log4j-1.2.17.jar
mybatis-3.4.1.jar
mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar
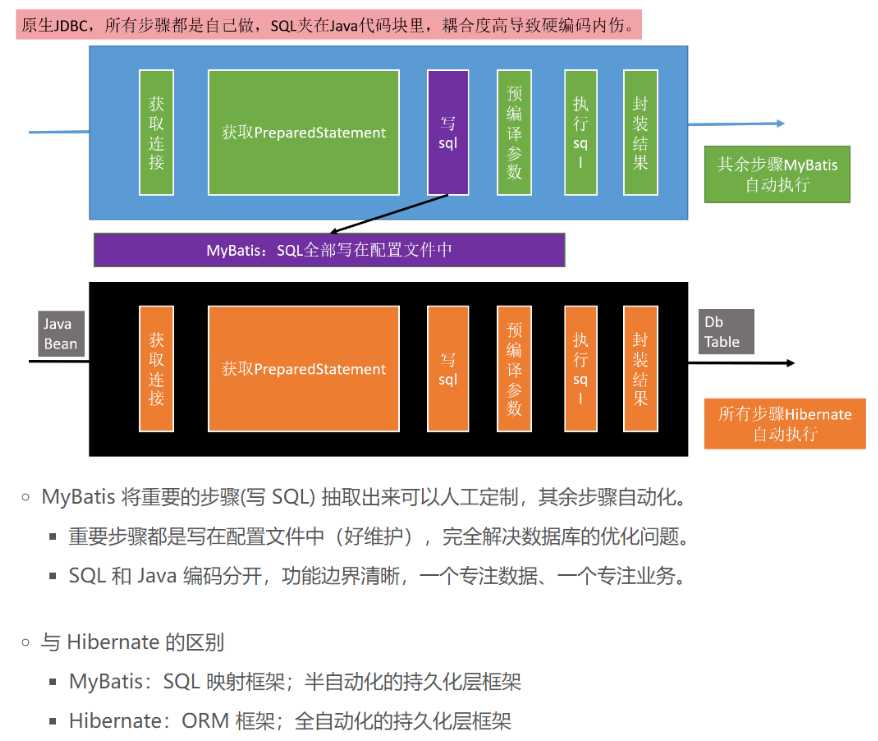
建议导入日志包,如此,在 mybatis 关键环节就会有日志打印。log4j.jar 还依赖类路径下的一个 log4j.xml 的配置文件。
指导 MyBatis 如何正确运行。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 配置连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 注册自己编写的SQL映射文件到全局配置文件中 -->
<mappers>
<!-- resource: 表示从类路径下找资源 -->
<mapper resource="EmployeeDao.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
编写接口中的每一个方法都如何向 DB 发送 SQL 语句。这个配置文件就相当于是接口的实现类。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
namespace(名称空间):写接口的全类名,相当于告诉 MyBatis
这个配置文件是实现哪个接口的 → [接口和XML绑定]
-->
<mapper namespace="cn.edu.nuist.dao.EmployeeDao">
<!--
public Employee getEmpByEid(Integer eid);
···········································
select: 用来定义一个查询操作
id: 唯一标识符,用来引用这条语句,需要和接口的方法名一致。相当于这个配置是对方法的实现
resultType: 指定方法运行后的返回值类型(查询操作必须指定)
标签体:SQL 语句
-->
<select id="getEmpByEid" resultType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid = #{eid}
</select>
<!-- public int updateEmp(Employee emp); -->
<update id="updateEmp">
UPDATE emp SET ename=#{ename}, email=#{email}, gender=#{gender} WHERE eid=#{eid}
</update>
<!-- public int deleteEmp(Integer eid); -->
<delete id="deleteEmp">
DELETE FROM emp WHERE eid=#{eid}
</delete>
<!-- public int insertEmp(Employee emp); -->
<insert id="insertEmp">
INSERT INTO emp(ename, gender, email) VALUES(#{ename}, #{gender}, #{email})
</insert>
</mapper>
public class HelloWorld {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
@Before
public void initSqlSessionFactory() {
try {
// 根据全局配置文件创建一个 SqlSessionFactory
// SqlSessionFactory 是 SqlSession 的工厂,负责创建 SqlSession 对象
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
// 1. 得到 SqlSession 对象:SQL 会话,代表和 DB 的一次会话 // 类比 getConnection()
// SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
// 2. 得到 dao 接口的实现
EmployeeDao employeeDao = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeDao.class);
// 3. 测试CRUD (接口式编程)
// 3.1 查询
Employee emp = employeeDao.getEmpByEid(1);
// System.out.println("查询:" + emp);
// 3.2 更新
emp.setEmail("Finch123@gmail.com");
employeeDao.updateEmp(emp);
// sqlSession.commit(); // 不提交更新操作没效果
// 4. 关闭 SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
sqlSession.commit()
openSession(true) 或者虽使用无参构造器但在操作完成后手动 sqlSession.commit()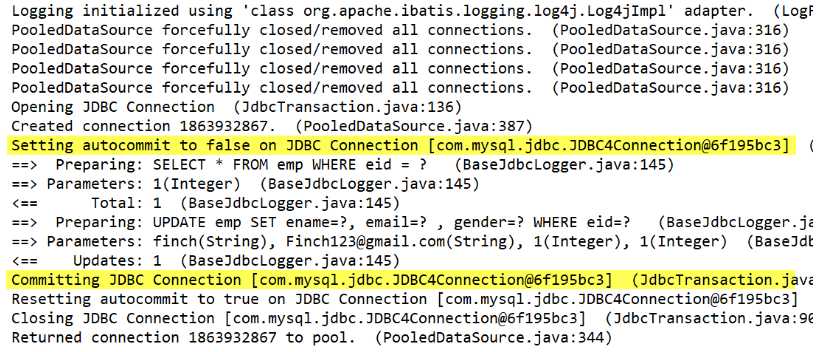
