补充知识:
要理解Gauss消去法,首先来看一个例子:

从上例子可以看出,高斯消去法实际上就是我们初中学的阶二元一次方程组,只不过那里的未知数个数$n=2$
$n>2$时,Gauss消去法的思路实际上和解二元一次方程组是一样的,方法如下:
下面通过一般化得到Gauss消元法的求解过程

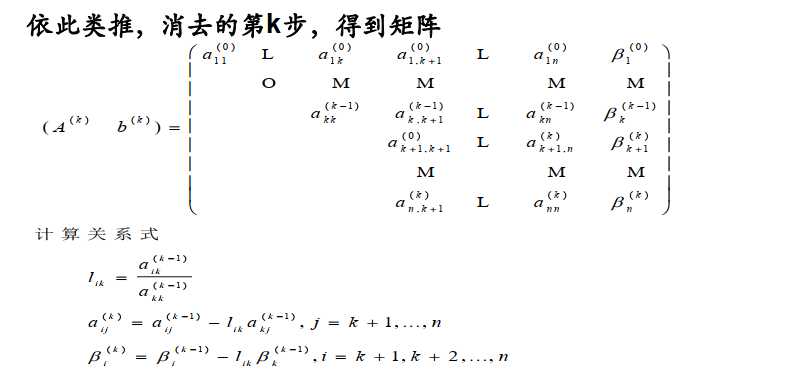

以上就是Gauss消去法的基本步骤,我们再回过头看看有没有什么问题?
我们在求比例$l_{ik}= \frac{a_{ik}^{\left (k-1 \right )}}{a_{kk}^{\left (k-1 \right )}}$时,如果分母很小,即:

$l_{ik}\rightarrow \infty$,那么
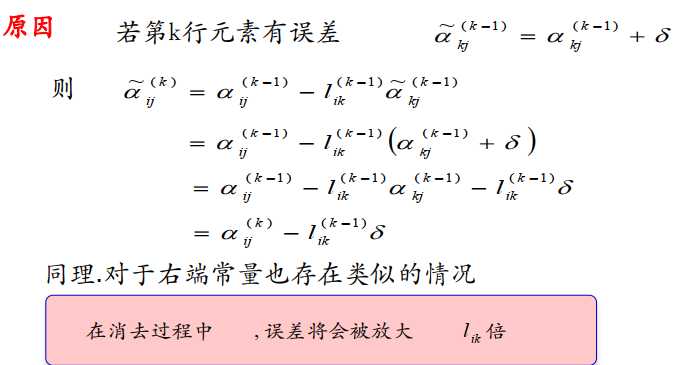
总结一下,能否使用Gauss消元法的情况

为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用列主元Gauss消元法。

参考了一些网上的代码,这里给出Gauss的Java实现
package peterxiazhe; import java.util.Scanner; public class Gauss { /** * 列主元高斯消去法 */ static double A[][]; static double b[]; static double x[]; static int n; //n表示未知数的个数 static int n_2; //记录换行的次数 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("--------------输入方程组未知数的个数---------------"); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); n = sc.nextInt(); A = new double[n][n]; b = new double[n]; x = new double[n]; System.out.println("--------------输入方程组的系数矩阵A:---------------"); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { A[i][j] = sc.nextDouble(); } } System.out.println("--------------输入方程组的常量向量b:---------------"); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { b[i] = sc.nextDouble(); } Elimination(); BackSubstitution(); PrintRoot(); } //消元法 public static void Elimination() { PrintA(); for(int k = 0; k < n; k++) { WrapRow(k); for(int i = k+1; i < n; i++) { double l = A[i][k] / A[k][k]; A[i][k] = 0; for(int j = k+1; j < n; j++) { A[i][j] = A[i][j] - l * A[k][j]; } b[i] = b[i] - l * b[k]; } //System.out.println("第" + k + "次消元后:"); //PrintA(); } } //回代法 public static void BackSubstitution() { x[n-1] = b[n-1] / A[n-1][n-1]; for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) { x[i] = (b[i] - solve(i)) / A[i][i]; } } public static double solve(int i) { double result = 0.0; for(int j = i; j < n; j++) result += A[i][j] * x[j]; return result; } //输出方程组的根 public static void PrintRoot() { System.out.println("--------------方程组的根为---------------"); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { System.out.println("x" + (i+1) + " = " + x[i]); } } //交换Swap函数??? public static void Swap(double[] ar, int x, int y) { Double tmp = ar[x]; ar[x] = ar[y]; ar[y] = tmp; } public static void PrintA() { //输出A的增广矩阵 //System.out.println("--------------增广矩阵---------------"); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.print(A[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(b[i]); } } //交换矩阵的行 public static void WrapRow(int k) { //k表示第k+1轮消元 double maxElement = Math.abs(A[k][k]); int WrapRowIndex = k; // 记住要交换的行 for(int i = k + 1; i < n; i++) { if (Math.abs(A[i][k]) > maxElement) { WrapRowIndex = i; maxElement = A[i][k]; } } if (WrapRowIndex != k) { //交换求得最大主元 n_2 += 1; System.out.println("k = " + k + "时," + "要交换的行为" + k + "和"+ WrapRowIndex); //先交换A for(int j = k; j < n; j++) { double[] arr = {A[k][j], A[WrapRowIndex][j]}; Swap(arr, 0, 1); A[k][j] = arr[0]; A[WrapRowIndex][j] = arr[1]; // double tmp = A[k][j]; // A[k][j] = A[WrapRowIndex][j]; // A[WrapRowIndex][j] = tmp; } //再交换b double[] arr = {b[k], b[WrapRowIndex]}; Swap(arr, 0, 1); b[k] = arr[0]; b[WrapRowIndex] = arr[1]; // double tmp = b[k]; // b[k] = b[WrapRowIndex]; // b[WrapRowIndex] = tmp; System.out.println("--------------交换后---------------"); PrintA(); } } }
注意:由于Java不支持对基本数据类型的引用传递,这里使用了一个小技巧。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiazhenbin/p/13692242.html