*github地址:https://github.com/zucc31801061/31801061subway
给出一副地铁线路图,例如:
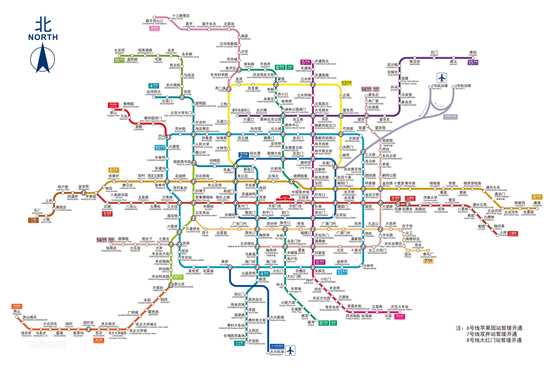
将其转化为格式如下的.txt文件:
线路1 站名1 站名2 ... 站名n 线路2 站名1 站名2 ... 站名n 线路n 站名1 站名2 ... 站名n
例如:

则可实现以下功能:
1、输入起点站与终点站可以查询之间最佳搭乘方法(最短路径)
2、可以查看所有线路,并可以通过选择线路查看该线路内的所有站点
Java
Dijkstra算法
Dijkstra算法是从起点开始,查找所有连通点中距离最近的中转点,然后再以中转站为起点来寻找下一个最近的连通点,直到遍历到终点结束。
由于地铁线路站与站之间的连通默认为无权图,故默认每个站点之间的距离为1
1.Station类
用于存储站点信息,各变量都拥有set和get方法
变量声明
private int staId;//站点编号(唯一) private String line;//该站点所属线路名 private String staName;//站点名
方法声明(具体不做解释,代码见github,下同)
public Station(int staId, String staName, String line);//定义Station public String getLine();//返回线路名 public void setLine(String line);//修改线路名 public int getStaId();//返回站点编号 public void setStaId(int staId);//修改站点编号 public String getStaName();//返回站点名 public void setStaName(String staName);//修改站点名
2.ReadTxt类
用于读取.txt文件并存储到对应的存储结构中
变量声明
static Set<String> lines = null;//地铁线路名 static List<Station> allStations = null;//所有站点信息(编号,站点名,所属线路),其中换乘站应有多条信息 static Map<String, List<Station>> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();//线路信息,线路名,线路所含站点信息 static int[][] graph = null;//站点间的连通信息
