实验任务一
#include <stdio.h> int main (){ int a=5,b=7,c=100,d,e,f; d=a/b*c; e=a*c/b; f=c/b*a; printf("d=%d,e=%d,f=%d\n",d,e,f); return 0; }
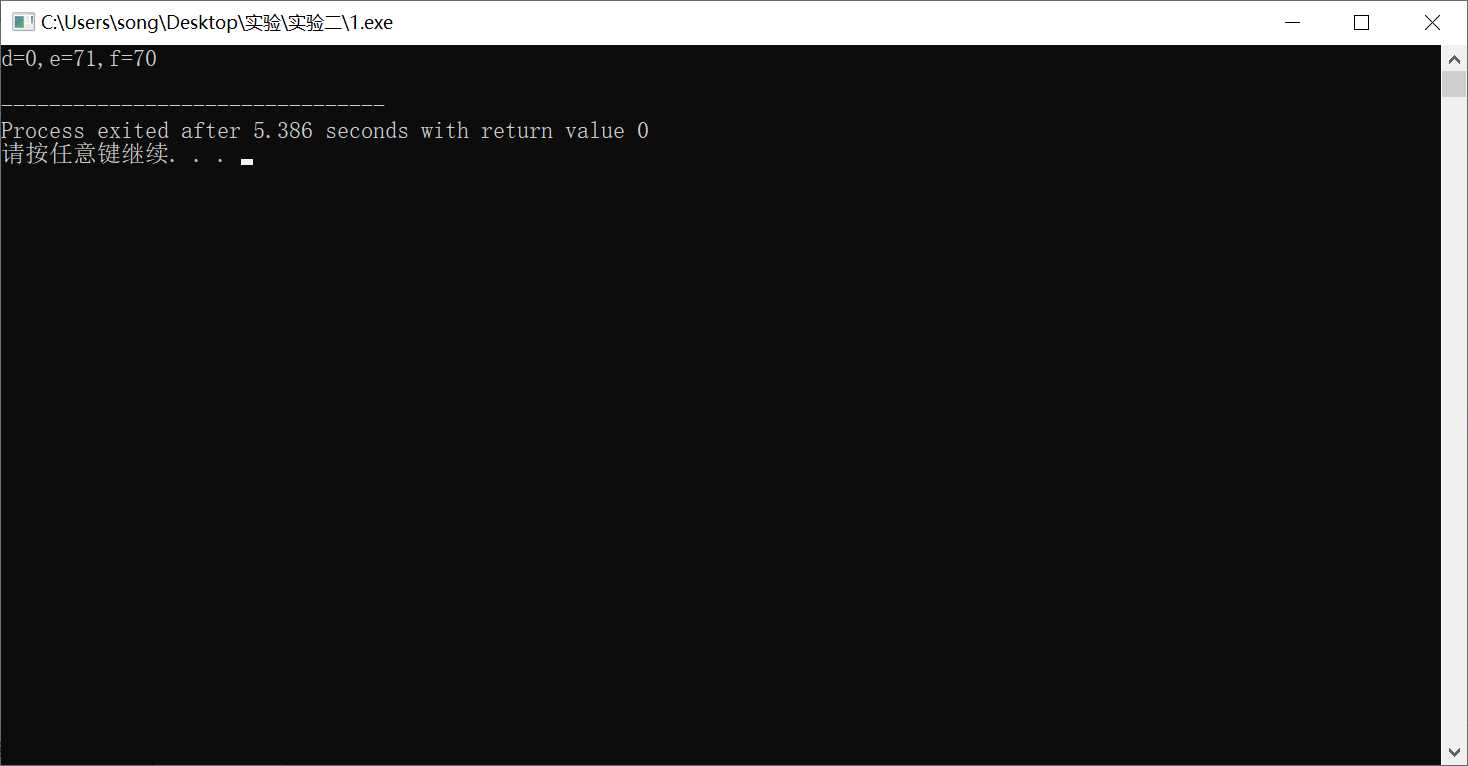
发现:
1.d = int(a/b) *c ; e=int (a*c /b) ; f= int (c/b)*a;
2.原因为:对于 / 运算符,整型/整型的结果会自动取整为不超过原来结果的最大整型。
实验任务2
#include <stdio.h> int main (){ int x=1234; float f=123.456; double m=123.456; char ch=‘a‘; char a[]="Hello,world!"; int