在多进程编程环境下,操作系统会使用进程号来对创建出的进程进行唯一标识进而实现任务调度。那么在多线程编程中也希望能够对创建出的线程进行唯一标识,这样可以将日志信息和线程关联起来,在程序运行崩溃或者CPU占用较高时,可以很快地根据日志信息定位到相应的线程。
pthread_self()函数gettid()系统调用pthread_self()使用使用pthread_create()(函数原型如下)系统调用新建一个线程的时候,pthread_create()函数会修改形参thread指针指向的值,指向新建线程的线程ID,其类型为pthread_t。
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start)(void *),void *arg);
新建线程在后续运行中如果想要获取自身的线程ID,可以通过Pthread库提供的pthread_self()函数来返回。
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_self()
示例代码
#include<iostream>
//使用了pthread,在编译的时候需要连接pthread库
#include<pthread.h>
using namespace std;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* threadFunc(void* obj){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
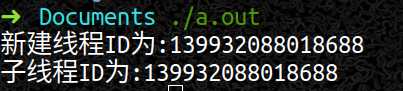
cout << "子线程ID为:" << pthread_self() << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
return nullptr;
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
pthread_t thread;
pthread_create(&thread,nullptr,&threadFunc,nullptr);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
cout << "新建线程ID为:" << thread << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
pthread_join(thread,nullptr);
return 0;
}
gettid()使用通过查看Linux系统中的man手册,可以得知gettid()相关头文件和函数原型如下:
#include<sys/types.h>
pid_t gettid(void)
但在实际的编程中会发现编译时会报错gettid()未声明和定义,这是因为头文件中sys/types.h没有声明该函数同时 glibc中也没有实现。此时需要我们自己使用系统调用封装一个gettid(),函数的封装方式如下:
#include<syscall.h>
#include<unistd.h>
pid_t gettid(){
return static_cast<pid_t>(syscall(SYS_gettid));
}
在单线程的进程中,getpid()函数的值和gettid()的值是相同的。而在多线程中,所有线程的getpid()值都是相同的,每个线程有自己的getpid()值。需要注意的是,不管是单线程还是多线程环境下,主线程的gettid()的值始终和getpid()值相同,可以通过这种方式来判断当前线程是否为主线程。
示例代码
#include<iostream>
#include<syscall.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
using namespace std;
pid_t gettid(){
return static_cast<pid_t>(syscall(SYS_gettid));
}
void* threadFun(void *obj){
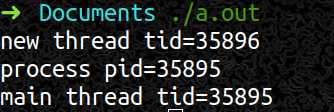
cout << "new thread tid=" << gettid() << endl;
return nullptr;
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
pthread_t thread;
pthread_create(&thread,nullptr,&threadFun,nullptr);
pthread_join(thread,nullptr);
cout << "process pid=" << getpid() << endl;
cout << "main thread tid=" << gettid() << endl;
return 0;
}
pthread_self()与gettid()对比pthread_self缺点
pthread_t,因为不知道确切类型。也就无法在日志中用pthread_t来表示当前线程的id。pthread_t的大小或者计算其hash值,所以无法作为关联容器的key。pthread_t值,用于表示绝不可能存在的id值。pthread_t值只在进程内有意义,与操作系统的任务调度无法建立起有效关联。pthread_t可能是一个结构体指针,指向一块动态分配的内存,而这块内存可能会被反复使用,这样就会造成pthread_t的重复。只能保证同一时刻不同线程的id不同,不能保证不同时刻各个线程的id不同。gettid()好处
pid_t,是一个小整数,可以在日志中输出id,可以在\proc文件系统中找到对应项:\proc\tid或\proc\pid\task\tidpid,短时间启动的多个线程会有不同的线程id0是非法值,操作系统第一个进程init的pid是1Linux上pthread_self()和gettid()介绍
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zrcsy/p/13772023.html