现
* C:获取三位数的个位,十位,百位
* D:判断这个三位数是否是水仙花数,如果是,统计变量++
* E:输出统计结果就可以了
*/
public class ForDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义统计变量,初始化值是0
int count = 0;
// 获取三位数,用for循环实现
for (int x = 100; x < 1000; x++) {
// 获取三位数的个位,十位,百位
int ge = x % 10;
int shi = x / 10 % 10;
int bai = x / 10 / 10 % 10;
// 判断这个三位数是否是水仙花数,如果是,统计变量++
if ((ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai * bai) == x) {
count++;
}
}
// 输出统计结果就可以了
System.out.println("水仙花数共有:" + count + "个");
}
}
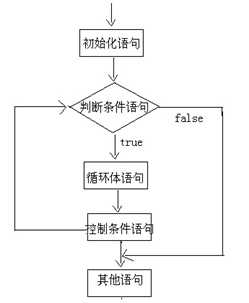
基本格式
while(判断条件语句) {
循环体语句;
}
扩展格式
初始化语句;
while(判断条件语句) {
循环体语句;
控制条件语句;
}
代码案例
package com.test.day03;
/*
* while循环语句的基本格式:
* while(判断条件语句) {
* 循环体语句;
* }
* 扩展格式:
* 初始化语句;
* while(判断条件语句) {
* 循环体语句;
* 控制条件语句;
* }
*
* 回顾for循环的语句格式:
* for(初始化语句;判断条件语句;控制条件语句) {
* 循环体语句;
* }
*/
public class WhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输出10次HelloWorld
/*
* for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) { System.out.println("HellloWorld"); }
*/
// while循环实现
int x = 1;
while (x <= 10) {
System.out.println("HellloWorld");
x++;
}
}
}
1)while循环实现1-100之间数据求和
示例代码,仅供参考
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 求1-100之和。
* 练习:统计水仙花个数。
*/
public class WhileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 回顾for循环实现
/*
* //定义求和变量 int sum = 0; //获取1-100之间的数据 for(int x=1; x<=100; x++) { //累加 sum +=
* x; } System.out.println("1-100的和是:"+sum);
*/
// while循环实现
// 定义求和变量
int sum = 0;
int x = 1;
while (x <= 100) {
sum += x;
x++;
}
System.out.println("1-100的和是:" + sum);
}
}
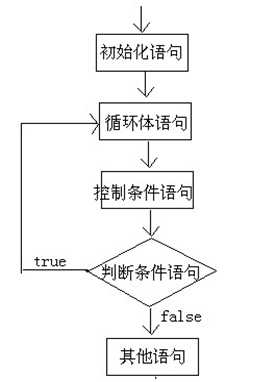
基本格式
do {
循环体语句;
}while((判断条件语句);
扩展格式
初始化语句;
do {
循环体语句;
控制条件语句;
} while((判断条件语句);
package com.test.day03;
/*
* do...while循环的基本格式:
* do {
* 循环体语句;
* }while(判断条件语句);
* 扩展格式:
* 初始化语句;
* do {
* 循环体语句;
* 控制条件语句;
* }while(判断条件语句);
* 执行流程:
* A:执行初始化语句;
* B:执行循环体语句;
* C:执行控制条件语句;
* D:执行判断条件语句,看是true还是false
* 如果是true,回到B继续
* 如果是false,就结束
*
* 练习:
* 求和案例
* 统计水仙花个数
*/
public class DoWhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输出10次 HelloWorld
/*
* for(int x=1; x<=10; x++) { System.out.println("HelloWorld"); }
*/
// do...while改写
int x = 1;
do {
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
x++;
} while (x <= 10);
}
}
虽然可以完成同样的功能,但是还是有小区别:
1)do…while循环至少会执行一次循环体。
2)for循环和while循环只有在条件成立的时候才会去执行循环体
3)for循环语句和while循环语句的小区别:
使用区别:控制条件语句所控制的那个变量,在for循环结束后,就不能再被访问到了,而while循环结束还可以继续使用,如果你想继续使用,就用while,否则推荐使用for。原因是for循环结束,该变量就从内存中消失,能够提高内存的使用效率。
代码案例
package com.test.day03;
/*
* 三种循环的区别:
* A:do...while至少执行一次循环体
* B:for,while循环先判断条件是否成立,然后决定是否执行循环体
*
* for和while的小区别:
* for循环的初始化变量,在循环结束后,不可以被访问。而while循环的初始化变量,是可以被继续使用的。
* 如果初始化变量,后面还要继续访问,就使用while,否则,推荐使用for。
*
* 循环的使用推荐:
* for -- while -- do...while
*/
public class DoWhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* int x = 3; while(x<3) { System.out.println("我爱林青霞"); x++; }
* System.out.println("--------------"); int y = 3; do {
* System.out.println("我爱林青霞"); y++; }while(y<3);
*/
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
System.out.println("爱生活,爱Java");
}
// 这里的x无法继续访问
// System.out.println(x);
System.out.println("-----------------");
int y = 1;
while (y <= 10) {
System.out.println("爱生活,爱Java");
y++;
}
System.out.println(y);
}
}

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/sugarit/p/13686302.html