y=3,z=4; printf("%d %d\n",y,z); printf("y=%d, z=%d\n", y,z); printf("%8d,%2d\n", x,x); printf("%f, %8f, %8.1f, %0.2f, %.2e\n",f,f,f,f,f); printf("%lf\n",m); printf("%3c\n", ch); printf("%s\n%15s\n%10.5s\n%2.5s\n%.3s\n",a,a,a,a,a); return 0; }
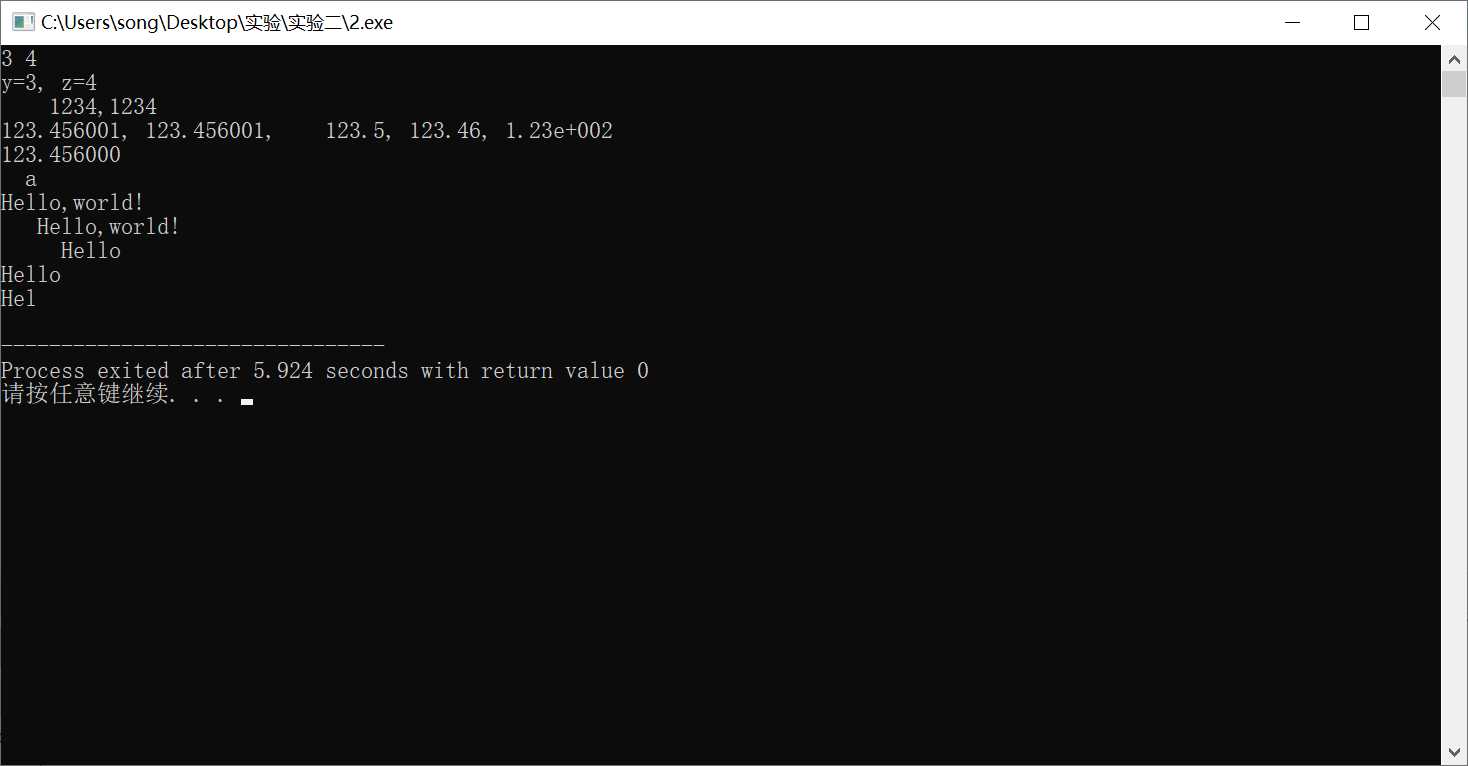
总结:
1.输出类型:%d整型 %f浮点型 %lf浮点型(特指double) %e 科学计数法输出浮点型 %c 字符型 %s 字符串型;
2.长度控制:若实际位数多于指定的宽度,则按实际位数输出,若实际位数少于定义的宽度则补以空格;