方法声明
public ReadTxt(String fileName);//运行下面两个方法并创建Main窗口 private void readFileContent(String fileName);//读取文件并存入相应存储结构 private void initialize();//初始化,给graph赋值为当前线路图的连通图
3.Dijkstra类
计算所有站点之间的最短路径并将其路径储存
变量声明
private Queue<Integer> visited = null;//已访问的站点 int[] length = null;//路径长度 private Map<String, List<Station>> map = null; static String nowLine = null;//当前地铁线 static String[] nextLine = null;//当前节点的下一换乘地铁线 static HashMap<Integer, String> route = null;//路径 static List<Station> list = null;
方法声明
public Dijkstra(int len, Map<String, List<Station>> map);//初始化赋值 private int getIndex(Queue<Integer> q, int[] length);//获取未访问点中距离源点最近的点 public String shortestroute(int v, int dest);//根据起始站点id初始化输出 public String dijkstra(int[][] weight, List<Station> list, int v, int dest);//计算最短路径
4.FrmMain类
程序的UI界面
5.SubwayStarter类
程序入口
1.读取文件的方法
private void readFileContent(String fileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
InputStreamReader read = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
lines = new LinkedHashSet<>();
allStations = new LinkedList<>();
List<Station> line_stations = null;
try {
if(file.isFile() && file.exists()){//判断文件是否存在
read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), "UTF-8");
br = new BufferedReader(read);
String tempStr = null;
int staId = 0;//站点编号
while ((tempStr = br.readLine())!= null) {//使用readLine方法,一次读一行,判断是否读到文件末尾
line_stations = new LinkedList<>();
String[] message = tempStr.split("\\s+");//分割线路站点信息
lines.add(message[0]);//读取地铁线路名
for(int i=1; i<message.length; i++) {
Station station = new Station(staId++, message[i], message[0]);//创建站点对象
allStations.add(station);
line_stations.add(station);//将站点加入当前线路
}
map.put(message[0], line_stations);//将路线加入map
}
br.close();
}
else{
System.out.println("找不到指定的文件");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("读取文件内容出错");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.初始化graph的方法
private void initialize() {
int count = 0;//站点数量
allStations = new LinkedList<>();
for (String st : map.keySet()) {//遍历map中地铁线路
count += map.get(st).size();
for (Station s : map.get(st)) {//遍历当前线路站点
allStations.add(s);
}
}
graph = new int[count][count];
