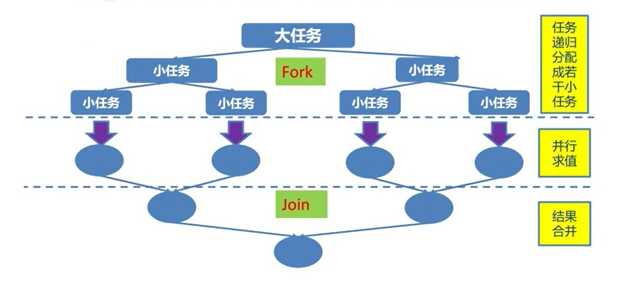
Fork Join 体现了分而治之
什么是分而治之?
规模为N的问题,如果N<阈值,直接解决,N>阈值,将N分解为K个小规模子问题,子问题互相对立,与原问题形式相同,将子问题的解合并得到原问题的解
Fork Join 框架:
就是在必要的情况下,将一个大任务,进行拆分(fork)成若干了小任务(拆到不可再拆时),再将一个个的小任务运算的结果进行join汇总
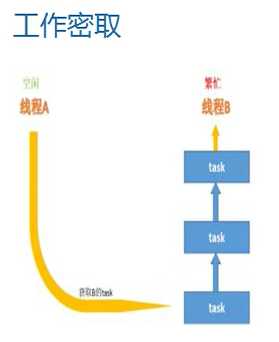
Fork Join的另一大特点:工作密取
什么是工作密取?
就是在按指定阈值拆分后,的多个线程,如果线程A的任务执行的比较快,获得到的CPU时间片比较多,那么在他执行完毕后,就会从未执行完毕的线程的任务中的尾部,进行任务窃取,任务完成后再把结果放回去,不会造成任务竞争,因为自身执行线程的任务是从头部开始获取的,而空闲的线程是从尾部窃取的.
Fork Join使用的标准范式
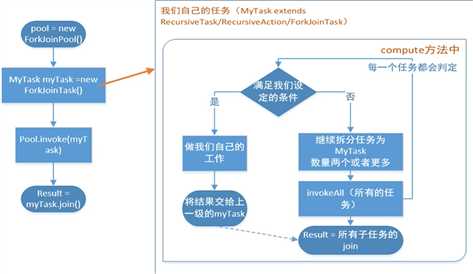
在使用的过程中我们是无法直接new 一个ForkJoinTask类的,他是一个抽象类,但是他提供了两个子类,RecursiveTask和ResursiveAction两个子抽象类.我们使用的时候,如果需要有返回值,我们就继承RecursiveTask,如果不需要返回值我们就继承RecursiveAction
Fork Join实战
Fork Join的同步用法同时演示返回结果值:统计整数数组中所有元素的和
先创建一个工具类用于制作整数数组
package org.dance.day2.forkjoin.sum; import java.util.Random; /** * 数组制作类 * @author ZYGisComputer */ public class MarkArray { public static final int ARRAY_LENGTH = 4000; /** * int数组生成器 * @return int数组 */ public static int[] markArray(){ Random random = new Random(); int[] array = new int[ARRAY_LENGTH]; for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_LENGTH; i++) { array[i] = random.nextInt(ARRAY_LENGTH*3); } return array; } }
然后创建一个单线程的求和类,用于和多线程的对比
package org.dance.day2.forkjoin.sum; import org.dance.tools.SleepTools; /** * 单线程实现求和 * @author ZYGisComputer */ public class SumNormal { public static void main(String[] args) { int count = 0; // 获取数组 int[] src = MarkArray.markArray(); long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < src.length; i++) { // 执行一毫秒的休眠 SleepTools.ms(1); count += src[i]; } System.out.println("The count is "+count+" spend time "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - l)); } }
使用继承RecursiveTask的ForkJoin框架类,完成多线程的求和计算
package org.dance.day2.forkjoin.sum; import org.dance.tools.SleepTools; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask; /** * 使用ForkJoin框架实现求和 * @author ZYGisComputer */ public class SumArray { /** * 因为需要返回值所以继承RecursiveTask类 * 因为计算的是整型,所以泛型是Integer */ private static class SumTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer> { // 计算阈值 private final static int THRESHOLD = MarkArray.ARRAY_LENGTH/10; // 源数组 private int[] src; // 开始坐标 private int fromIndex; // 结束坐标 private int toIndex; /** * 通过创建时传入 * @param src 元素组 * @param fromIndex 开始坐标 * @param toIndex 结束坐标 */ public SumTask(int[] src, int fromIndex, int toIndex) { this.src = src; this.fromIndex = fromIndex; this.toIndex = toIndex; } /** * 覆盖执行方法 * @return 整型 */ @Override protected Integer compute() { // 如果 结束下标减去开始下标小于阈值的时候,那么任务就可以开始执行了 if( toIndex - fromIndex < THRESHOLD ){ int count = 0; // 从开始下标开始循环,循环到结束下标 for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++) { // 休眠1毫秒 SleepTools.ms(1); count += src[i]; } return count; }else{ // 大于阈值 继续拆分任务 // 从formIndex---------------------->到toIndex // 计算中间值,从formIndex----------计算mid------------>到toIndex int mid = (fromIndex + toIndex) / 2; // 左侧任务 从formIndex------------>到mid结束 SumTask left = new SumTask(src, fromIndex, mid); // 右侧任务 从mid+1开始------------->到toIndex结束 SumTask right = new SumTask(src, mid+1,toIndex); // 调用任务 invokeAll(left,right); // 获取结果 return left.join() + right.join(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建ForkJoin任务池 ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(); // 制作源数组 int[] src = MarkArray.markArray(); long l = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 创建一个任务 下标因为从0开始所以结束下标需要-1 SumTask sumTask = new SumTask(src, 0, src.length - 1); // 提交同步任务 Integer invoke = forkJoinPool.invoke(sumTask); // 无论是接收invoke方法的返回值还是调用任务的Join方法都可以获取到结果值 System.out.println("The count is "+invoke+" spend time "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - l)); System.out.println("The count is "+sumTask.join()+" spend time "+(System.currentTimeMillis() - l)); } }
运行结果对比:
现在是4000大小的数组,每次循环休眠1毫秒
单线程执行的结果:
The count is 23751855 spend time 5395
多线程执行的结果:
The count is 23387745 spend time 1487
The count is 23387745 spend time 1487
结果对比多线程比单线程快大概3倍的时间
接下来我们去掉休眠时间,再次进行结果对比:
单线程执行结果:
The count is 23460518 spend time 0
多线程执行结果:
The count is 24078313 spend time 3
The count is 24078313 spend time 3
然后我们惊奇的发现,多线程比单线程还要慢,为什么呢,是因为在小数据量的情况下,单线程,执行期间没有花费上下文切换时间,多线程执行期间是需要花费线程之间上下文切换的时间的,每次上下文切换时间之前说过,大概花费5000-20000个时钟周期的,所以多线程执行会比单线程慢一些,所以说我们在用多线程的时候,就需要考虑线程之间的上下文切换问题,并不一定多线程就一定是好,我们只是看需求,而选择,就像Redis一样设计的时候就是单线程的,但是他的强大,却是比多线程的memcached更加强大,所以说没有肯定的结论,只有适合和不适合.