3.精确度:‘ . 数字’ 表示精确到小数点后几位。
实验任务三
#include <stdio.h> int main(){ double x,y; char c1,c2,c3; int a1,a2,a3; scanf ("%d%d%d",&a1,&a2,&a3); printf("%d,%d,%d\n",a1,a2,a3); getchar(); scanf("%c%c%c",&c1,&c2,&c3); printf("%c %c %c\n",c1,c2,c3); scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y); printf("%f,%f\n",x,y); return 0; }
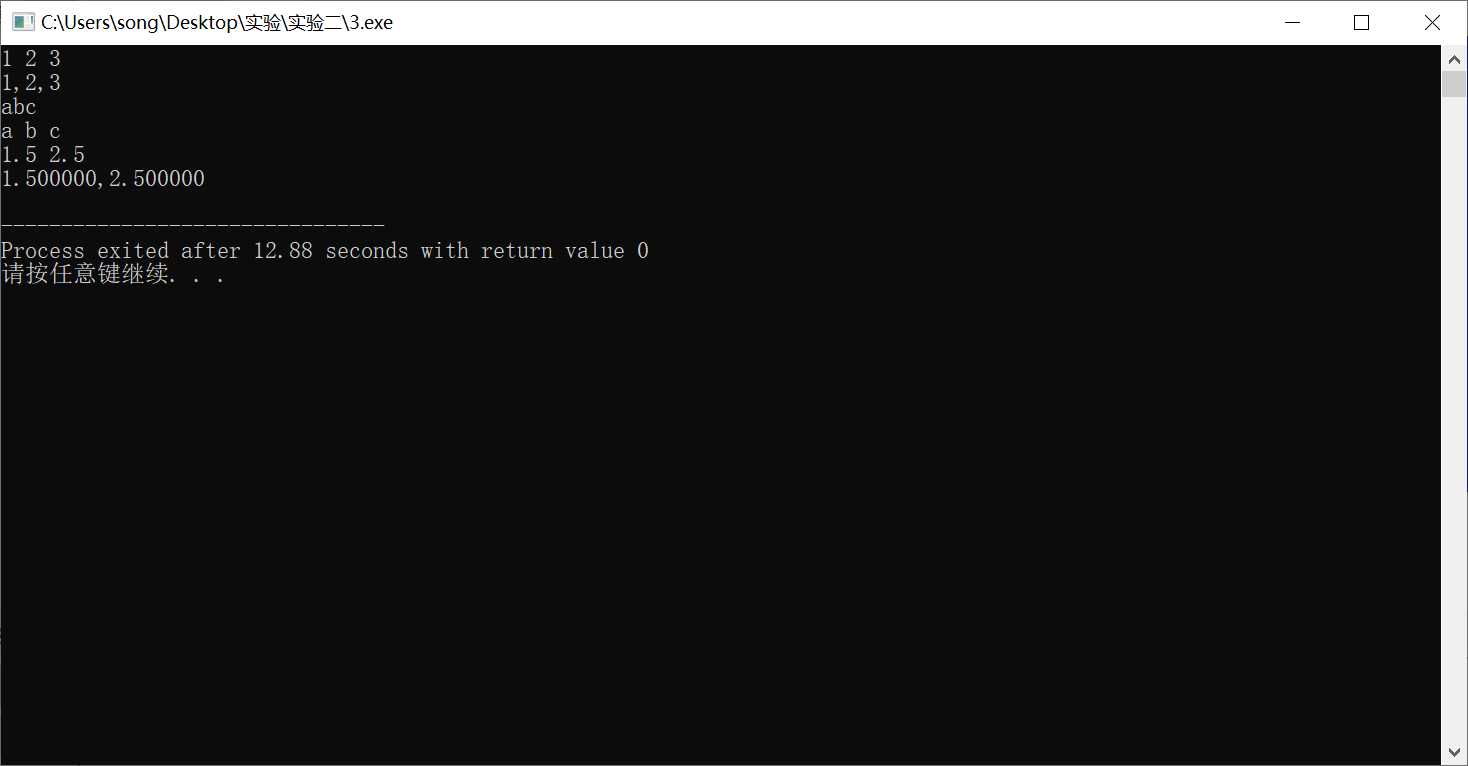
实验任务四