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++)
graph[i][j] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
String name = allStations.get(i).getStaName();
graph[i][i] = 0;
for (Station s : allStations) {
if (s.getStaName().equals(name)) {//可换乘站和环线起止站的连通
int id = s.getStaId();
if (id - 1 >= 0) {
if (allStations.get(id - 1).getLine().equals(allStations.get(id).getLine())) {
graph[i][id - 1] = 1;
graph[id - 1][i] = 1;
}
}
if (id + 1 < count) {
if (allStations.get(id + 1).getLine().equals(allStations.get(id).getLine())) {
graph[i][id + 1] = 1;
graph[id + 1][i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.Dijkstra算法
public String dijkstra(int[][] weight, List<Station> list, int v, int dest) {
Dijkstra.list = list;
//路径HashMap route;
route = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
route.put(i, "");
}
//初始化路径长度数组length
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
route.put(i, route.get(i) + "" + list.get(v).getStaName());
if (i == v) {
length[i] = 0;
}
//连通站点
else if (weight[v][i] != -1) {
length[i] = weight[v][i];
//获取当前站点所属的线路
nowLine = list.get(v).getLine();
StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer();
for (Station s : map.get(nowLine)) {
sbf.append(s.getStaName());
}
//起点站和下一站点是否属于同一地铁线
if (sbf.indexOf(list.get(i).getStaName()) != -1) {
route.put(i, route.get(i) + "\n\t-->" + list.get(i).getStaName());
nextLine[i] = nowLine;
}
else {
route.put(i, route.get(i) + "\n-->换乘" + list.get(i).getLine() + "\n\t-->" + list.get(i).getStaName());
nextLine[i] = list.get(i).getLine();
}
}
//不连通
else
length[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
visited.add(v);
//迭代寻找最优线路
while (visited.size() < list.size()) {
int k = getIndex(visited, length);// 获取未访问点中距离源点最近的点
visited.add(k);
if (k != -1) {
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
if (weight[k][j] != -1) {// 判断k点能够直接到达的点
//通过遍历各点,比较是否有比当前更短的路径,有的话,则更新length,并更新route。
if (length[j] > length[k] + weight[k][j]) {
length[j] = length[k] + weight[k][j];
nowLine = nextLine[k];
StringBuffer sbf = new StringBuffer();
for (Station s : map.get(nowLine)) {
sbf.append(s.getStaName());
}
//判断到下一站点是否需要换乘
if (sbf.indexOf(list.get(j).getStaName()) != -1) {
