作用:
全局配置文件能够对一些默认配置值进行修改,也可以对自定义属性值进行注入
配置文件位置:
src/main/resource
类路径下的/config
application.properties
默认配置值的修改
可定义一些SpringBoot项目的相关属性:系统属性、环境变量、命令参数、自定义配置文件名称和位置等
server.address=
server.port=
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=
spring.config.additional-location=
spring.config.location=
spring.config.name=
自定义属性值的注入
宠物类:Pet.java
人类:Person.java
配置文件:application.properties
person.id=1
person.name=andy
person.hobby=play,keeping,run
person.family=father,mother
person.map.k1=v1
person.map.k2=v2
person.pet.type=cat
person.pet.name=miao
测试类
application.yaml
概念
SpringBoot支持的一种JSON超集文件格式
以数据为核心,更为直观且容易被计算机识别的数据序列化格式
格式:“ key:(空格) value”,使用缩进控制层级关系‘
写法
1、值为普通数据类型(数字、字符串、布尔等)
字符串不需要额外添加引号
person
2、值为数组和单列集合
缩进式写法
person
行内式写法,[] 可省略
person
3、值为Map集合或对象
缩进式写法
person:
map:
k1: v1
k2: v2
行内式写法
person:
map: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
默认配置值的修改
server
自定义属性值的注入
宠物类同上
人类同上
application.yaml
person
测试类
使用SpringBoot全局配置文件配置属性时,如果配置的属性是SpringBoot默认提供的属性,那么SpringBoot内部会自动扫描并读取属性值
如果配置的是用户自定义的属性,则需要在程序中注入这些配置属性方可生效
1、使用@ConfigurationProperties()注入属性
SpringBoot提供的注解
将配置文件中自定义的属性值批量注入某个Bean对象的多个对应属性中
要保证配置文件中的属性与对应实体类的属性名一致
测试
properties文件
person.id=1
person.name=andy
实体类
2、使用@Value注入属性
Spring框架提供的
用来读取配置文件中的属性值并逐个注入Bean对象的对应属性中
SpringBoot框架默认继承了该注解
测试
实体类
3、两种注解对比分析
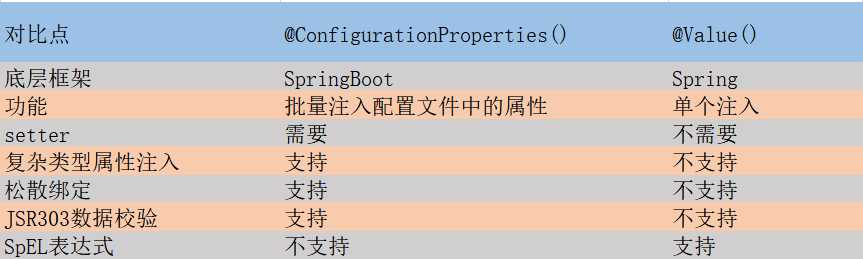
松散绑定
@ConfigurationProperties支持松散绑定语法
如果Person类中有一个字符串类型的属性为firstName,在配置文件中进行配置时可以使用如下配置方式
person.firstName=hmx
person.first-name=hmx
person.first_name=hmx
person.FIRST_NAME=hmx
person
JSR303数据校验
@ConfigurationProperties支持JSR303数据校验
校验配置文件中注入对应Bean属性的值是否符合相关值得规则
需要引入Spring框架支持的数据校验规则:@Validated
//空检查
1、@Null:验证对象是否为null
2、@NotNull:验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
3、@NotBlank:检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
4、@NotEmpty:检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
?
//Booelan检查
1、@AssertTrue:验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
2、@AssertFalse:验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
?
//长度检查
1、@Size(min=, max=):验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
2、@Length(min=, max=):验证带批注的字符串是否介于包含的最小值和最大值之间。
?
//日期检查
1、@Past:验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
2、@Future:验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
3、@Pattern:验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
?
//数值检查
//建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上
//因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为"",Integer为null
?
1、@Min:验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值
2、@Max:验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值
3、@DecimalMax:被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值.
这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
4、@DecimalMin:被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值.
这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
5、@Digits:证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法
6、@Digits(integer=,fraction=):验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字
interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。
7、@Range(min=, max=):检查数字是否介于min和max之间.
?
1、@Range(min=10000,max=50000,message="range.bean.wage")
2、@Valid:递归的对关联对象进行校验,
如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验
如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证)
3、@CreditCardNumber:信用卡验证
4、@Email:验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。
5、@ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=)
6、@URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
SpEL表达式
@Value支持SpEL表达式语法,即“#{xx}”
使用@PropertySource加载配置文件
指定自定义配置文件的位置和名字
测试
实体类
配置文件
properties
测试类
使用@ImportResource加载XML配置文件
传统的Spring项目配置主要基于XML文件
SpringBoot框架默认不再使用XML文件配置项目,且XML文件不会加载到Spring容器中
@ImportResource注解标注在一个配置类上通常放在应用启动类上,使用时需要指定XML配置文件的路径和名称
测试
实体类
public class MyService {
}
XML配置文件
主程序启动类
//加载自定义XML配置文件位置
测试类
使用@Configuration编写自定义配置类
指定配置类
@Bean注解方法返回的对象都将作为Bean注入Spring容器
默认情况下,使用@Bean注解的方法名就是组件名
测试
实体类
public class MyService {
}
配置类
//定义该类是一个配置类
测试类
两种方式不会互相干扰
使用Profile文件进行多环境配置
使用方式一:多properties文件
配置文件名必须满足application-{profile}.properties的格式,{profile}对应具体的环境标识
application-dev.properties
application-test.properties
application-prod.properties
激活环境配置
命令行
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
全局配置文件application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev
测试
application-dev.properties
server.port=8081
application-test.properties
server.port=8082
application-prod.properties
server.port=8083
application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev
控制台输出
Tomcat started on port(s): 8081 (http) with context path ‘‘
使用方式二:yaml多文档模式
yaml文件
spring
控制台输出
Tomcat started on port(s): 8081 (http) with context path ‘‘
使用@Profile注解进行多环境配置
作用于类,并通过value属性指定配置环境
使用@Profile注解配置的环境,需要在全局配置文件中激活
测试
接口类:目的配置数据库
public interface DBConnector {
public void configure();
}
三个实现类:对应三个不同的数据库环境配置
//实现类1
//实现类2
//实现类3
在全局配置文件中激活环境配置
spring
测试类
随机值设置
SpringBoot内嵌的RandomValuePropertySource类,对一些隐秘属性值或者测试用例属性值进行随机值注入
语法:${random.xxx}$,xxx表示需要指定生成的随机数类型和范围
//配置随机字符串 ${random.value}
?
//配置随机整数 ${random.int}
?
//配置随机long类型数 ${random.long}
?
//配置随机UUID类型数 ${random.value}
?
//配置小于10的随机整数 ${random.int(10)}
?
//配置范围在【1024,65536】之间的随机整数 ${random.int[1024,65536]}
参数间引用
在多个具有相互关联的配置属性中,只需要对其中一处属性进行预配置,其他地方都可以引用
语法:${xxx},xxx表示先前在配置文件中已经配置过的属性名
app.name = QQ
app.description = ${app.name} is a communication app
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/LittleSkinny/p/13695355.html