本来应该先讲一下 Collection 的其他实现方式的,但相比于 Map 来说,Map 更为常用,先讲一下Map好啦。
java 中的 Map 是用存储 key-value 形式的键值对的,Collection 属于单列集合,而 Map 是双列集合。
Map 中不允许有重复的 key 值,每一个 key 映射一个值。
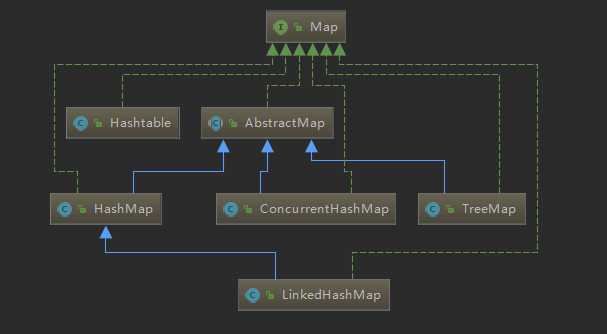
Map 的常用实现类的类图如下所示:
分析一下Map当中的声明方法:
(1)size()
int size(); // 该方法返回的是Map中键值对(key-value)的数量,当键值对的数量超过Integer.MAX_VALUE时,返回的是Integer.MAX_VALUE
(2)isEmpty()
boolean isEmpty(); // 判断Map中是否存在键值对,有的话返回false,没有的话返回true
(3)containsKey(Object key)
boolean containsValue(Object value); // 当Map中存在至少一个键值对的值为value时返回true,不存在时返回false
(4)get(Object key)
V get(Object key); // 返回Map中键对应的值,不存在键时则返回null
(5)put(K key, V value)
V put(K key, V value); // 往Map中存入键值对
(6)remove(Object key)
V remove(Object key); // 根据键删除键值对
(7)putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m); // 将一个Map中的元素全部复制到另一个Map当中去
(8)clear()
void clear(); // 清空Map中的键值对
(9)keySet()
Set<K> keySet(); // 返回Map中键的集合,因为它内部的key是不重复的,因此返回Set
(10)values()
Collection<V> values(); // 与keySet()不同的是,返回的是Map中value集合,元素是可能重复的
(11)entrySet()
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet(); // 返回的是Map中的键值对(Map.Entry)集合
(12)getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue)
/** * @param key Map中将要寻找的键值 * @param defaultValue 没有找到键对应的值时,返回的defaultValue * @return 返回key对应的value值,不存在对应的key时,则返回defaultValue * 注意该方法体是存在已Map接口中的,使用了default进行修饰,在接口中存在方法体,这是java 1.8 所允许的,方法需要被 defalt 或者 static 进行修饰 * @since 1.8 */ default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) { V v; // 判断containsKey(key)是因为在HahMap中允许键值对中的值为null return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) ? v : defaultValue; }
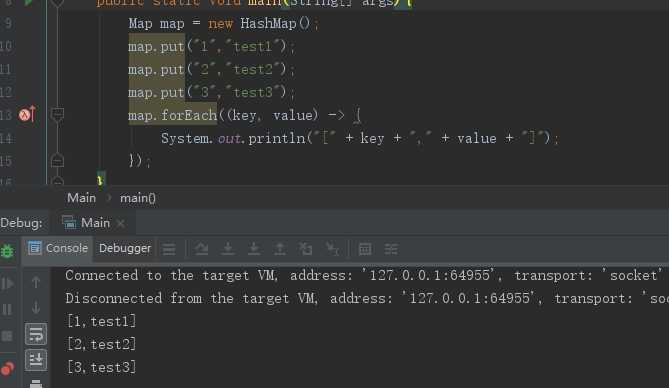
(13)forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action)
/** * 这是java 1.8 开始提供的方法,目的是遍历Map中的键值对,可以看到该方法内部使用的是内部的entrySet()进行遍历,在遍历过程中将key与value传入BiConsumer调用 * * @param action The action to be performed for each entry * removed during iteration * @since 1.8 */ default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) { K k; V v; try { k = entry.getKey(); v = entry.getValue(); } catch(IllegalStateException ise) { // this usually means the entry is no longer in the map. throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise); } action.accept(k, v); } }
使用方法如下:
(14)putIfAbsent(K key, V value)
/** * 先调用get(key) 方法 * 存在几种情况: * 1、Map中不存在对应的key, 调用put(key, value)存入键值对 * 2、Map中存在对应的key,但是对应的值为null,调用put(key, value)存入键值对 * 3、Map中存在对应的key,但是对应的值不为null,则值不会被更新 * 最后返回先前通过 get(key)获取到的返回值 **/ default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) { V v = get(key); if (v == null) { v = put(key, value); } return v; }
剩下的都是java 1.8开始才提供的方法内容,平时很少用到,先不讲了。
讲一下Map.Entry,它是Map中的内部接口,Map中的每个元素都是一个Entry。interface Entry<K,V> {
/** * 返回元素的键(key) */ K getKey(); /** * 返回元素的值(value) */ V getValue(); /** * 设置当前元素的值(value) */ V setValue(V value); /** * 判断两个元素是否相等,即同时判断key和value */ boolean equals(Object o); /** * 返回Hash码,具体在实现中重写*/ int hashCode(); /** * 返回一个根据key比较的Comparator * * @param <K> the {@link Comparable} type of then map keys * @param <V> the type of the map values * @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} in natural order on key. * @see Comparable * @since 1.8 */ public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() { return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey()); } /** * 返回一个根据key比较的Comparator
* * @param <K> the type of the map keys * @param <V> the {@link Comparable} type of the map values * @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} in natural order on value. * @see Comparable * @since 1.8 */ public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() { return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue()); } /** * Returns a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by key using the given * {@link Comparator}. * * <p>The returned comparator is serializable if the specified comparator * is also serializable. * * @param <K> the type of the map keys * @param <V> the type of the map values * @param cmp the key {@link Comparator} * @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by the key. * @since 1.8 */ public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) { Objects.requireNonNull(cmp); return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey()); } /** * Returns a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by value using the given * {@link Comparator}. * * <p>The returned comparator is serializable if the specified comparator * is also serializable. * * @param <K> the type of the map keys * @param <V> the type of the map values * @param cmp the value {@link Comparator} * @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by the value. * @since 1.8 */ public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) { Objects.requireNonNull(cmp); return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable) (c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue()); } }
putIfAbsent(K key, V value)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/guaniu2750/p/13669947.html