@Test
public void test2() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
EmployeeDao employeeDao = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeDao.class);
// org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy@4566e5bd
System.out.println(employeeDao);
// class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy5
System.out.println(employeeDao.getClass());
}
Dao<I> ← 实现 ← DaoImplMapper<I> ← 绑定 ← XxxMapper.xml文档的顶层结构如下:

引入外部配置文件
dbconfig.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql:///test
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mybatis-config.xml
<!-- resource: 类路径下;url: 网路|磁盘路径下 -->
<properties resource="dbconfig.properties"></properties>
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 配置连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
如果属性在不只一个地方进行了配置,那么 MyBatis 将按照下面的顺序来加载:
因此,通过方法参数传递的属性具有最高优先级,resource/url 属性中指定的配置文件次之,最低优先级的是 properties 属性中指定的属性。
会改变 MyBatis 的运行时行为
以 mapUnderscoreToCamelCase(是否开启自动驼峰命名规则映射,即从数据库列名 A_COLUMN 到 Java 属性名 aColumn 的类似映射)为例:
<settings>
<!-- 默认 false -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
类型别名是为 Java 类型设置一个短的名字,可以方便我们引用某个类。
<typeAlias> 为一个 JavaBean 起别名;不写 alias 属性,则默认别名为简单类名(不区分大小写)。<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Department"/>
<typeAlias type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" alias="emp"/>
</typeAliases>
<package> 可以批量为这个包下的每一个类创建一个默认的别名,就是简单类名(不区分大小写)。<typeAliases>
<package name="cn.edu.nuist.bean"/>
</typeAliases>
@Alias("别名")值得注意的是,MyBatis已经为许多常见的 Java 类型内建了相应的类型别名。它们都是大小写不敏感的,我们在起别名的时候千万不要占用已有的别名。

无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement) 中设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时, 都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型。

日期类型的处理:

可以重写类型处理器或创建你自己的类型处理器来处理不支持的或非标准的类型。
org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler<I> 或继承 org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler=""/>
</typeHandlers>
插件是 MyBatis 提供的一个非常强大的机制,我们可以通过插件来修改 MyBatis 的一些核心行为。插件通过动态代理机制,可以介入四大对象的任何一个方法的执行。
实际开发中我们使用 Spring 管理数据源,并进行事务控制的配置来覆盖下述配置。
<environment> 进行配置并指定唯一标识符 id。<environments> 中的 default 属性指定一个环境的标识符来快速的切换环境。<environments default="mysql">
<!--
id 是当前环境的唯一标识
每一个环境都需要一个事务管理器和一个数据源
-->
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
TransactionFactory<I>,type=全类名/别名DataSourceFactory<I>,定义数据源的获取方式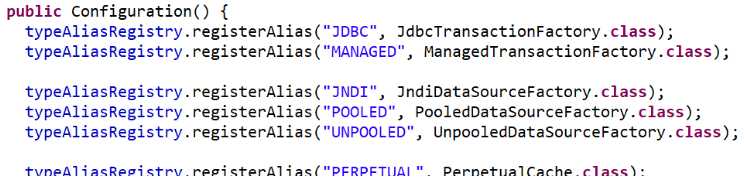
