systemd提供自己的日志文件系统(logging system),成为journal,使用systemd日志,无需额外安装日志服务(rsyslog)
配置文件/etc/systemd/journald.conf
默认情况下(当Storage=auto,配置文件/etc/systemd/journald.conf中),日志记录被写入/var/log/journal/目录,此目录为systemd软件包的一部分,若被删除,systemd不会自动创建它,直到下次升级软件包时才会重建该目录.如果该目录缺失,systemd会将日志记录于/run/systemd/journal目录,这意味着,系统重启后日志将丢失.
默认日志最大限制为所在文件系统容量的 10%,即:如果 /var/log/journal 储存在 50GiB 的根分区中,那么日志最多存储 5GiB 数据。可以修改 /etc/systemd/journald.conf 中的 SystemMaxUse 来指定该最大限制。如限制日志最大 50MiB:
SystemMaxUse=50M
systemd提供了 socket /run/systemd/journal/syslog,以兼容传统日志服务。所有系统信息都会被传入。要使传统日志服务工作,需要让服务链接该 socket,而非 /dev/log(官方说明)。
In /etc/systemd/journald.conf enable the following:
ForwardToConsole=yes
TTYPath=/dev/tty12
MaxLevelConsole=info
重启journald
systemctl restart systemd-journald
journalctl --boot -0 显示本次启动日志
journalctl --boot -1 显示上次启动日志
journalctl --boot -2 显示上上次启动日志
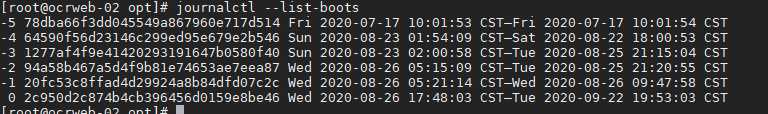
journalctl --list-boots Show terse information about recorded boot
journalctl --list-boots
journalctl --boot -0

从2020-08-26 17:48:03到现在的日志
jounalctl --boot -1
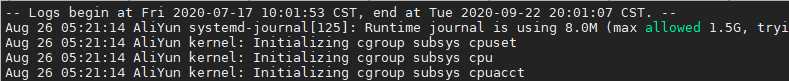
journalctl --boot -2
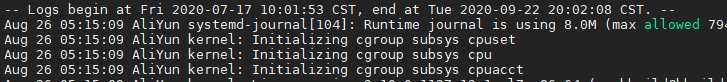
journalctl --boot -3
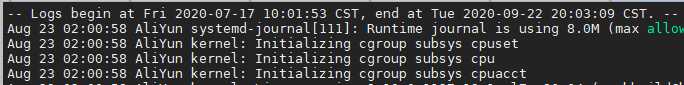
journalctl --boot -4
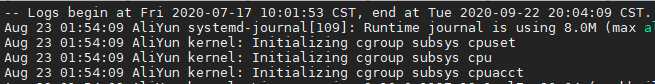
journalctl --since ‘2020-8-26‘
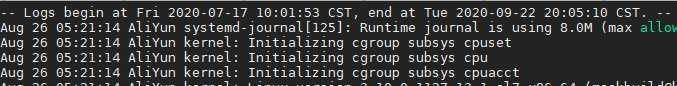
journalctl --since ‘2020-9-4 1:1:1‘
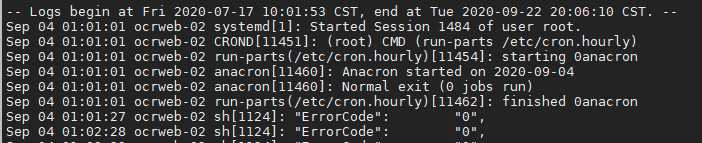
相对日期过滤
journalctl --since ‘20 minutes ago‘
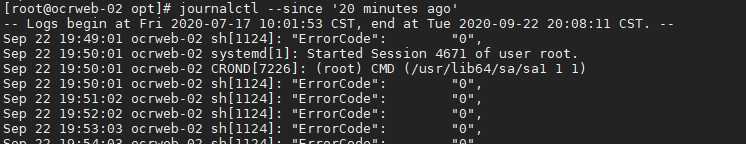
显示最新日志
journalctl -f
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dissipate/p/13714675.html