route.put(j, route.get(k) + "\n\t-->" + list.get(j).getStaName());
nextLine[j] = nowLine;
}
else {
StringBuffer temp = new StringBuffer();
for (String str : map.keySet()) {
temp = new StringBuffer();
for (Station s : map.get(str)) {
temp.append(s.getStaName());
}
if (temp.indexOf(list.get(j).getStaName()) != -1 && temp.indexOf(list.get(k).getStaName()) != -1) {
route.put(j,route.get(k) + "\n-->换乘" + str + "\n\t-->" + list.get(j).getStaName());
nextLine[j] = str;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
visited.clear();
return this.shortestroute(v, dest);
}
1.初始化界面
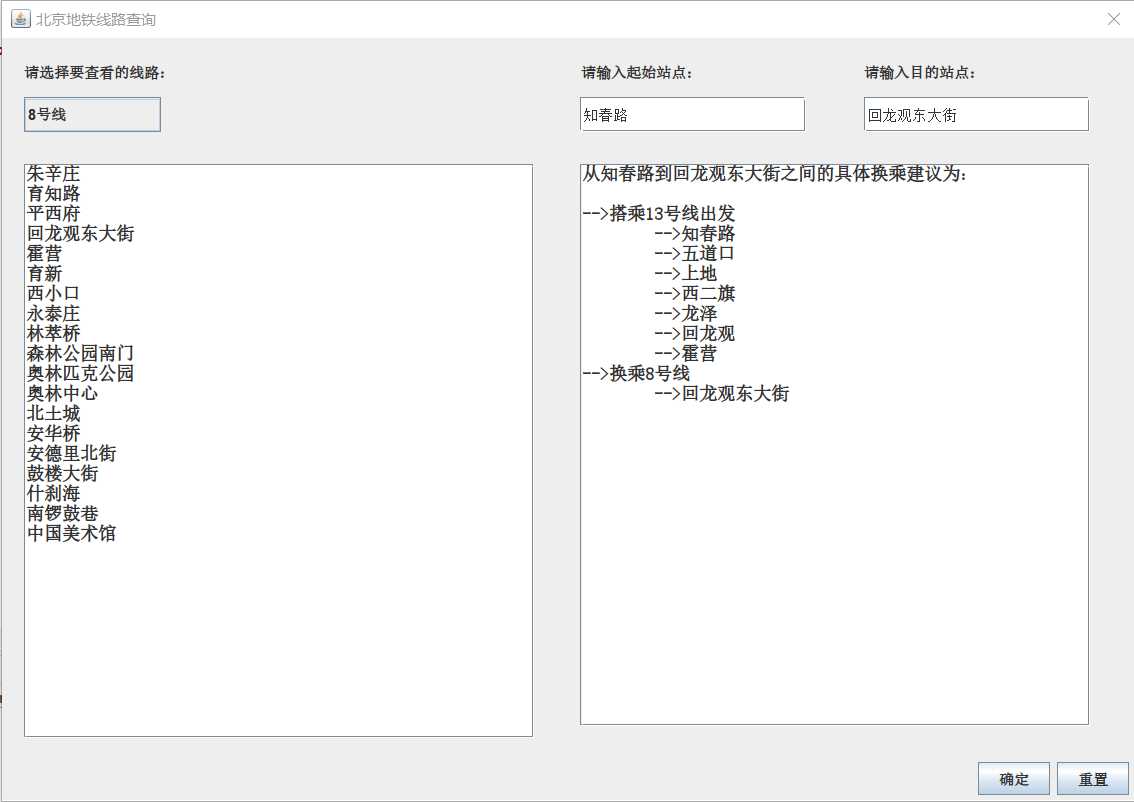
2.完整运行结果
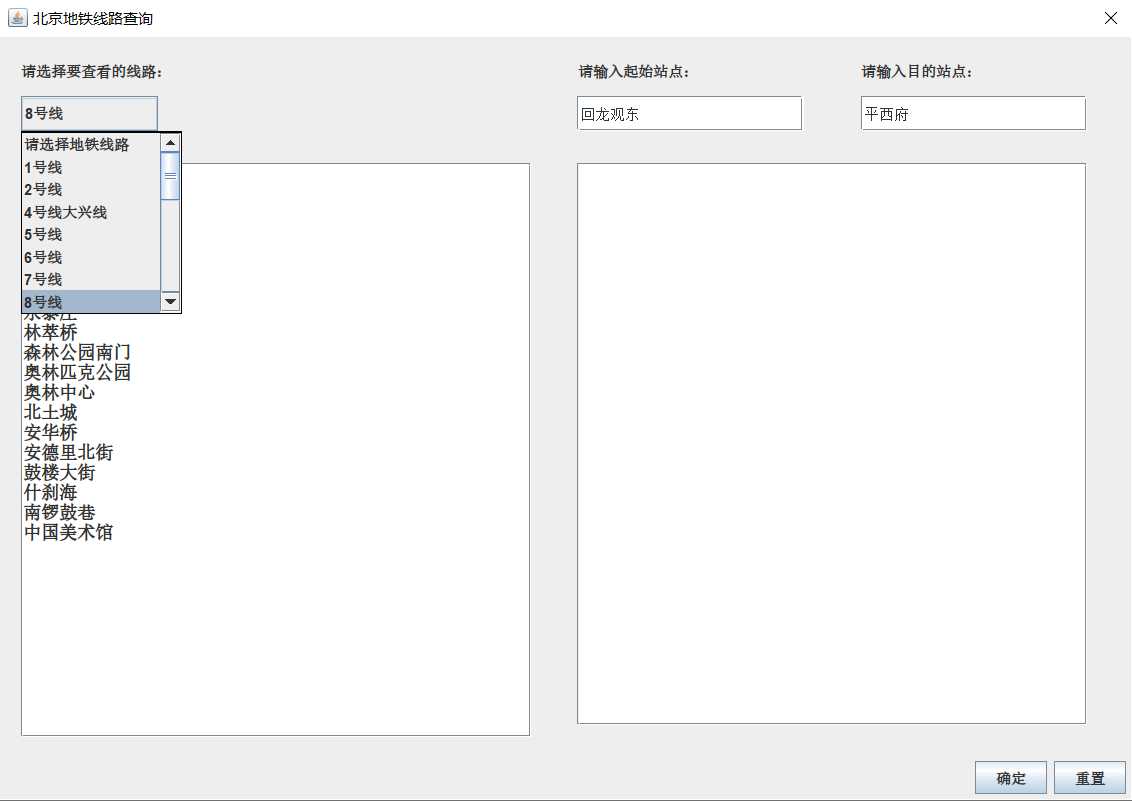
3.查看对应线路的站点
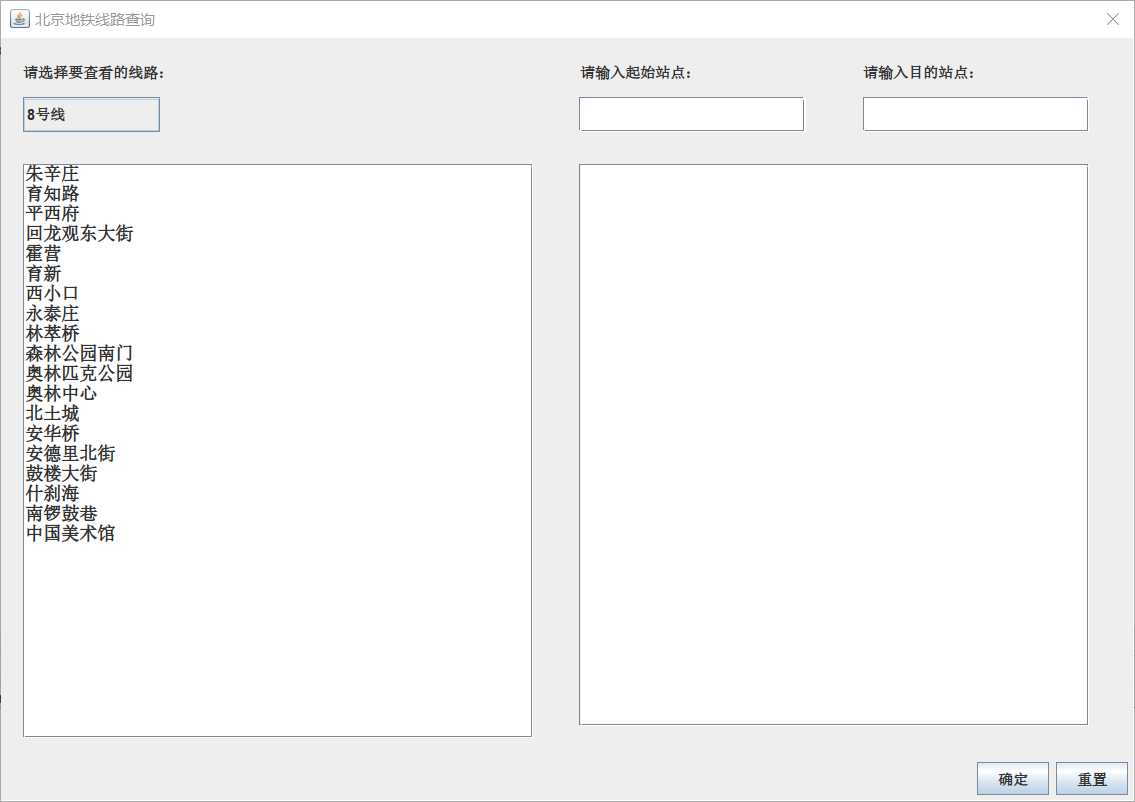
4.部分错误提示框
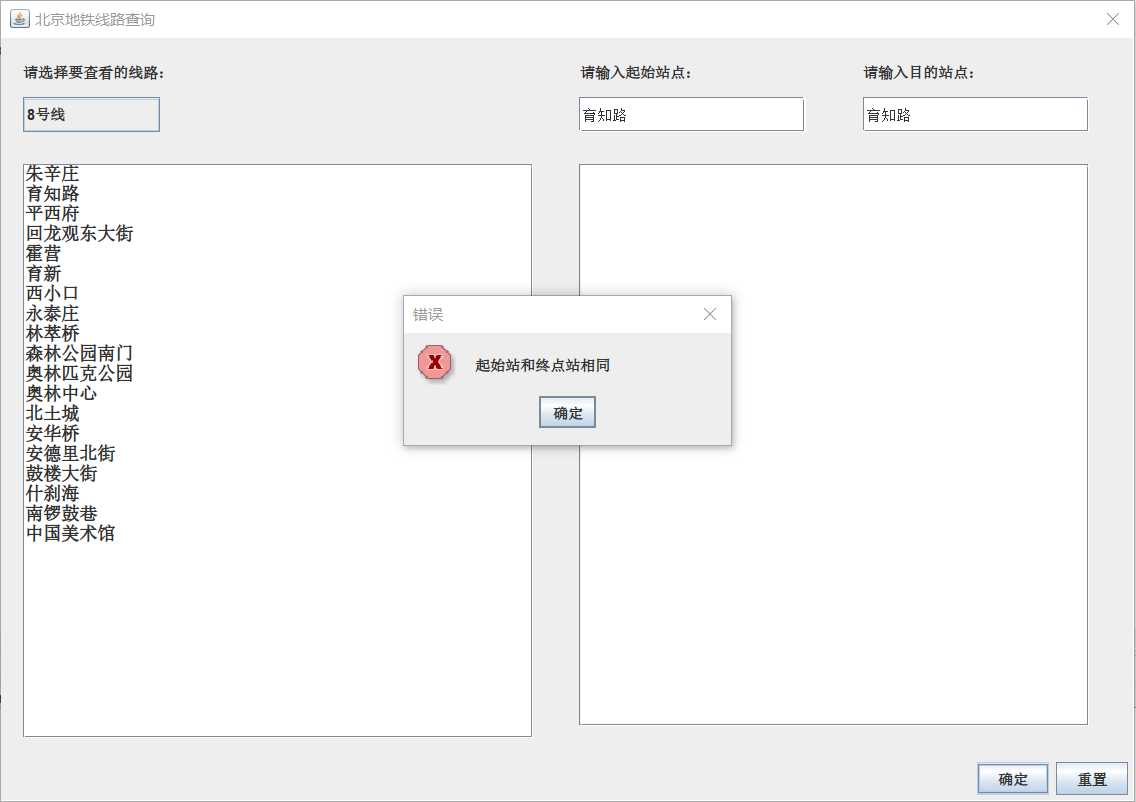
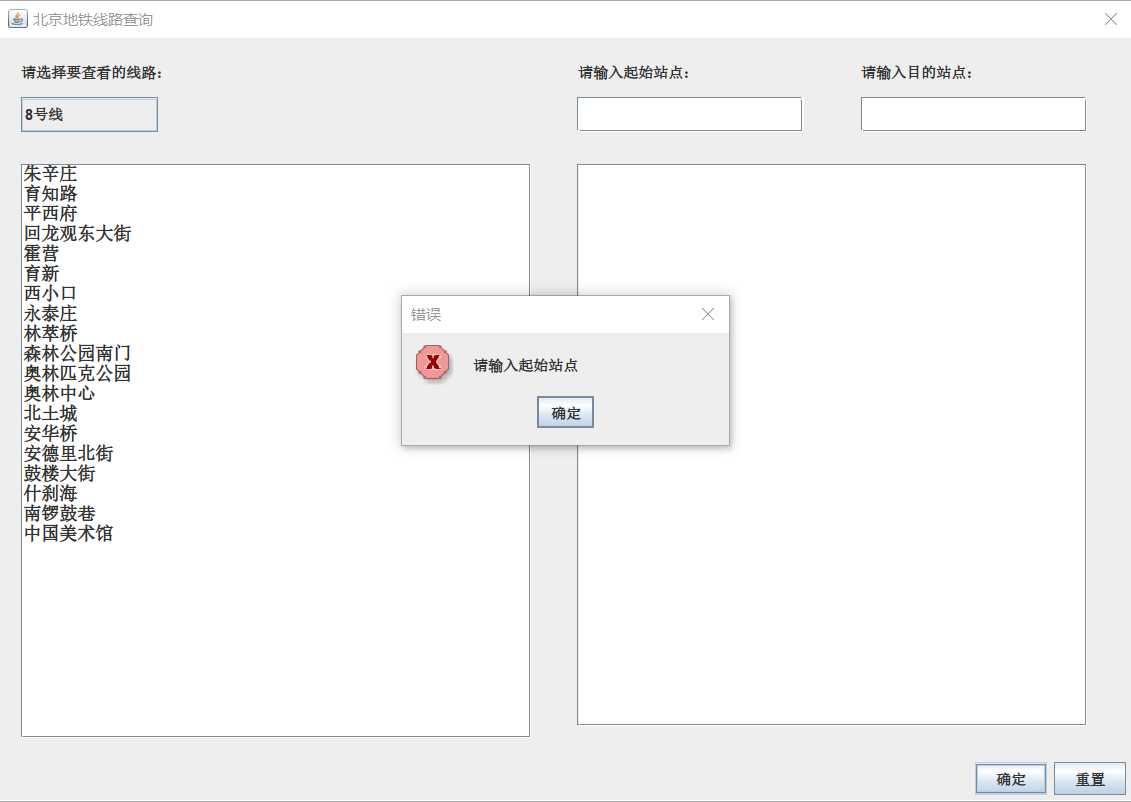
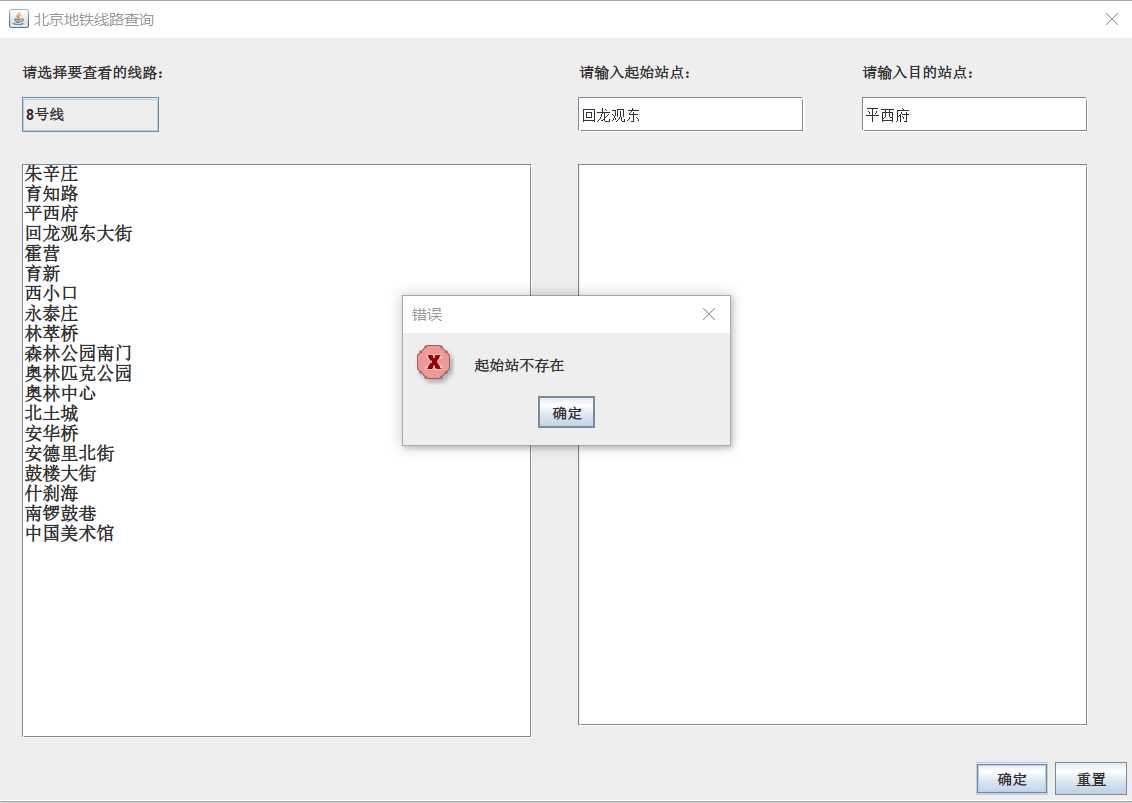
一开始以为要把环线的首尾站和换乘站点区分开来,花了很多功夫,后面发现可以直接在连通图上实现,和换乘站归为一类
最短路径的算法需要固定站点,所以建立在staid的基础上,所以当输入站点名字有很多不同站点时需要一一对应的遍历最短路径,觉得这里的算法可以优化
*github地址在博客首
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zucc31801061/p/13929354.html