MyBatis 可以根据不同的数据库厂商执行不同的语句。
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<!-- name: 数据库厂商标识 -->
<!-- value: 为标识起一个别名,方便 SQL 语句标签使用 databaseId 属性引用 -->
<property name="MySQL" value="mysql"/>
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlServer"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="orcl"/>
</databaseIdProvider>
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);DatabaseMetaData#getDatabaseProductName() 返回的字符串进行设置。由于通常情况下这个字符串都非常长而且相同产品的不同版本会返回不同的值,所以最好通过设置属性别名来使其变短VendorDatabaseIdProvider 解析数据库厂商标识,也可以通过实现 DatabaseIdProvider<I> 来自定义MyBatis匹配规则如下:
databaseId=nulldatabaseId=配置指定的值,否则依旧为 null<mappers>
<mapper resource="EmployeeDao.xml"/>
<mapper class="file:///D:/EmployeeDao.xml"/>
<mapper class="cn.edu.nuist.dao.EmployeeDao"/>
</mappers>
要求 SQL 映射文件名必须和接口名相同并且在同一目录下。
<mapper>
<package name="cn.edu.nuist.dao"/>
</mappers>

映射文件指导着 MyBatis 如何进行数据库增删改查。
MyBatis 允许接口的增删改方法直接定义 int、long、boolean 及其包装类类型的返回值。

<!--
在支持主键自增的数据库:
useGeneratedKeys="true" 使用自增主键获取主键值策略
底层调用了原生JDBC获取自增主键的方法:ResultSet getGeneratedKeys()
keyProperty="eid" 将刚才自增的主键值封装给 JavaBean 的哪个属性
-->
<insert id="insertEmp" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="eid">
INSERT INTO emp(ename, gender, email) VALUES(#{ename}, #{gender}, #{email})
</insert>

<!-- 不支持主键自增的数据库 -->
<insert id="insertEmp2" databaseId="orcl">
<!-- 提前查询自增主键列的最大值+1 -->
<!--
order="BEFORE" 当前标签体中的 SQL 在 insert-SQL 之前运行
keyProperty 指出查出的主键值赋值给 JavaBean 的哪个属性
resultType 查询结果的数据类型
-->
<selectKey order="BEFORE" resultType="int" keyProperty="eid">
SELECT EMP_SEQ.nextval FROM dual;
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO emp(eid, ename, gender, email)
VALUES(#{eid}, #{ename}, #{gender}, #{email})
</insert>
·····································································
<insert id="insertEmp3" databaseId="orcl">
<!--
order="AFTER" 当前标签体中的 SQL 在 insert-SQL 之后运行
先运行插入SQL → 再拿出当前的主键值赋给 JavaBean 的指定属性
可能会有问题;还是用 BEFORE 吧
-->
<selectKey order="AFTER" resultType="int" keyProperty="eid">
SELECT EMP_SEQ.curravl FROM dual;
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO emp(eid, ename, gender, email)
VALUES(EMP_SEQ.nextval, #{ename}, #{gender}, #{email})
</insert>
#{随便写}{POJO的属性名}Employee getEmpByEidAndEname(eid, ename) 为例
#{参数名} 方式无效,直接抛出异常 ↓;得使用 #{0}, #{param1}BindingException: Parameter ‘eid‘ not found.
