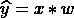
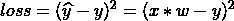
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
# our model for the forward pass
def forward(x):
return x * w
# 损失函数
def loss(x, y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y) * (y_pred - y)
#权重准备空列表
w_list = []
mse_list = []
for w in np.arange(0.0, 4.1, 0.1):
# Print the weights and initialize the lost
print("w=", w)
l_sum = 0
for x_val, y_val in zip(x_data, y_data):
# For each input and output, calculate y_hat
# Compute the total loss and add to the total error
y_pred_val = forward(x_val)#计算预测值
l = loss(x_val, y_val)#计算损失
l_sum += l
print("\t", x_val, y_val, y_pred_val, l)
# Now compute the Mean squared error (mse) of each
# Aggregate the weight/mse from this run
print("MSE=", l_sum / 3)#mse均方误差
w_list.append(w)
mse_list.append(l_sum / 3)
# Plot it all
plt.plot(w_list, mse_list)
plt.ylabel(‘Loss‘)
plt.xlabel(‘w‘)
plt.show()
损失在w=2时为最小,为最优值
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangqingqing24630/p/13888149.html