#include <stdio.h> int main(){ char x; x = getchar(); if(x>=‘0‘&&x<=‘9‘) printf("%c是数字字符\n", x); else if(x>=‘a‘&&x<=‘z‘||x>=‘A‘&&x<=‘Z‘) printf("%c是英文字母\n", x); else printf("%c是其它字符\n", x); return 0; }
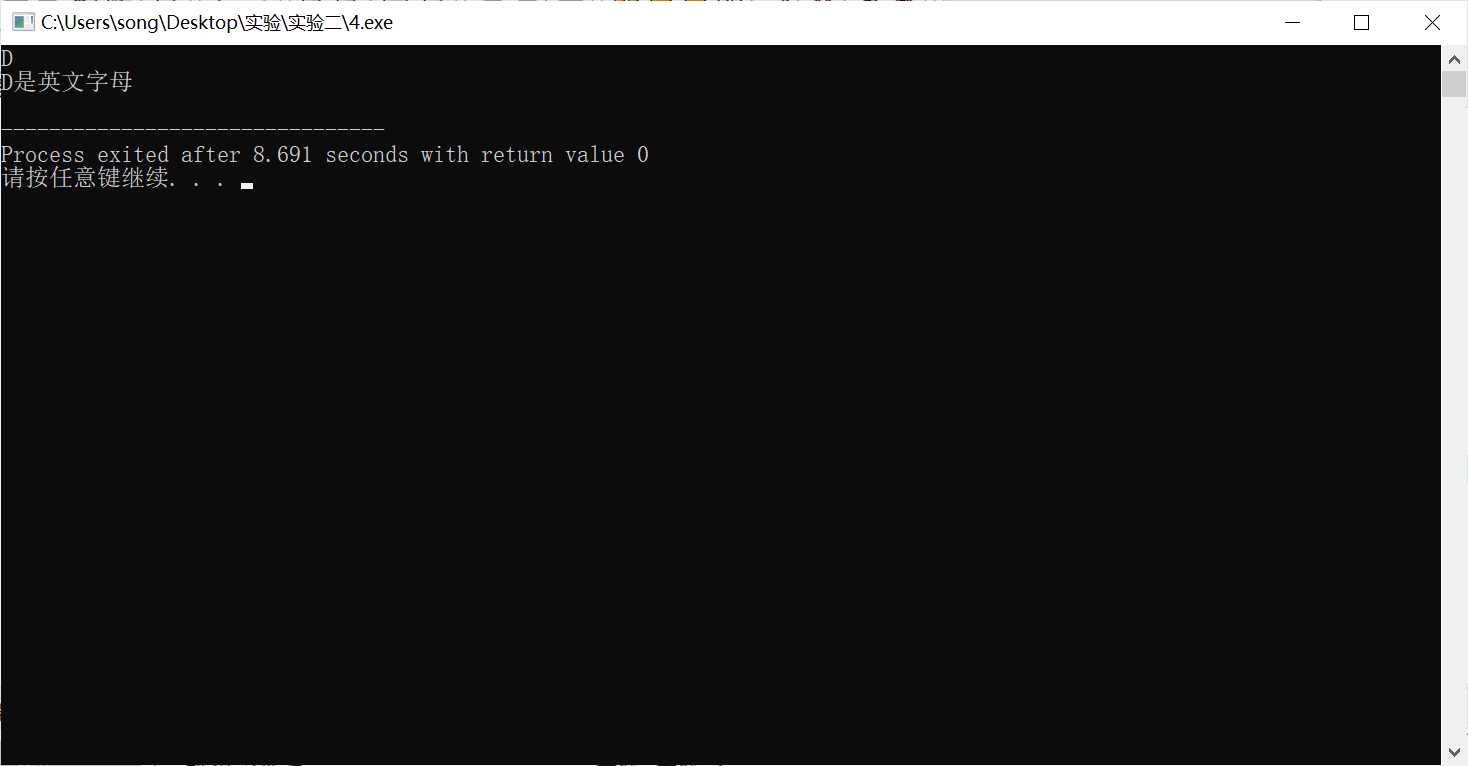
实验任务五
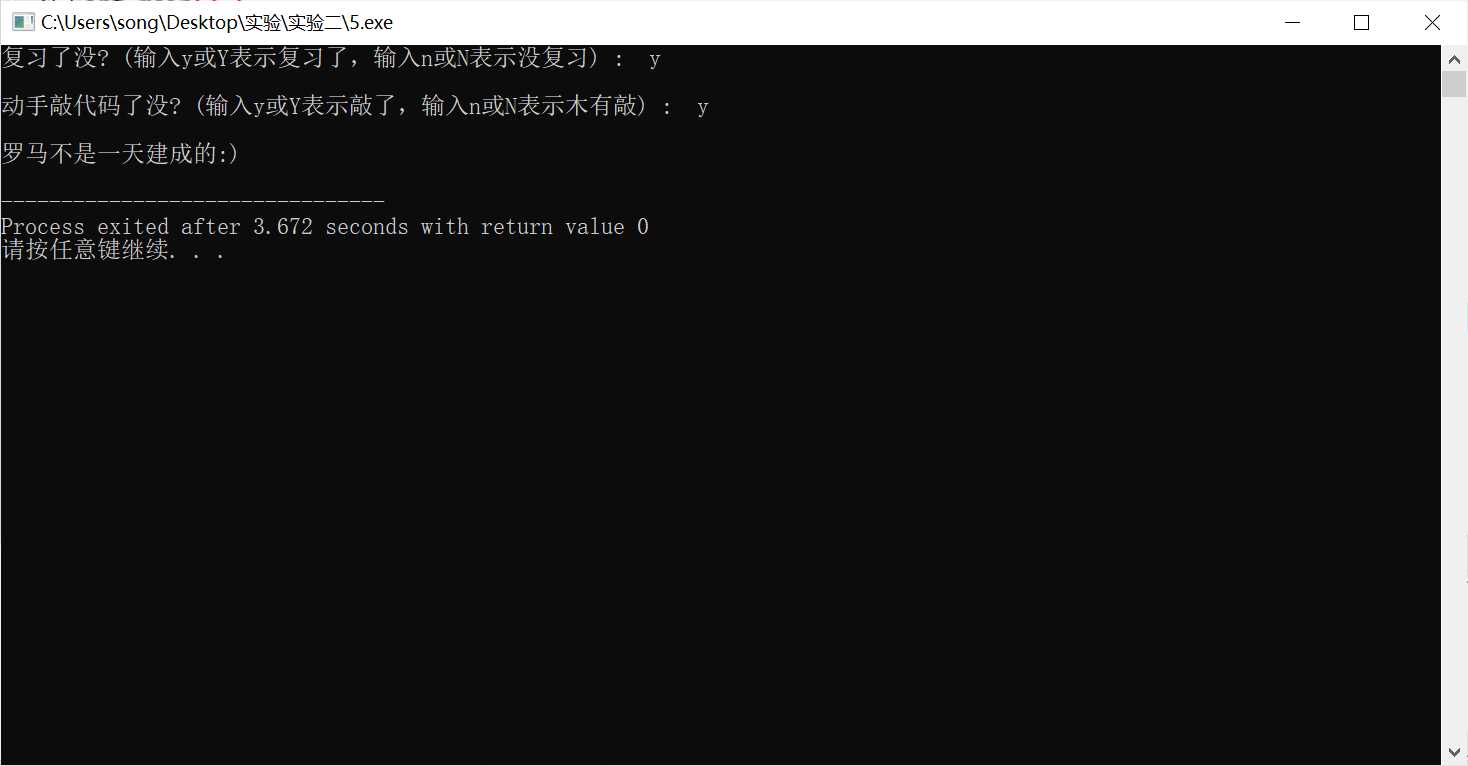
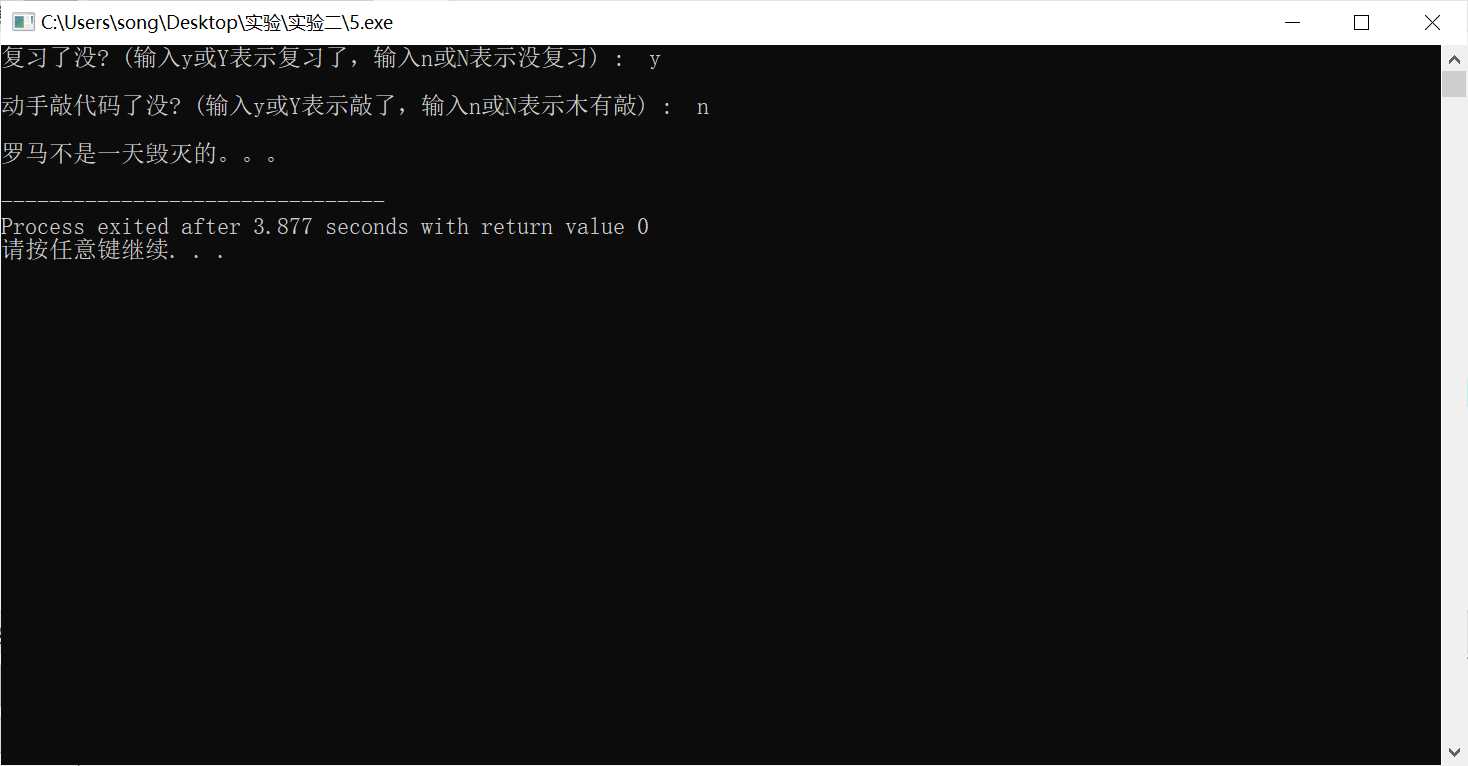
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char ans1, ans2; printf("复习了没? (输入y或Y表示复习了,输入n或N表示没复习) : "); ans1 = getchar(); // 从键盘输入一个字符,赋值给ans1 getchar(); // 思考这里为什么要加这一行 printf("\n动手敲代码了没? (输入y或Y表示敲了,输入n或N表示木有敲) : "); ans2 = getchar(); if((ans1==‘y‘||ans1==‘Y‘)&&(ans2==‘y‘||ans2==‘Y‘)) printf("\n罗马不是一天建成的:)\n"); else printf("\n罗马不是一天毁灭的。。。\n"); return 0; }
实验任务六
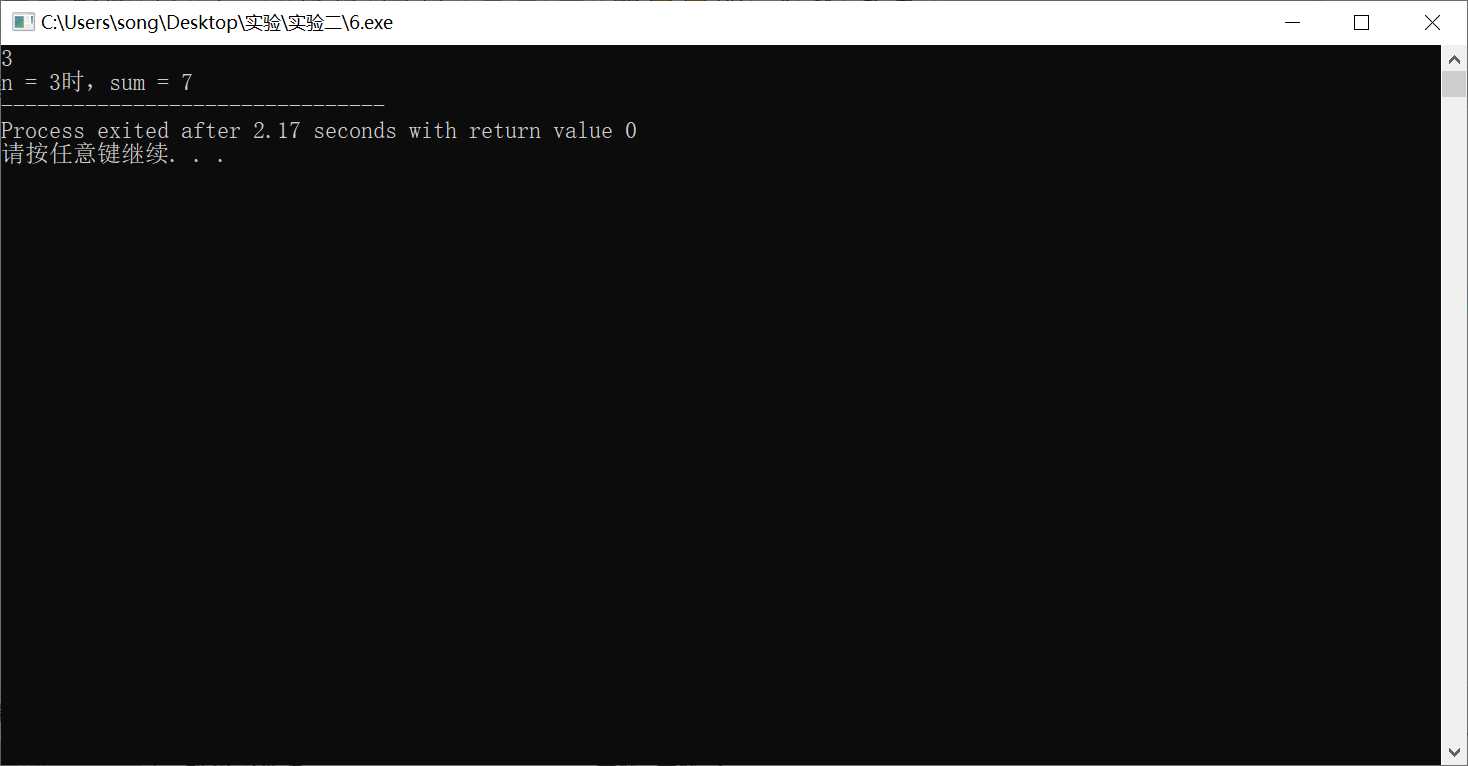
#include <stdio.h> int main (){ int n,sum,t; sum=2; scanf("%d",&n); if (n>=1 && n<=10){ for (t=1;t<=n;t++){ sum=sum*2; } sum=sum-1; printf("n = %d时,sum = %d",n,sum); } else { printf ("beyond limitation!"); } }
实验任务七
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <windows.h> int main (){ int n,i,j; for(n=1;n<=5;n++){ for (j=1;j<n;j++){ printf(" "); } for (j=1;j<=(11-2*n);j++){ printf (" 0 "); if (j<(11-2*n)){ printf (" "); } } printf ("\n"); for (j=1;j<n;j++){ printf(" "); } for (j=1;j<=(11-2*n);j++){ printf ("<H>"); if (i<(11-2*n)){ printf (" "); } } printf ("\n"); for (j=1;j<n;j++){ printf(" "); } system("color f0"); for (j=1;j<=(11-2*n);j++){ printf ("I I"); if (i<(11-2*n)){ printf (" "); } } printf ("\n\n"); } system("color f0"); Sleep(2000); for (n=1;n<=10;n++){ system("color f4"); Sleep(500); system("color f6"); Sleep(500); system("color f2"); Sleep(500); system("color f1"); Sleep(500); system("color f9"); Sleep(500); system("color f5"); Sleep(500); } return 0; }
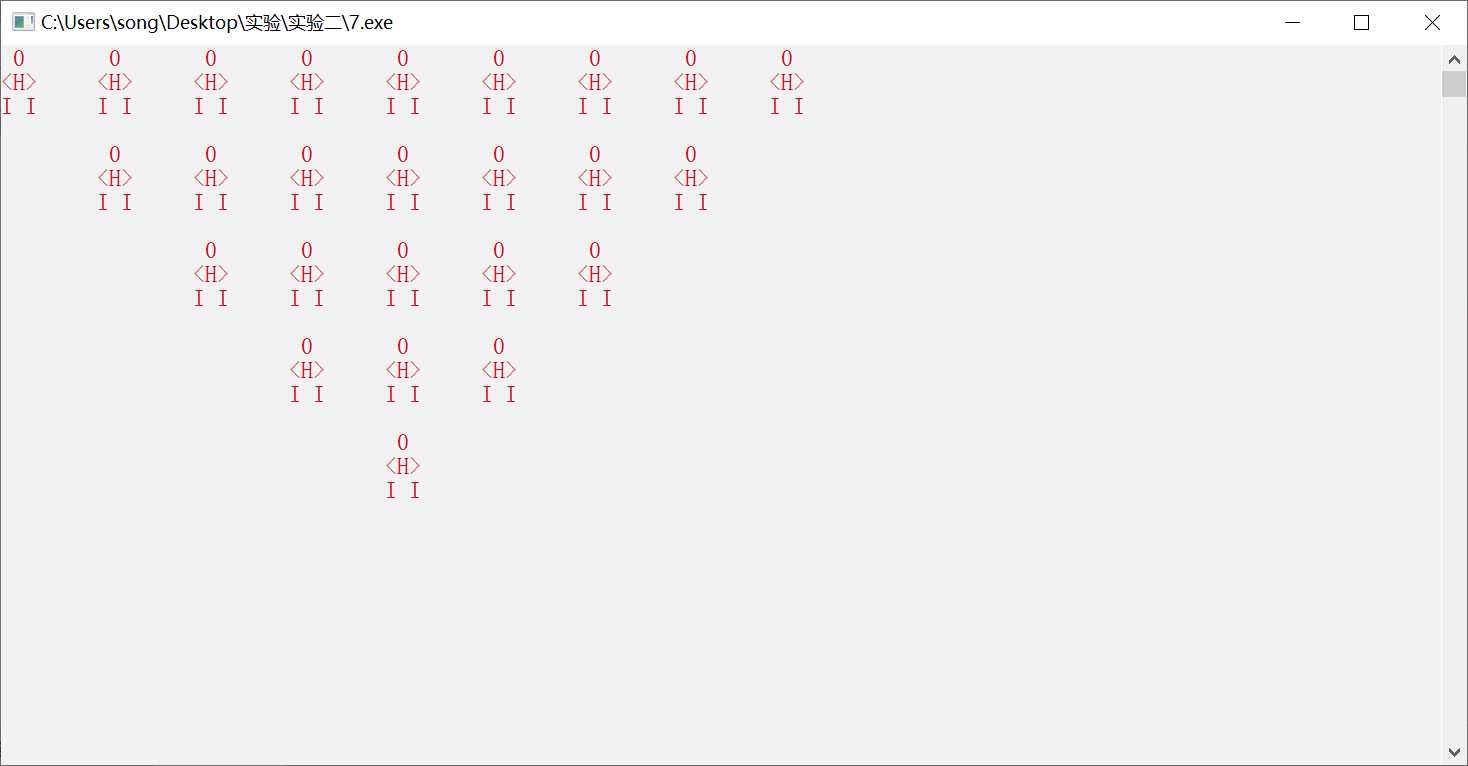
*注:颜色为动态变化效果哦
总结:1.实现改变颜色的语句
其中x代表背景颜色,y代表输出内容颜色
#include <stdlib.h>
{
system (color xy);
}
x,y均为十六进制字符 其对应颜色如下:

2.实现停顿
#include <windows.h>
{
Sleep(time);
}
注意Sleep开头大写,time为一实数代表停顿时间,单位为毫秒
实验2 C语言表达式编程应用及输入输出函数( 后附炫彩小人:) )
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/deemmo/p/13900365.html