Available parameters are [0, 1, param1, param2]
@Param("指定的key")#{key} 即可使用场景:
private static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
// 获取每个标注了@Param注解的参数,将注解的value值赋给name变量
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
// 全局配置: useActualParamName(JDK 8),name=参数名
if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
// name中保存当前参数的索引
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
// 保存进 map
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
// 继而保存到 names 中
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
// 没有参数,方法直接返回
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
// 参数列表上没有@param注解 && 参数只有一个
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
return args[names.firstKey()]; // 单个参数直接返回
} else {
// 遍历构造器初始化好的 names{0=0, 1=1}
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<Object>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
// names 的 value 作为 key,args[names 的 key] 作为 value
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
// #{param1}, #{param2} ... 能拿到的原因 ↓
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
思考:
method(Integer id, @Param("e") Employee emp)
> id → #{param1}
> lastName → #{param2.lastName} | #{e.lastName}
method(@Param("eid")Integer eid, @Param("ename")String ename, Employee emp)
> Integer eid → #{id} | #{param1}
> String ename → #{param2}
> Employee emp(email) → #{param3.email}
method(List<Integer> ids)
> 第一个 id 的值 → #{list[0]}
#{key}:获取参数的值,预编译到 SQL 中。安全。${key}:获取参数的值,拼接到 SQL 中。有 SQL 注入问题SQL 语句不是什么位置都支持预编译的。比如 FROM 的表名、ORDER BY 的字段,,这些地方都不行。这时候,如果要向这些位置传递参数,就必须要用 ${} 的方式:ORDER BY ${paramName}; FROM ${tableName}
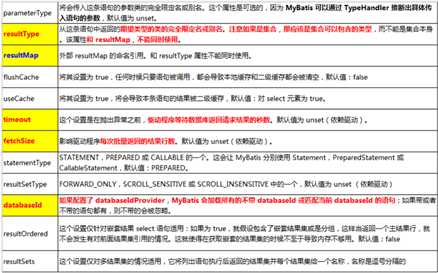
#{...} 更丰富的用法:参数位置支持的属性
javaType、jdbcType、mode、numericScale、resultMap、typeHandler、jdbcTypeName、expression
但实际上通常被设置的只有:可能为空的列名指定 jdbcType


test1
<!-- public List<Employee> getAllEmps() -->
<!-- 方法返回值如果是集合类型,值应该是集合元素的类型! -->
<select id="getAllEmps" resultType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee">
SELECT * FROM emp
</select>
查询多条记录→ resultType="Employee" → 查询结果封装到一个 List 里
test2
<!-- public Map<String, Object> getEmpByEidRetMap(Integer id) -->
<select id="getEmpByEidRetMap" resultType="map">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid=#{eid}
</select>
查询单条记录 → resultType="map" → 封装到一个 Map 里,字段名为 key,字段值为 value
test3
<!--
@MapKey("eid")
public Map<Integer, Employee> getAllEmpsRetMap()
-->
<select id="getAllEmpsRetMap" resultType="map">
SELECT * FROM emp
</select>
查询多条记录 → resultType="map" → 查询结果封装到一个 Map 里 (依照 @MapKey
注解可知,结果所封装的Map中的 key 为 eid 字段的值,但 value 也是一个 [Map:
每条记录的字段名为 key,字段值为 value],value 的封装同 test2
--------------
插一句:这个查询结果的实际类型是 Map<Integer, HashMap<String, Object>>,
可是方法声明返回值是 Map<Integer, Employee> 鸭?这是怎么赋上值的?都说无反
射无框架,所以底层是用反射绕过泛型检查赋上的吗...