接下来我们往大调整整型数组的大小
4000调整为1亿,然后对比结果
单线程执行结果:
The count is -331253431 spend time 51
多线程执行结果:
The count is 75277814 spend time 49
The count is 75277814 spend time 50
我们可以发现,所用的执行时间,已经大概一致了
继续调大1亿调整为3亿,继续对比结果
单线程执行结果:
The count is 57724808 spend time 205
多线程执行结果:
The count is 1028352167 spend time 106
The count is 1028352167 spend time 106
现在单线程已经是多线程的执行时间的两倍了,由此可见,当数据量越来越大的时候,单线程的性能往往就会逐渐降低,而多线程的优势就渐渐体现出来了
所谓的同步用法就是在调用
forkJoinPool.invoke(sumTask);
之后主线程就在这里阻塞了,需要等待,执行完成后,主线程才能继续往下执行,接下里我们看异步用法
Fork Join的异步用法同时演示不要求返回值:遍历指定目录(含子目录)寻找指定类型文件
package org.dance.day2.forkjoin; import org.dance.tools.SleepTools; import java.io.File; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool; import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveAction; /** * 使用ForkJoin框架实现不定个数的任务执行 * @author ZYGisComputer */ public class FindDirsFiles { /** * 因为搜索文件不需要返回值,所以我们继承RecursiveAction */ private static class FindFilesByDirs extends RecursiveAction{ private File path; public FindFilesByDirs(File path) { this.path = path; } @Override protected void compute() { // 创建任务容器 List<FindFilesByDirs> findFilesByDirs = new ArrayList<>(); // 获取文件夹下所有的对象 File[] files = path.listFiles(); if(null!=files){ for (File file : files) { // 判断是否是文件夹 if (file.isDirectory()){ // 添加到任务容器中 findFilesByDirs.add(new FindFilesByDirs(file)); }else{ // 如果是一个文件,那么检查这个文件是否符合需求 if(file.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".txt")){ // 如果符合 打印 System.out.println("文件:"+file.getAbsolutePath()); } } } // 判断任务容器是否为空 if(!findFilesByDirs.isEmpty()){ // 递交任务组 for (FindFilesByDirs filesByDirs : invokeAll(findFilesByDirs)) { // 等待子任务执行完成 filesByDirs.join(); } } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建ForkJoin池 ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool(); File path = new File("E:/"); // 创建任务 FindFilesByDirs findFilesByDirs = new FindFilesByDirs(path); // 异步调用 这个方法是没有返回值的 forkJoinPool.execute(findFilesByDirs); System.out.println("Task is Running................"); SleepTools.ms(1); // 在这里做这个只是测试ForkJoin是否为异步,当执行ForkJoin的时候主线程是否继续执行 int otherWork = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { otherWork += i; } System.out.println("Main thread done sth.......,otherWork:"+otherWork); // 如果是有返回值的话,可以获取,当然这个join方法是一个阻塞式的,因为主线程执行的太快了,ForkJoin还没执行完成主线程就死亡了,所以在这里调用一下阻塞,等待ForkJoin执行完成 findFilesByDirs.join(); System.out.println("Thread end!"); } }
执行结果:
Task is Running................ Main thread done sth.......,otherWork:4950 文件:E:\dance\activiti-ruoyi\RuoYi-Process\ruoyi-admin\src\main\resources\static\file\rml.txt 文件:E:\dance\activiti-ruoyi\RuoYi-Process\ruoyi-admin\target\classes\banner.txt 文件:E:\dance\activiti-ruoyi\RuoYi-Process\ruoyi-admin\target\classes\static\ajax\libs\jquery-ztree\3.5\log v3.x.txt 文件:E:\dance\activiti-ruoyi\RuoYi-Process\ruoyi-admin\target\classes\static\file\rml.txt ........................ Thread end!
从执行结果中可以看到,主线程的执行时在ForkJoin执行之前就执行了,但是代码中却是在ForkJoin执行之后执行的,所以说这是异步的,线程是并行执行的,异步执行只能通过调用任务线程的Join方法获取返回值,execute方法是没有返回值的
作者:彼岸舞
时间:2020\09\18
内容关于:并发编程
本文来源于网络,只做技术分享,一概不负任何责任
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/flower-dance/p/13692728.html