--------------
所以,resultMap 要写元素类型 → resultType="Employee"
默认 MyBatis 自动封装结果集时是按照列名和属性名一一对应(忽略大小写) 的规则;现有一种情况,列名和属性名不一样,也不允许使用别名,这要怎么对应呢?→ 使用 resultMap(自定义结果集),即自己定义表列名和对象属性名的映射规则。
<!-- public Employee getEmpByEid(Integer eid); -->
<select id="getEmpByEid" resultMap="empMap">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid = #{baishizhu}
</select>
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" id="empMap">
<!-- 主键列映射规则(用 result 也能映射出来;但用 id 的话,底层会有优化) -->
<id column="emp_id" property="eid"/>
<!-- 普通字段列映射规则 -->
<result column="emp_email" property="email"/>
<result column="emp_gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="emp_ename" property="ename"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Employee getEmpWithDeptByEid(Integer eid); -->
<select id="getEmpWithDeptByEid" resultMap="empWithDeptMap">
SELECT emp.*, dept.dname FROM emp LEFT JOIN dept
ON emp.did = dept.did WHERE eid=#{eid}
</select>
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" id="empWithDeptMap">
<!-- 主键列映射规则 -->
<id column="eid" property="eid"/>
<!-- 普通字段列映射规则 -->
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="ename" property="ename"/>
<!-- 复杂对象映射:使用级联属性方式封装联合查询的结果 -->
<result column="did" property="dept.did"/>
<result column="dname" property="dept.dname"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" id="empWithDeptMap">
<id column="eid" property="eid"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="ename" property="ename"/>
<!-- association 可以指定 property 关联的 javaType 的封装规则 -->
<association property="dept" javaType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Department">
<id column="did" property="did"/>
<result column="dname" property="dname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- public Department getDeptByDid(Integer did) -->
<select id="getDeptByDid" resultMap="deptWithEmps">
SELECT emp.*, dept.dname FROM dept LEFT JOIN emp
ON dept.did = emp.did WHERE dept.did = #{did}
</select>
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Department" id="deptWithEmps">
<id column="did" property="did"/>
<result column="dname" property="dname"/>
<!--
collection 定义关联的集合类型属性其元素的封装规则
ofType: collection 中元素的类型
property: 集合类型属性名
-->
<collection property="empList" ofType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee">
<id column="eid" property="eid"/>
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="ename" property="ename"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
EmployeeDao.xml
<!-- public Employee getEmpByEid(Integer eid); -->
<select id="getEmpByEid" resultMap="empMap">
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE eid = #{baishizhu}
</select>
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" id="empMap">
<!-- 主键列映射规则 -->
<id column="eid" property="eid"/>
<!-- 普通字段列映射规则 -->
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="ename" property="ename"/>
<!-- >>> 分步查询 <<<
select: 分步查询SQL的id
column: 分步查询SQL需要的参数(得是上一步的查询结果中的某个字段名)
property: 分步查询的结果所要保存到的 resultMap-type 对象的哪个属性中
-->
<association column="did" property="dept"
select="cn.edu.nuist.dao.DepartmentDao.getDeptInfoByDid">
</association>
</resultMap>
DepartmentDao.xml
<!-- public Department getDeptInfoByDid(Integer did); -->
<select id="getDeptInfoByDid" resultType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Department">
SELECT * FROM dept WHERE did = #{did}
</select>
分步查询 SQL 需要多个参数,该怎么传呢?
将多列的值封装成 map 传递,即:column="{key1=column1, key2=column2, ...}"。key 是分步查询 SQL 语句 #{...} 中的值,column 就是我们上一步查询结果的某个字段名。
相关全局设置:
fetchType="eager | lazy" 属性来覆盖该项的开关状态。默认值:false鉴别器。MyBatis 可以使用 discriminator 判断某个值,然后根据某列的值改变封装行为。
要求:如果查出来的 Employee为女性,其 Department 信息也要查出来;如果是男性,不查部门信息,且 email 属性值设为ename
<resultMap type="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee" id="empMap">
<!-- 主键列映射规则 -->
<id column="eid" property="eid"/>
<!-- 普通字段列映射规则 -->
<result column="email" property="email"/>
<result column="gender" property="gender"/>
<result column="ename" property="ename"/>
<!--
column: 指定判定的列名
javaType: 列值对应的Java类型
-->
<discriminator javaType="integer" column="gender">
<!-- resultType/resultMap 不能少! -->
<case value="0" resultType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee">
<association column="did" property="dept"
select="cn.edu.nuist.dao.DepartmentDao.getDeptInfoByDid">
</association>
</case>
<case value="1" resultType="cn.edu.nuist.bean.Employee">
<result column="ename" property="email"/>
</case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujiaqi1101/p/13696882.html